(Press-News.org) Berkeley, CA — The installed cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) power systems in the United States fell substantially in 2010 and into the first half of 2011, according to the latest edition of an annual PV cost tracking report released by the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
The average installed cost of residential and commercial PV systems completed in 2010 fell by roughly 17 percent from the year before, and by an additional 11 percent within the first six months of 2011. These recent installed cost reductions are attributable, in part, to dramatic reductions in the price of PV modules. Galen Barbose of Berkeley Lab's Environmental Energy Technologies Division and co-author of the report explains: "Wholesale PV module prices have fallen precipitously since about 2008, and those upstream cost reductions have made their way through to consumers."
The report indicates that non-module costs—such as installation labor, marketing, overhead, inverters, and the balance of systems—also fell for residential and commercial PV systems in 2010. "The drop in non-module costs is especially important," notes report co-author and Berkeley Lab scientist Ryan Wiser, "as those are the costs that can be most readily influenced by solar policies aimed at accelerating deployment and removing market barriers, as opposed to research and development programs that are also aimed at reducing module costs." According to the report, average non-module costs for residential and commercial systems declined by roughly 18 percent from 2009 to 2010.
Turning to utility-sector PV, costs varied over a wide range for systems installed in 2010, with the cost of systems greater than 5,000 kilowatts (kW) ranging from $2.90 per Watt (W) to $6.20/W, reflecting differences in project size and system configuration, as well as the unique characteristics of certain individual projects. Consistent with continued cost reductions, current benchmarks for the installed cost of prototypical, large utility-scale PV projects generally range from $3.80/W to $4.40/W.
The market for solar PV systems in the United States has grown rapidly over the past decade, as national, state and local governments offered various incentives to expand the solar market and accelerate cost reductions. The study—the fourth in Berkeley Lab's "Tracking the Sun" report series—describes trends in the installed cost of PV in the United States, and examined more than 115,000 residential, commercial and utility-sector PV systems installed between 1998 and 2010 across 42 states, representing roughly 78 percent of all grid-connected PV capacity installed in the United States. Naïm Darghouth, also with Berkeley Lab, explains that "the study is intended to provide policy makers and industry observers with a reliable and detailed set of historical benchmarks for tracking and understanding past trends in the installed cost of PV."
Costs Differ by Region and by Size and Type of System
The study also highlights differences in installed costs by region and by system size and installation type. Comparing across U.S. states, for example, the average cost of PV systems installed in 2010 and less than 10 kilowatts (kW) in size ranged from $6.30/W to $8.40/W depending on the state. The report also found that residential PV systems installed on new homes had significantly lower average installed costs than those installed as retrofits to existing homes.
Based on these data and on installed cost data from the sizable German and Japanese PV markets, the authors suggest that PV costs may be driven lower through large-scale deployment programs, but that other factors are also important in achieving cost reductions.
The report also shows that PV installed costs exhibit significant economies of scale. Among systems installed in 2010, those smaller than 2 kW averaged $9.80/W, while large commercial systems >1,000 kW averaged $5.20/W; partial-year data for 2011 suggests that average costs declined even further in 2011. Large utility-sector systems installed in 2010 registered even lower costs, with a number of systems in the $3.00/W to $4.00/W range.
Cost Declines for PV System Owners in 2010 Were Partially Offset by Falling Incentives
The average size of direct cash incentives provided through state and utility PV incentive programs has declined steadily since their peak in 2002. The dollar-per-Watt benefit of the federal investment tax credit (ITC) and Treasury grant in lieu of the ITC, which are based on a percentage of installed cost, also fell in 2010 as a result of the drop in average installed costs.
The reduced value of federal, state, and utility incentives in 2010 partially offset the decline in installed costs. Therefore, while pre-incentive installed costs fell by $1.00/W and $1.50/W for residential and commercial PV in 2010, respectively, the decline in "net" (or post-incentive) installed costs fell by $0.40/W for residential PV and by $0.80/W for commercial PV.
INFORMATION:
The report "Tracking the Sun IV: An Historical Summary of the Installed Cost of Photovoltaics in the United States from 1998 to 2010," by Galen Barbose, Naïm Darghouth, and Ryan Wiser, may be downloaded from
http://eetd.lbl.gov/ea/emp/reports/lbnl-5047e.pdf.
The research was supported by funding from the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy and by the Clean Energy States Alliance, a national nonprofit coalition of leading state clean energy programs that work together to advance renewable energy project deployment in their states and across the country.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 12 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
END
Watching children on the playground, we see them run, climb, slide, get up, and do it all again. While their movements are continuous, we language-users can easily divide them up and name each one. But what about people—babies—who don't yet have words? How do they make sense of a world in motion?
