(Press-News.org) More species could be saved from extinction under climate change thanks to a new model scientists have developed to guide allocation of conservation funding.
The international team, led by Dr Brendan Wintle of the University of Melbourne and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Environmental Decisions, is the first to develop a pioneering decision-support model that incorporates both ecological and economic information to guide conservation investment in the face of climate change. The work is published today [Monday 19 September] in the journal Nature Climate Change.
"The best part about this model is that it can be applied to a range of environments, including many of Australia's native ecosystems, to suggest how to allocate funding," Dr Wintle said.
Although scientists knew that high extinction rates were predicted to increase under climate change, there was little advice to guide how money could be best spent to minimise extinctions.
"Our analysis supports the existing evidence that climate change will substantially accelerate extinction rates. So the first step is that we urgently need to limit global warming to avoid a mass extinction."
"Given that we are probably committed to a two degree warming by 2050, we need to develop effective strategies for minimizing the number of species that go extinct as a result.
"We only have a limited amount of money to spend on managing biodiversity, so the question becomes, how do we most effectively allocate these funds?
"We needed a systematic approach to guide conservation investment to minimize extinctions and avoid wasting money. An advantage of our approach is that it makes the costs of a plan explicit, reducing the opportunity for politicization of decisions."
The scientists combined ecological predictions with an economic decision framework to prioritize conservation activities, and tested the model on one of world's most biodiverse and highly threatened ecosystems; the South African fynbos.
"An interesting result of our analysis is that the optimal allocation of money depends strongly on the yearly conservation budget. For example if budgets were small then the whole budget would be dedicated to fire-fighting capacity. However, if more money were available, investment would be directed toward avoiding habitat loss due to clearing and weed invasion," Dr Wintle said.
INFORMATION:
The team included scientists from the University of Melbourne, the ARC Centre of Excellence for Environmental Decisions, CSIR South Africa, the NERP Environmental Decisions Hub, RMIT University, NSW Office of Environment & Heritage, University of NSW, the University of Queensland and a group of European researchers.
More information:
Dr Brendan Wintle; E: b.wintle@unimelb.edu.au , T: +61 3 8344 3306, M: 0425 828 470
Dr Nerissa Hannink (Media office); E: nhannink@unimelb.edu.au , T: +61 3 8344 8151, M: 0430 588 055
Sally Sherwen (Media office); E: sherwens@unimelb.edu.au, M: 0412 230 863
END
In a new study, Chen-Yu Zhang's group at Nanjing university present a rather striking finding that plant miRNAs could make into the host blood and tissues via the route of food-intake. Moreover, once inside the host, they can elicit functions by regulating host "target" genes and thus regulate host physiology.
MicroRNAs are a class of 19-24 nucleotide non-coding RNAs that do not code for proteins. MicroRNAs bind to target messenger RNAs to inhibit protein translation. In previous studies, the same group has demonstrated that stable microRNAs (miRNAs) in mammalian serum ...
Researchers from Taiwan have confirmed a bidirectional relation between schizophrenia and epilepsy. The study published today in Epilepsia, a journal of the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE), reports that patients with epilepsy were nearly 8 times more likely to develop schizophrenia and those with schizophrenia were close to 6 times more likely to develop epilepsy.
Prior clinical studies have shown a prevalence of psychosis among epilepsy patients and studies of psychiatric illness have found a strong relationship between schizophrenia and epilepsy, suggesting ...
Gulf War Illness (GWI)—the chronic health condition that affects about one in four military veterans of the 1991 Gulf War—appears to be the result of several factors, which differed in importance depending upon the locations where veterans served during the war, according to a Baylor University study.
Published online today in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, the study investigated links between GWI and veterans' locations during the war. GWI was most prevalent in veterans who served in forward areas of Iraq and Kuwait, where it was most strongly associated ...
Call a bird "birdbrained" and they may call "fowl." Cornell University researchers have proven that the capacity for learning in birds is not linked to overall brain size, but to the relative size and proportion of their specific brain regions.
Songbirds with upper brain regions that are larger in relation to lower regions have a greater capacity for learning songs. Higher brain areas control the majority of cognitive and learning functions, while lower brain areas control more motor functions, according to the new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy ...
Like DNA, fingerprints are unique to each person or set of identical twins. That makes them a valuable identification tool for everything from crime detection to international travel. But what happens when the tips of our fingers are missing those distinctive patterns of ridges?
It's not the premise for a science fiction movie, but a real-life condition known as adermatoglyphia. It's also known as "Immigration Delay Disease," because affected individuals experience difficulty in passing through security or checkpoints where fingerprint identification is required. Now ...
This has been a good year for Kepler, NASA's planet-hunting satellite telescope.
Last week, a team of astronomers announced they had discovered a planet that orbits two stars – a discovery that already has the field rethinking how planets are formed. And earlier this year, it was announced there are hundreds of possible planets in a small region of the Milky Way Galaxy, including 20 that have already been confirmed. Planets are also being found in a diversity of solar systems. All of this possible because of Kepler.
Three prominent researchers – Jack J. Lissauer, NASA's ...
In advance of a United Nations conference today on the global challenges of treating cancer and other diseases, the UBC Graduate School of Journalism has launched an ambitious multimedia site, The Pain Project, which documents one of the greatest challenges to treating chronic illnesses: severely constrained access to morphine.
The Pain Project, www.internationalreporting.org/pain, results from a year-long investigation by UBC's International Reporting Program (IRP). Teams traveled to India, Ukraine and Uganda to determine how these countries manage the pain of patients ...
EUGENE, Ore. -- (Sept. 19, 2011) -- The thought of toys being given out as part of children's meal deals might be easier to swallow, and better for you, if the toys are part of a collectible set and tied to healthy, nutrition-rich food choices. Who says? Kids and their parents do.
The findings of a new study come during a time of debate over obesity in the United States -- about one-third of adults are now obese, as are 17 percent of children ages 2-19, notes the Centers for Disease Control -- and the growing belief that toys with fast-food meals only serve to put fatty, ...
SalesFUSION, the maker of SalesFUSION 360, an integrated sales and marketing demand generation platform, debuted a new native version of its marketing automation application for Dynamics CRM 2011 this summer. Known as inDynamics because of its native email and web analytics features, SalesFUSION's unique approach on integrating marketing and sales for Microsoft CRM brings the power and feature set of an enterprise app inside the Dynamics CRM framework.
SalesFUSION recently announced that over 110 companies are actively using its marketing automation platform with Dynamics ...
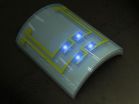
Daejeon, the Republic of Korea, August 8, 2011—Can a flexible LED conformably placed on the human heart, situated on the corrugated surface of the human brain, or rolled upon the blood vessels, diagnose or even treat various diseases? These things might be a reality in the near future.
The team of Professor Keon Jae Lee (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST) has developed a new concept: a biocompatible, flexible Gallium Nitride (GaN) LED that can detect prostate cancer.
GaN LED, a highly efficient light emitting device, has been commercialized in LED ...