Diamonds show depth extent of Earth's carbon cycle
2011-09-16
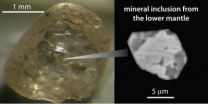
(Press-News.org) Washington, D.C.—Scientists have speculated for some time that the Earth's carbon cycle extends deep into the planet's interior, but until now there has been no direct evidence. The mantle–Earth's thickest layer –is largely inaccessible. A team of researchers analyzed diamonds that originated from the lower mantle at depths of 435 miles (700 kilometers) or more, and erupted to the surface in volcanic rocks called kimberlites. The diamonds contain what are impurities to the gemologist, but are known as mineral inclusions to the geologist. Analysis shows compositions consistent with the mineralogy of oceanic crust. This finding is the first direct evidence that slabs of oceanic crust sank or subducted into the lower mantle and that material, including carbon, is cycled between Earth's surface and depths of hundreds of miles. The research is published in the September 15, 2011, online Science Express.
The mantle extends from as little as 5 to 1,800 miles (10-2,900 kilometers) beneath the Earth's surface. Most diamonds are free from inclusions and come from depths less than 120 miles (200 km). But in a few localities researchers have found super-deep diamonds from the depths of the convecting upper and lower mantle, as well as the transition zone in between. Whereas inclusions in diamonds from the depths of the upper mantle and transition zone have been consistent with a surface-rock origin, none from the lower mantle have borne this signature until now.
The team,* which included Carnegie scientists, was led by former Carnegie postdoctoral fellow Michael Walter, now a professor at the University of Bristol, UK. The scientists analyzed minute (one to two hundredths of a millimeter) mineral grains from six diamonds from the Juina region in Brazil. The analysis showed that diamond inclusions initially crystallized as a single mineral that could form only at depths greater than 435 miles (700 km). But the inclusions recrystallized into multiple minerals as they were carried up to the surface—first probably from a mantle upwelling known as a plume, then as they erupted to the surface in kimberlites
The diamonds were analyzed for carbon at Carnegie. Four of the diamonds contained low amounts of carbon-13, a signature not found in the lower mantle and consistent with an ocean-crust origin at Earth's surface. "The carbon identified in other super-deep, lower mantle diamonds is chiefly mantle-like in composition," remarked co-author Steven Shirey * at Carnegie. "We looked at the variations in the isotopes of the carbon atoms in the diamonds. Carbon originating in a rock called basalt, which forms from lava at the surface, is often different from that which originates in the mantle, in containing relatively less carbon-13. These super-deep diamonds contained much less carbon-13, which is most consistent with an origin in the organic component found in altered oceanic crust."
"I find it astonishing that we can use the tiniest of mineral grains to show some of the motions of the Earth's mantle at the largest scales," concluded Shirey.
INFORMATION:
* The researchers on the paper are M.J. Walter, S. Kohn, G. Bulanova, and C. Smith of University of Bristol, UK; D. Araujo of Universidade de Brasilia-DF Brazil; A. Steele of Carnegie's Geophysical Laboratory, and S. Shirey, E. Gaillou, and J. Wang of Carnegie's Department of Terrestrial Magnetism. Funding was provided by the NSF in the US, the National Environmental Research Council (NERC) in the UK, and the Carnegie Institution for Science.
The Carnegie Institution for Science (carnegiescience.edu) is a private, nonprofit organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with six research departments throughout the U.S. Since its founding in 1902, the Carnegie Institution has been a pioneering force in basic scientific research. Carnegie scientists are leaders in plant biology, developmental biology, astronomy, materials science, global ecology, and Earth and planetary science.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2011-09-16
The carbon cycle, upon which most living things depend, reaches much deeper into the Earth than generally supposed—all the way to the lower mantle, researchers report.
The findings, which are based on the chemistry of an unusual set of Brazilian diamonds, will be published online by the journal Science, at the Science Express Web site, on 15 September. Science is published by AAAS, the non-profit, international science society.
"This study shows the extent of Earth's carbon cycle on the scale of the entire planet, connecting the chemical and biological processes that ...
2011-09-16
Snooker, rugby, football and cricket fans will be well served by the upcoming A Question of Sport Live show in Glasgow.