An upcoming study in Psychological Science, a journal published by the Association for Psychological Science, finds that infants at seven to nine months are able to slice up the flow of events, even before they start to speak. And the researchers believe they've identified the ...
Researchers have identified promising new therapies for ependymoma, a rare tumor with few treatment options. St. Jude Children's Research Hospital investigators led the effort, which used a new, faster drug development system that combines the latest drug screening technology with the first accurate animal model of the tumor.
Investigators identified several dozen new and existing drugs as possible ependymoma treatment candidates. The drugs were found by screening 5,303 existing medicines, natural products and other compounds for activity against the tumor, which develops ...
To highlight Pain Awareness Month in September, The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the nation's largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — is announcing two forthcoming publications focused on pain relief and medication for seniors.
Paired with its other recent research findings, GSA aims to provide readers with information on how new advances in pain prevention, treatment, and management may improve care and quality of life for older adults.
Both new publications are part of GSA's From Publication to Practice series, which aims ...
PHILADELPHIA - The changing tide of Alzheimer's diagnosis presents new challenges to the public, physicians and lawmakers: if you could find out your Alzheimer's risk, would you want to know? How should doctors tell you your risk? And what does it mean for the many newly diagnosed Americans still in the workplace?
Despite the emergence of new tools that can diagnose Alzheimer's earlier, no effective interventions have been identified to stop the progression of the disease. A new report from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania tackles the ...
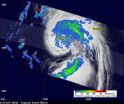
NASA's TRMM satellite peers through clouds and can decipher the rate rain is falling within a tropical cyclone, and data from the satellite shows that the heaviest rainfall is occurring in the northwestern quadrant of the storm, away from Bermuda.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite traveled above tropical storm Maria on Thursday, September 15, 2011 at 1001 UTC ( 6:01 a.m. EDT). TRMM has the ability to measure rainfall rates and cloud heights, two factors that are important and helpful to the National Hurricane Center (NHC) meteorologists who are ...
A new model of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) that mirrors both symptoms of the disease and the timing of its treatment in humans has been created by University of Chicago researchers, according to a new study.
Using the model, researchers isolated a single neurotransmitter receptor in a specific brain region responsible for their model's OCD-like symptoms, offering new insight into the cause of the disorder. Further research with the model may point the way to new treatments for both OCD and autism, said Nancy Shanahan, PhD, lead author of the paper in Biological ...
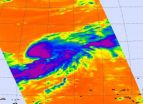
Tropical Storm Roke is showing some signs of intensification on NASA infrared satellite imagery, as areas of strong convection and very cold cloud tops were spotted. Kadena Air Base in Okinawa is now in Roke's sights and should be making preparations.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Roke yesterday and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument showed powerful convection building around the storm's center and over the northern edge. Meanwhile, dry air is wrapping into the low-level center from the southwest, and limiting cloud development.
Infrared imagery provides ...
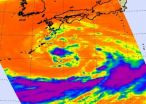
Infrared satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite yesterday showed powerful convection building in the low pressure area known as System 94W and provided forecasters with an inside look that the low was strengthening. System 94W did intensify and became Tropical Storm Sonca today.
Infrared imagery is gathered by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies on NASA's Aqua satellite. It provides valuable information to forecast organizations such as the Joint Typhoon Warning Center and National Hurricane Center about cloud temperatures and heights and ...
Cake Decorating Teacher's blog is dedicated to serving online viewers with a listing of easy to make recipes. Weekly blog posts include delicious dessert recipes at www.cakedecoratingteacher.com along with how to instructions for their readers convenience.
Life has never been this easy when it comes to finding free access to great baking recipes since the Internet and its listing of blog sites such as Cake Decorating Teacher. Posts can easily be viewed under the posts section of their website. To stay updated on the latest posts readers can subscribe to the blog's RSS ...
AMES, Iowa – Even though a dwarf galaxy clear across the Milky Way looks to be a mouse, it may have once been a bear that slashed through the Milky Way and created the galaxy's spiral arms, writes an Iowa State University astronomer in the journal Nature.
Curtis Struck, an Iowa State professor of physics and astronomy, uses a News & Views commentary in the Sept. 15 issue of Nature to add context and color to a study published in the same issue by a research team led by Chris W. Purcell of the University of Pittsburgh.
The Purcell group reports that the Sagittarius Dwarf ...