(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA - The changing tide of Alzheimer's diagnosis presents new challenges to the public, physicians and lawmakers: if you could find out your Alzheimer's risk, would you want to know? How should doctors tell you your risk? And what does it mean for the many newly diagnosed Americans still in the workplace?
Despite the emergence of new tools that can diagnose Alzheimer's earlier, no effective interventions have been identified to stop the progression of the disease. A new report from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania tackles the ethical and logistical challenges of safely and effectively communicating a diagnosis of pre-clinical Alzheimer's disease in light of the gulf between diagnosis and treatment. The study appears in the October 11 print edition of Neurology.
Alzheimer's disease is among the most feared diseases of aging. The disease has been known for its role in memory loss and other clinical symptoms. But increasingly, patients learn they have the disease before symptoms start impacting their ability to function in daily life.
"We need to develop systems now, to navigate the challenges of a pre-clinical Alzheimer's diagnosis," said Jason Karlawish, MD, Professor of Medicine and Medical Ethics, author of the paper and leading voice on the ethics of Alzheimer's. "It's only a matter of time before we are able identify Alzheimer's before the patient is ill, like we've done with cholesterol and heart disease. Given the unique nature of this disease, which strips people of their independence as the disease progresses, safeguards are needed to protect those at high risk or with a pre-clinical diagnosis."
On the individual level, people strongly differ in their desire to know their risk and will react differently to a high Alzheimer's risk score or diagnosis in the early stages of the disease. In some cases, biomarker test results can be harmful; patients may develop anxiety or serious depression. To safely and effectively communicate a diagnosis of pre-clinical Alzheimer's disease, Dr. Karlawish recommends that researchers and clinicians track the emotional and physical impact of a pre-clinical diagnosis, then develop and disseminate best practices.
When an effective Alzheimer's therapy or intervention is found, a process will be necessary to ensure the patients who stand to benefit most are prioritized accordingly. Both prognostic and predictive evidence should be gauged against not only an individual's risk but the entire population at risk, especially if failure to intervene could cause large numbers of people to be impacted by any disease progression. A "National Alzheimer's Education Program" is proposed, to address how to translate research results into clinical practice for those with pre-clinical disease.
"The Alzheimer's disease label does not equate to disability," said Dr. Karlawish. In order to ensure that patients' daily lives (i.e. driving, financial planning, work status) aren't negatively or prematurely limited, laws and policies need to be revised to prevent stigma, discrimination and, when patients do suffer disability, exploitation.
"The discovery of pre-clinical Alzheimer's disease may be how we prevent the tsunami of Alzheimer's disease dementia, but we must not drown in the challenges created by our own discovery," warned Dr. Karlawish.
###
The study was sponsored by the Marian S. Ware Alzheimer Program and a Robert Wood Johnson Investigator Award in Health Policy Research.
Penn Medicine is one of the world's leading academic medical centers, dedicated to the related missions of medical education, biomedical research, and excellence in patient care. Penn Medicine consists of the Raymond and Ruth Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (founded in 1765 as the nation's first medical school) and the University of Pennsylvania Health System, which together form a $4 billion enterprise.
Penn's Perelman School of Medicine is currently ranked #2 in U.S. News & World Report's survey of research-oriented medical schools and among the top 10 schools for primary care. The School is consistently among the nation's top recipients of funding from the National Institutes of Health, with $507.6 million awarded in the 2010 fiscal year.
The University of Pennsylvania Health System's patient care facilities include: The Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania -- recognized as one of the nation's top 10 hospitals by U.S. News & World Report; Penn Presbyterian Medical Center; and Pennsylvania Hospital – the nation's first hospital, founded in 1751. Penn Medicine also includes additional patient care facilities and services throughout the Philadelphia region.
Penn Medicine is committed to improving lives and health through a variety of community-based programs and activities. In fiscal year 2010, Penn Medicine provided $788 million to benefit our community.
END
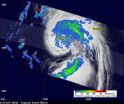
NASA's TRMM satellite peers through clouds and can decipher the rate rain is falling within a tropical cyclone, and data from the satellite shows that the heaviest rainfall is occurring in the northwestern quadrant of the storm, away from Bermuda.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite traveled above tropical storm Maria on Thursday, September 15, 2011 at 1001 UTC ( 6:01 a.m. EDT). TRMM has the ability to measure rainfall rates and cloud heights, two factors that are important and helpful to the National Hurricane Center (NHC) meteorologists who are ...