Quizmaster Sue Barker and captains Phil Tufnell and Matt Dawson are set to be joined onstage at the event by special guests Dennis Taylor, Chris Cusiter and Anthony Stokes.
Former World Snooker champion Taylor spent two decades in the top 16 of the rankings and was also a huge hit with fans of the sport. Since retiring, he has become an important part of the BBC commentary team for live snooker coverage.
Celtic striker Stokes, who began his ...
2011-09-16
Fans of the British rock group Mogwai will be descending on Barcelona next month to see the band perform as part of their global tour.
The Scottish musicians will be putting on a show at the Casino L'Alianca Del Poblenou on October 28th, with proceedings to get underway at 20:00 local time.
Mogwai have been playing together since the mid-1990s and are a five-piece act fronted by Stuart Braithwaite, with the band having won acclaim for their innovative musical stylings.
Having recorded six previous studio albums and worked on the soundtrack for Darren Aronofsky's ...
2011-09-16
VIDEO:
Scripps Research Institute Professors Hugh Rosen and Michael Oldstone discuss their recent findings pinpointing the cells that orchestrate a dangerous immune reaction called "cytokine storms, " opening up entirely new possibilities...
Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA, CA – September 15, 2011 – Researchers at The Scripps Research Institute have found a novel mechanism by which certain viruses such as influenza trigger a type of immune reaction that ...
2011-09-16
Visitors to Berlin next month will be able to enjoy a colourful spectacle when the seventh annual Festival of Lights commences in the German capital next month.
Taking place between October 12th and 23rd 2011, the event will see more than 50 of the city's most famous landmarks and public spaces brightened up with illuminations and projections.
Among the locations that will be lit up are the Brandenburg Gate, Berlin Cathedral and the radio tower, while the Europa-Center and Kaiser Wilhelm Memorial Church will also be involved for the first time.
The festival ...
2011-09-16
Most people know that unhealthy lifestyles are the cause of many of their personal challenges in life, from being overweight to chronic fatigue to PMS/PMDD symptoms, just to name a few - challenges which can determine the very quality of their lives.
Yet few succeed in breaking free of these unhealthy lifestyles. Why?
According to Jing Jin, the founder of cycleharmony.com, "It's because they've taken on an impossible task. An unhealthy lifestyle is almost impossible to break because it takes vigilance and an energy that few of us have. Think about the chocoholic ...
2011-09-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study of interracial marriages in the United States since the 1980s suggests that the racial boundary between blacks and whites continues to break down – but is not yet close to disappearing.
Marriages between African Americans and whites increased rapidly between 1980 and 2008, outpacing the rate of unions between whites and other ethnic and racial groups, including Latinos, Asian Americans and American Indians.
Still, the total number of marriages between blacks and whites continues to be much smaller than those between whites and other racial ...
2011-09-16
Most of the time, being ill with the flu is little more than a nuisance. Other times, it can spark an exaggerated immune response and turn deadly. Researchers reporting in the September 16th issue of the journal Cell, a Cell Press publication, have now traced the origins of this severe immune response -- called a cytokine storm -- to its source.
Cytokines are the chemical signals that drive inflammation, and cytokine storms are thought to be the cause of many of the deaths attributed to the 1918 worldwide influenza pandemic and to the more recent outbreaks of swine ...
2011-09-16
In the midst of dramatically rising gold prices, Tungsten Depot announces an affordable alternative for exquisitely designed wedding bands and other fine jewelry. In fact, Tungsten Rings are quickly becoming the superior high-quality option for individuals looking for style, distinction and panache when selecting custom fit wedding rings or other tungsten jewelry that is designed to last a lifetime.
As one of the hardest metals on the planet, tungsten has unmatched durability in the jewelry industry yet is far more economical to purchase, usually a fraction of the cost ...
2011-09-16
SAN FRANCISCO — Scientists at the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute have begun to uncover how the virus that causes most Merkel cell carcinoma – a rare and aggressive skin cancer – operates, meaning that a rational chemotherapeutic target for this cancer could be developed in the near future.
Patrick Moore, M.D., M.P.H., an American Cancer Society professor in the laboratory of Yuan Chang and Patrick Moore at the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute in Pittsburgh, Pa., presented these study results at the Second AACR International Conference on Frontiers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Diamonds show depth extent of Earth's carbon cycle