(Press-News.org) An international research team has discovered that a pervasive human RNA modification provides the physiological underpinning of the genetic regulatory process that contributes to obesity and type II diabetes.
European researchers showed in 2007 that the FTO gene was the major gene associated with obesity and type II diabetes, but the details of its physiological and cellular functioning remained unknown.
Now, a team led by University of Chicago chemistry professor Chuan He has demonstrated experimentally the importance of a reversible RNA modification process mediated by the FTO protein upon biological regulation. He and 10 co-authors from Chicago, China and England published the details of their finding in the Oct. 16 advance online edition of Nature Chemical Biology.
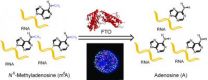
He and his colleagues have shown, for the first time, the existence of the reversible RNA modification process — called methylation — and that it potentially impacts protein expression and function through its action on a common RNA base: adenosine. The process is reversible because it can involve the addition or removal of a methyl group from adenosine. The team found that the FTO protein mediates cellular removal of the methyl group.
"An improved understanding of the normal functions of FTO, as exemplified by this work, could aid the development of novel anti-obesity therapies," said Stephen O'Rahilly, professor of clinical biochemistry and director of the Metabolic Research Laboratories at the University of Cambridge. O'Rahilly, a leading researcher in obesity and metabolic disease who also has studied
FTO, was not directly involved in He's project.
"Variants around the FTO gene have consistently been associated with human obesity and artificial manipulation of the fto gene in mice clearly demonstrates that FTO plays a crucial role in the regulation of body weight," O'Rahilly explained. "However, the development of a deeper understanding of the normal biological role of FTO has been challenging."
Scientists already had demonstrated that FTO removes methyl groups from nucleic acids, but only on one rare type of DNA or RNA methylation. The new research from He and his colleagues shows that FTO also acts on the common messenger RNA modification called N6-methyladenosine, O'Rahilly said.
The paper arose from He's investigations of the AlkB family of proteins that act on nucleic acids. Based on this work, He and his collaborators proved that human cells exhibit reversible methylation of RNA bases, which significantly impact critical life processes.
Important but mysterious
Every human messenger RNA carries on average three to six methylations on adenosine. Scientists knew these methylations were extremely important but their function remained a mystery, He said. "For the first time, we show that these methylations are reversible and play a key role in human energy homeostasis," the process by which the body maintains a complex biochemical dynamic equilibrium.
The modification of N6-methyladenosine in messenger RNA is pervasive throughout the mammal kingdom and many other organisms. Despite its abundance, this modification's exact functional role remains unknown, He said. But his team's discovery strongly indicates that the modification has major roles in messenger RNA metabolism.
The finding may open a new research field — RNA epigenetics — for delving into the realm of biological regulatory processes, He said. The epigenetics of DNA and histones (proteins that package DNA in human cells) have become well-explored topics on the frontiers of biological research over the last 10 to 20 years. "It is safe to say 50 percent of biologists work on subjects related to epigenetics one way or another," He said.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) for decades has reigned as king over biological research on epigenetics of nucleic acids, as He noted in the December 2010 issue of Nature Chemical Biology. RNA (ribonucleic acid) modification was regarded more as a vassal that merely fine-tunes gene expression and regulation, until this recent discovery, which confirms the speculation by He and others that RNA modification has secretly wielded a far greater genetic influence than anyone had previously suspected. That's why, as He wrote last year, "reversible RNA modification might represent another realm for biological regulation in the form of 'RNA epigenetics.'"
INFORMATION:
Citations: "N6-Methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO," by Guifang Jia, Ye Fu, Xu Zhao, Qing Dai, Guanqun Zheng, Ying Yang, Chengqi Yi, Tomas Lindahl, Tao Pan, Yun-Gui Yang and Chuan He, Nature Chemical Biology, advance online publication Oct. 16, 2011.
"RNA epigenetics?" by Chuan He, Nature Chemical Biology, Dec. 2010.
Funding: National Institutes of Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chicago Biomedical Consortium, Beijing Institute of Genomics.
New research links common RNA modification to obesity
2011-10-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NewBlueFX Announces Titler Pro Bundle With Sony Vegas Pro 11
2011-10-19
Innovative video effects creator and technology developer NewBlue, Inc. announces the inclusion of their new Titler Pro with Vegas Pro 11 from Sony, along with 13 other NewBlue plug-ins from 6 best-selling video plug-in collections. NewBlue Titler Pro (MSRP $299.95) is designed for the professional editor's schedule; to make it easy for editors to quickly create 2D & 3D graphics on a timeline.
Titler Pro title animations use the computer's GPU to blend sophisticated 3D modeling with 2D raster processing to generate imagery in real time. Titler Pro also boasts an ...
