(Press-News.org) EVANSTON, Ill. --- A new Northwestern University study provides compelling evidence that human males are biologically wired to care for their offspring, conclusively showing for the first time that fatherhood lowers a man's testosterone levels.
The effect is consistent with what is observed in many other species in which males help take care of dependent offspring. Testosterone boosts behaviors and other traits that help a male compete for a mate. After they succeed and become fathers, "mating-related" activities may conflict with the responsibilities of fatherhood, making it advantageous for the body to reduce production of the hormone.
"Humans are unusual among mammals in that our offspring are dependent upon older individuals for feeding and protection for more than a decade," said Christopher W. Kuzawa, co-author of the study and associate professor of anthropology in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences. He also is a faculty fellow at the Institute for Policy Research at Northwestern. "Raising human offspring is such an effort that it is cooperative by necessity, and our study shows that human fathers are biologically wired to help with the job."
Past studies showing that fathers tend to have lower testosterone levels were small and not conclusive regarding whether fatherhood diminished testosterone or whether men with low testosterone in the first place were more likely to become fathers. The new study takes a novel approach by following a large group of men who were not fathers and seeing whether their hormones changed after becoming fathers.
"It's not the case that men with lower testosterone are simply more likely to become fathers," said Lee Gettler, a doctoral candidate in anthropology at Northwestern and co-author of the study. "On the contrary, the men who started with high testosterone were more likely to become fathers, but once they did, their testosterone went down substantially. Our findings suggest that this is especially true for fathers who become the most involved with child care."
The new study's findings also suggest that fathers may experience an especially large, but temporary, decline in testosterone when they first bring home a newborn baby. "Fatherhood and the demands of having a newborn baby require many emotional, psychological and physical adjustments," Gettler said. "Our study indicates that a man's biology can change substantially to help meet those demands."
The authors also suggest that their findings may provide insight into one reason why single men often have poorer health than married men and fathers. "If fathers have lower testosterone levels, this might protect them against certain chronic diseases as they age," Kuzawa said.
The study followed a group of 624 males aged 21.5 to 26 years old for 4.5 years in the Philippines.
"Longitudinal Evidence That Fatherhood Decreases Testosterone in Human Males" was published Sept. 12, 2011, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
INFORMATION:
The study's co-authors, along with Gettler and Kuzawa, are Thomas W. McDade, professor of anthropology and Institute for Policy Research faculty fellow, Northwestern University, and Alan Feranil, director, Office of Population Studies Foundation, University of San Carlos, Cebu City, Philippines. The research was funded by the National Science Foundation and the Wenner Gren Foundation.
(Contacts: Lee Gettler, lgettler@u.northwestern.edu; Christopher Kuzawa, kuzawa@northwestern.edu)
NORTHWESTERN NEWS: www.northwestern.edu/newscenter/
END
CHICAGO – Among patients who have had an ischemic stroke, use of cholesterol-lowering statin medications is not associated with subsequent intracerebral hemorrhage (bleeding in the brain), according to a report published Online First by Archives of Neurology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
According to background information in the article, after stroke or transient ischemic attack, patients are at increased risk for recurrent events. Results from the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Lowering of Cholesterol Levels (SPARCL) trial and the Heart Protection Study (HPS) ...
CHICAGO – Intranasal insulin therapy appears to provide some benefit for cognitive function in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease, according to a report published Online First today by Archives of Neurology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
According to background information in the article, insulin plays a role in a number of functions of the central nervous system. "The importance of insulin in normal brain function is underscored by evidence that insulin dysregulation contributes to the pathophysiology of Alzheimer disease (AD), ...
CHICAGO – Many U.S. adults believe that only extremely effective drugs without serious adverse effects are approved, but providing explanations to patients highlighting uncertainties about drug benefits may affect their choices, according to a report in the September issue of Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals. The article is part of the journal's Less Is More series.
Approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not necessarily ensure that a drug has a large or important benefit, or that all serious adverse effects of the ...
CHICAGO – Long-term use of nonaspirin anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is associated with an increased risk of renal cell cancer (RCC), according to a report in the September issue of Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
According to background information in the article, in the United States, kidney cancer is the seventh leading type of cancer among men and the ninth leading type of cancer among women. The most common type of kidney cancer, renal cell cancer, accounts for 85 percent of all cases. Analgesics (pain-relieving medications) are ...
CHICAGO – An association has been found between infection associated with cardiovascular implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) and increases in mortality and hospital care costs, according to a report published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals. The article is part of the journal's Health Care Reform series.
Therapy with CIEDs, which include pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and cardiac resynchronization therapy/defibrillator devices, can reduce illness and death rates in appropriately selected patients, ...
Skin Solutions Medical Spa has been serving the Denver Metro area for the past 15 years and was recently nominated for Denver 7's A-List as Denver's best Medical Spa. The spa stands out in the community by providing the highest level of customer service while producing state-of-the-art cosmetic procedures and aesthetic treatments that are safe and effective. The announcement of Express Rejuvenation Day shows the spa's commitment to provide even more quality to their clients and community.
Skin Solutions Medical Spa's new Express Rejuvenation Day was driven by the demand ...
A new set of harmonized guidelines for the management of risk factors for cardiovascular disease will make it much easier for physicians to care for their patients, according to the authors of the C-CHANGE guidelines published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) (pre-embargo link only) http://www.cmaj.ca/site/embargo/cmaj101508.pdf.
The Canadian Cardiovascular Harmonized National Guideline Endeavour (C-CHANGE) Initiative harmonized and integrated more than 400 separate recommendations from 8 sets of guidelines into one comprehensive but simplified resource. ...
Young children who watch fast-paced, fantastical television shows may become handicapped in their readiness for learning, according to a new University of Virginia study published in the October issue of the journal Pediatrics.
U.Va. psychologists tested 4-year-old children immediately after they had watched nine minutes of the popular show "SpongeBob SquarePants" and found that their executive function – the ability to pay attention, solve problems and moderate behavior – had been severely compromised when compared to 4-year-olds who had either watched nine minutes of ...
Monmouth Junction, NJ (September 12, 2011): A new study finds that infections following cardiac device implantations or replacement result in extremely high costs, both financially and in terms of patient mortality, even months after affected patients return home. Infections associated with pacemakers and defibrillators led to 4.8 to 7.7-fold increases in admission mortality, 1.6 to 2.1-fold increases long term mortality, 2.5 to 4.0-fold increases in hospital length of stay, and 1.4 to 1.8-fold increases in cost compared to pacemaker and defibrillator implantations without ...
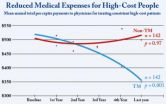
According to a study published this week in the September/October 2011 issue of the American Journal of Health Promotion (Vol. 26, No. 1, pp. 56-60), people with consistently high health care costs experienced a 28 percent cumulative decrease in physician fees after an average of five years practicing the stress-reducing Transcendental Meditation technique compared with their baseline. Both between and within group comparisons were statistically significant. This study has major policy implications.
In most populations, a small fraction of people account for the majority ...