A new model of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) that mirrors both symptoms of the disease and the timing of its treatment in humans has been created by University of Chicago researchers, according to a new study.
Using the model, researchers isolated a single neurotransmitter receptor in a specific brain region responsible for their model's OCD-like symptoms, offering new insight into the cause of the disorder. Further research with the model may point the way to new treatments for both OCD and autism, said Nancy Shanahan, PhD, lead author of the paper in Biological ...
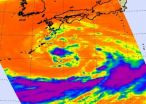
Tropical Storm Roke is showing some signs of intensification on NASA infrared satellite imagery, as areas of strong convection and very cold cloud tops were spotted. Kadena Air Base in Okinawa is now in Roke's sights and should be making preparations.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Roke yesterday and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument showed powerful convection building around the storm's center and over the northern edge. Meanwhile, dry air is wrapping into the low-level center from the southwest, and limiting cloud development.
Infrared imagery provides ...
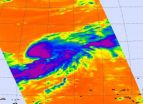
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite yesterday showed powerful convection building in the low pressure area known as System 94W and provided forecasters with an inside look that the low was strengthening. System 94W did intensify and became Tropical Storm Sonca today.
Infrared imagery is gathered by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite. It provides valuable information to forecast organizations such as the Joint Typhoon Warning Center and National Hurricane Center about cloud temperatures and heights and ...
Cake Decorating Teacher's blog is dedicated to serving online viewers with a listing of easy to make recipes. Weekly blog posts include delicious dessert recipes at www.cakedecoratingteacher.com along with how to instructions for their readers convenience.
Life has never been this easy when it comes to finding free access to great baking recipes since the Internet and its listing of blog sites such as Cake Decorating Teacher. Posts can easily be viewed under the posts section of their website. To stay updated on the latest posts readers can subscribe to the blog's RSS ...
AMES, Iowa – Even though a dwarf galaxy clear across the Milky Way looks to be a mouse, it may have once been a bear that slashed through the Milky Way and created the galaxy's spiral arms, writes an Iowa State University astronomer in the journal Nature.
Curtis Struck, an Iowa State professor of physics and astronomy, uses a News & Views commentary in the Sept. 15 issue of Nature to add context and color to a study published in the same issue by a research team led by Chris W. Purcell of the University of Pittsburgh.
The Purcell group reports that the Sagittarius Dwarf ...
After nearly two years of committed planning and design, the 2011 Solar Decathlon Team Massachusetts heads to Washington, D.C. where its completed "4D Home" will participate alongside 19 other collegiate entries in this year's competition. A unique dwelling that boasts both affordable and sustainable design elements, the "4D Home" is fully solar-powered, cost-effective and energy-efficient.
"Team Massachusetts showcases public higher education at its best. The creation of this self-sustaining home designed and developed by students at Massachusetts ...
From the very beginning our philosophers and scientists realized that the key to great societies was wisdom. They saw that wisdom was real and that if only they could figure out what it is and how to teach it; they would be able to create wise societies. Ever since the times of Aristotle till today, man has been trying to figure out wisdom by putting wisdom under the microscope. As wisdom is an innate property of the pure self it is a secondary entity; just like fragrance is a property of the flower. It is exactly like a symptom of a disease. So by putting wisdom under ...
PHILADELPHIA--It is a commonly held that information on Wikipedia should not be trusted, since it is written and edited by non-experts without professional oversight. But researchers from the Kimmel Cancer Center at Jefferson have found differently, according to a study published online Sept. 15 in the Journal of Oncology Practice.
Reassuringly, they found that cancer information found on a wiki was actually similar in accuracy and depth to the information on a peer-reviewed, patient-oriented cancer web site. There is one caveat, however: they found that the information ...
Cincinnati, OH, September 16, 2011 -- Pharmaceutical poisoning remains a common childhood injury, despite years of concerted prevention efforts, such as improved safe guards on packaging. Over half a million children are exposed to pharmaceuticals each year. A new study soon to be published in The Journal of Pediatrics attempts to understand this growing problem to aid in the progress of reducing the number of childhood injuries due to pharmaceutical poisoning.
Dr. Randall Bond and colleagues from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and the University of Cincinnati ...