Farmland floods do not raise levels of potentially harmful flame retardants in milk
2011-10-19
WASHINGTON, Oct. 12, 2011 — As millions of acres of farmland in the U.S. Midwest and South recover from Mississippi River flooding, scientists report that river flooding can increase levels of potentially harmful flame retardants in farm soils. But the higher levels apparently do not find their way into the milk produced by cows that graze on these lands.
That's the reassuring message in the latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS) award-winning "Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions" podcast series.
Iain Lake, Ph.D., notes in the podcast that the flame ...
Muscling toward a longer life: Genetic aging pathway identified in flies
2011-10-19
Researchers at Emory University School of Medicine have identified a set of genes that act in muscles to modulate aging and resistance to stress in fruit flies.
Scientists have previously found mutations that extend fruit fly lifespan, but this group of genes is distinct because it acts specifically in muscles. The findings could help doctors better understand and treat muscle degeneration in human aging.
The results were published online this week by the journal Developmental Cell.
The senior author is Subhabrata Sanyal, PhD, assistant professor of cell biology at ...
"Impact of US Domestic Tonnage Regulations on Design, Maintenance and Manning" Topic of Free WorkBoat.com Webinar on October 26
2011-10-19
Designing a vessel to meet a tonnage parameter has proven to be the bane of designers, builders and owners since the earliest days of the maritime industry. Today, regulations initially established over 140 years ago in a surveyor's office in London can dramatically affect the construction of virtually every commercial vessel at work in the United States.
"Every boat needs to have a tonnage certificate for whatever its type of function and any modification to a vessel can result in ramifications to the tonnage certificate," said David Krapf, editor in chief ...
Amorphous diamond, a new super-hard form of carbon created under ultrahigh pressure
2011-10-19
An amorphous diamond – one that lacks the crystalline structure of diamond, but is every bit as hard – has been created by a Stanford-led team of researchers.
But what good is an amorphous diamond?
"Sometimes amorphous forms of a material can have advantages over crystalline forms," said Yu Lin, a Stanford graduate student involved in the research.
The biggest drawback with using diamond for purposes other than jewelry is that even though it is the hardest material known, its crystalline structure contains planes of weakness. Those planes are what allow diamond ...
Canadian Pharmacy Customers Save Big on Wellbutrin XL
2011-10-19
Canada Drug Pharmacy offers Wellbutrin XL at a cheaper price, much cheaper when compared to purchasing the same drug from traditional retail stores. As more and more people turn to the internet to shop online, they are also searching for ways to save money. One of the benefits of buying Canadian drugs from CanadaDrugPharmacy.com is that the price of prescription medications is cheaper than traditional brick and mortar pharmacies. Purchasing online is also convenient since the consumers don't have to leave their house to buy their medicine. Customers can now log-in to Canada ...
Chinese-Americans don't overborrow, MU study finds
2011-10-19
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Bad mortgage loans and rampant consumer debt were two of the primary causes for the recent economic recession in the U.S. Despite a national trend of debt problems, a University of Missouri researcher has found one American population that holds almost no consumer debt outside of typical home mortgages. Rui Yao, an assistant professor of personal financial planning in the College of Human Environmental Sciences at the University of Missouri, found that while 72 percent of Chinese-American households hold a mortgage, only five percent of those households ...
Impurity atoms introduce waves of disorder in exotic electronic material
2011-10-19
UPTON, NY - It's a basic technique learned early, maybe even before kindergarten: Pulling things apart - from toy cars to complicated electronic materials - can reveal a lot about how they work. "That's one way physicists study the things that they love; they do it by destroying them," said Séamus Davis, a physicist at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and the J.G. White Distinguished Professor of Physical Sciences at Cornell University.
Davis and colleagues recently turned this destructive approach - and a sophisticated tool for "seeing" ...
Trudeau Institute reports new approach to treating Listeria infections
2011-10-19
Saranac Lake, N.Y.—Research underway at the Trudeau Institute could lead to new treatments for people sickened by Listeria and other sepsis-causing bacteria. Dr. Stephen Smiley's laboratory has published a study in the scientific journal Infection and Immunity that supports a new approach to treating these infections.
Listeria can cause serious illness, especially among the elderly, the very young and those with compromised immune systems. The bacteria can also cause significant complications in pregnant women, including miscarriage.
The CDC is reporting that one miscarriage ...
Diamonds, silver and the quest for single photons
2011-10-19
Building on earlier work showing how nanowires carved in impurity-laden diamond crystal can efficiently emit individual photons, researchers have developed a scalable manufacturing process to craft arrays of miniature, silver-plated-diamond posts that enable even greater photon control.
The development supports efforts to create robust, room-temperature quantum computers by setting the stage for diamond-based microchips. Additionally, the technology could support new tools capable of measuring magnetic fields at the nanometer scale.
Appearing early online in Nature ...