(Press-News.org) We've all experienced it: The frustration of entering a room and forgetting what we were going to do. Or get. Or find.
New research from University of Notre Dame Psychology Professor Gabriel Radvansky suggests that passing through doorways is the cause of these memory lapses.
"Entering or exiting through a doorway serves as an 'event boundary' in the mind, which separates episodes of activity and files them away," Radvansky explains.
"Recalling the decision or activity that was made in a different room is difficult because it has been compartmentalized."
The study was published recently in the Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology.
Conducting three experiments in both real and virtual environments, Radvansky's subjects – all college students – performed memory tasks while crossing a room and while exiting a doorway.
In the first experiment, subjects used a virtual environment and moved from one room to another, selecting an object on a table and exchanging it for an object at a different table. They did the same thing while simply moving across a room but not crossing through a doorway.
Radvansky found that the subjects forgot more after walking through a doorway compared to moving the same distance across a room, suggesting that the doorway or "event boundary" impedes one's ability to retrieve thoughts or decisions made in a different room.
The second experiment in a real-world setting required subjects to conceal in boxes the objects chosen from the table and move either across a room or travel the same distance and walk through a doorway. The results in the real-world environment replicated those in the virtual world: walking through a doorway diminished subjects' memories.
The final experiment was designed to test whether doorways actually served as event boundaries or if one's ability to remember is linked to the environment in which a decision – in this case, the selection of an object – was created. Previous research has shown that environmental factors affect memory and that information learned in one environment is retrieved better when the retrieval occurs in the same context. Subjects in this leg of the study passed through several doorways, leading back to the room in which they started. The results showed no improvements in memory, suggesting that the act of passing through a doorway serves as a way the mind files away memories.
### END
Walking through doorways causes forgetting, new research shows
2011-11-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA's TRMM satellite sees deadly tornadic thunderstorms in Southeastern US
2011-11-21
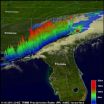
Tornadoes are expected to accompany severe storms in the springtime in the U.S., but this time of year they also usually happen. When a line of severe thunderstorms associated with a cold front swept through the U.S. southeast on Nov. 16, TRMM collected rainfall data on the dangerous storms from space.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew over the southeastern United States on November 16, 2011 at 2310 UTC (6:10 p.m. EST) when tornadoes were occurring with a line of thunderstorms that stretched from western Florida north through North Carolina. ...
A failing sense of smell can be reversed
2011-11-21
NEW YORK, November 20, 2011 – In a new study scientists at NYU Langone Medical Center have shown that the sense of smell can be improved. The new findings, published online November 20, 2011, in Nature Neuroscience, suggest possible ways to reverse the loss of smell due to aging or disease.
Smell is unique among our senses, explains Donald A. Wilson, PhD, professor of child and adolescent psychiatry at NYU Langone Medical Center and senior research scientist at the Emotional Brain Institute at Nathan S. Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research, who led the study. The ...
U-M researchers find genetic rearrangements driving 5 to 7 percent of breast cancers
2011-11-21
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — Researchers at the University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center have discovered two cancer-spurring gene rearrangements that may trigger 5 to 7 percent of all breast cancers.
These types of genetic recombinations have previously been linked to blood cancers and rare soft-tissue tumors, but are beginning to be discovered in common solid tumors, including a large subset of prostate cancers and some lung cancers.
Looking at the genetic sequencing of 89 breast cancer cell lines and tumors, researchers found two distinct types of genetic rearrangements ...
Style-Passport Launches New "Winter Sun" Collection for Year-Round Jetsetters
2011-11-21
Winter is great; who doesn't love wrapping up warm, sipping hot cocoa, making snowmen and - of course - Christmas? However, for those heading abroad and swapping frosty paths for sun-kissed beaches, buying your holiday clothes at this time of year can be more daunting than Christmas dinner with the in-laws! Help is at hand, as online fashion retailer Style-Passport have launched their winter sun collection.
Boasting beautiful bikinis, stunning sarongs and contemporary kaftans (amongst other things), Style-Passport's winter sun range is perfect for picking up the beach ...
Huskies lend insight into mercury risk
2011-11-21
Researchers have highlighted the serious health risks associated with the diets of indigenous people by linking the accumulation of mercury in their primary food source to a decrease in the power of antioxidants.
Published today, 21 November, in IOP Publishing's journal Environmental Research Letters, the study used Alaskan huskies to demonstrate the risk posed by contaminants, such as mercury, in the subsistence diets that both indigenous people and huskies live on.
Huskies are an ideal model for humans as they are exposed to the same environmental hazards and have ...
Climate change effect on release of CO2 from peat far greater than assumed
2011-11-21
Climate change effect on release of CO2 from peat far greater than assumed
Drought causes peat to release far more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than has previously been realised.
Much of the world's peatlands lie in regions predicted to experience increased frequency and severity of drought as a result of climate change- leading to the peat drying out and releasing vast stores of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. It's the very wetness of the peat that has kept the air out, locking in centuries of carbon dioxide that would normally be released from the ...
Novel ALS drug slows symptom progression, reduces mortality in phase 2 trial
2011-11-21
Treatment with dexpramipexole – a novel drug believed to prevent dysfunction of mitochondria, the subcellular structures that provide most of a cell's energy – appears to slow symptom progression in the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Promising results of a phase 2 trial of dexpramipexole are receiving advance online publication in Nature Medicine. Some preliminary results of the study were presented at the 2009 International Symposium on ALS/MND and the 2010 American Academy of Neurology annual meeting.
"Today there are only two FDA-approved ...
UGA scientists invent long-lasting, near infrared-emitting material
2011-11-21
Athens, Ga. – Materials that emit visible light after being exposed to sunlight are commonplace and can be found in everything from emergency signage to glow-in-the-dark stickers. But until now, scientists have had little success creating materials that emit light in the near-infrared range, a portion of the spectrum that only can be seen with the aid of night vision devices.
In a paper just published in the early online edition of the journal Nature Materials, however, University of Georgia scientists describe a new material that emits a long-lasting, near-infrared glow ...
Study finds sex a significant predictor of happiness among married seniors
2011-11-21
The more often older married individuals engage in sexual activity, the more likely they are to be happy with both their lives and marriages, according to new research presented in Boston at The Gerontological Society of America's (GSA) 64th Annual Scientific Meeting.
This finding is based on the 2004� General Social Surveys, a public opinion poll conducted on a nationally representative sample of non-institutionalized English and Spanish-speaking person 18 years of age or older living in the U.S. The data analysis was conducted by Adrienne Jackson, PT, PhD, MPA, ...
Recipient's immune system governs stem cell regeneration
2011-11-21
A new study in Nature Medicine describes how different types of immune system T-cells alternately discourage and encourage stem cells to regrow bone and tissue, bringing into sharp focus the importance of the transplant recipient's immune system in stem cell regeneration.
The study, conducted at the Center for Craniofacial Molecular Biology at the Ostrow School of Dentistry of USC, examined how mice with genetic bone defects responded to infusions of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, or BMMSC.
Under normal conditions, the mice's T-cells produced an inflammatory response ...