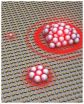
(Press-News.org) University of Illinois researchers have shown that by tuning the properties of laser light illuminating arrays of metal nanoantennas, these nano-scale structures allow for dexterous optical tweezing as well as size-sorting of particles.
"Nanoantennas are extremely popular right now because they are really good at concentrating optical fields in small areas," explained Kimani Toussaint, Jr., an assistant professor of mechanical science and engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "In this work, we demonstrate for the first time the use of arrays of gold Bowtie Nanoantenna Arrays (BNAs) for multipurpose optical trapping and manipulation of submicrometer- to micrometer-sized objects. We think that this could be a fruitful area to pursue, particularly because of the growing interest in lab-on-a-chip devices."
According to the researchers, the excellent field enhancement and confinement properties of BNAs enable highly efficient, optical tweezers which permit high-speed manipulation of submicrometer to micrometer-sized objects in aqueous environments using remarkably low-input power densities. These characteristics could be useful for optofluidic applications (e.g., lab-on-a-chip devices), manipulating biological matter with reduced specimen photo damage, formation of optical matter, and basic physics studies of colloidal dynamics.
"In contrast to other plasmonic tweezers, we find that BNAs permit particle trapping, manipulation and sorting utilizing only the optical parameter space, namely, low input power densities, wavelength and polarization," said Brian Roxworthy, a graduate student in Toussaint's research group and first author on the paper, "Application of Plasmonic Bowtie Nanoantenna Arrays for Optical Trapping, Stacking, and Sorting," which appears in the journal Nano Letters.
Using empirically obtained "optical trapping phase diagrams" to achieve the desired trapping response, the researchers demonstrated several types of particle manipulation, including single-beam optical tweezing of single particles over the entire nanoantenna area, single-beam optical tweezing of 2D hexagonal packed particles over the entire nanoantenna area, and optical sorting of particles by size; stacking of submicron to micron-sized particles in 3D.
According to Toussaint, this is the first demonstration of a range of particle manipulation behavior for a given nanoantenna array.
"We actually excite our nanoantennas off resonance, which to our knowledge is a first, and at the right input optical power, we take advantage of thermal effects combined with optical forces to enable tweezing of tens of particles at a time," Toussaint explained. "We show that very low power densities are required to achieve the aforementioned behavior. For example, we were able to carry out experiments using a standard laser pointer."
In addition to Toussaint, the lead investigator for the project, co-investigators include Gang Logan Liu, an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at Illinois, and former Illinois faculty member Nicholas Fang, who is now at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
INFORMATION:
Optical nanoantennas enable efficient multipurpose particle manipulation
2012-01-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Discrimination may harm your health, according to new Rice study
2012-01-13
Racial discrimination may be harmful to your health, according to new research from Rice University sociologists Jenifer Bratter and Bridget Gorman.
In the study, "Is Discrimination an Equal Opportunity Risk? Racial Experiences, Socio-economic Status and Health Status Among Black and White Adults," the authors examined data containing measures of social class, race and perceived discriminatory behavior and found that approximately 18 percent of blacks and 4 percent of whites reported higher levels of emotional upset and/or physical symptoms due to race-based treatment. ...
A scarcity of women leads men to spend more, save less
2012-01-13
The perception that women are scarce leads men to become impulsive, save less, and increase borrowing, according to new research from the University of Minnesota's Carlson School of Management.
"What we see in other animals is that when females are scarce, males become more competitive. They compete more for access to mates," says Vladas Griskevicius, an assistant professor of marketing at the Carlson School and lead author of the study. "How do humans compete for access to mates? What you find across cultures is that men often do it through money, through status and ...
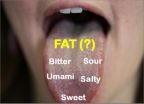
Receptor for tasting fat identified in humans
2012-01-13
Why do we like fatty foods so much? We can blame our taste buds.
Our tongues apparently recognize and have an affinity for fat, according to researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. They have found that variations in a gene can make people more or less sensitive to the taste of fat.
The study is the first to identify a human receptor that can taste fat and suggests that some people may be more sensitive to the presence of fat in foods. The study is available online in the Journal of Lipid Research.
Investigators found that people with ...
Research team discovers genes and disease mechanisms behind a common form of muscular dystrophy
2012-01-13
SEATTLE – Continuing a series of groundbreaking discoveries begun in 2010 about the genetic causes of the third most common form of inherited muscular dystrophy, an international team of researchers led by a scientist at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center has identified the genes and proteins that damage muscle cells, as well as the mechanisms that can cause the disease. The findings are online and will be reported in the Jan. 17 print edition of the journal Developmental Cell.
The discovery could lead to a biomarker-based test for diagnosing facioscapulohumeral muscular ...
Planets around stars are the rule rather than the exception
2012-01-13
LIVERMORE, Calif. --There are more exoplanets further away from their parent stars than originally thought, according to new astrophysics research.
In a new paper appearing in the Jan. 12 edition of the journal, Nature, astrophysicist Kem Cook as part of an international collaboration, analyzed microlensing data that bridges the gap between a recent finding of planets further away from their parent stars and observations of planets extremely close to their parent star. The results point to more planetary systems resembling our solar system rather than being significantly ...
ONR's information discovery and sharing environment undergoes 'Marathon' experiment
2012-01-13
The ability to catch international smugglers and terrorists just got upgraded with a Jan. 12 demonstration of collaborative software funded by the Office of Naval Research (ONR).
The Mission-Focused Autonomy (MFA) program was put into practice for the Joint Interagency Task Force (JIATF) South in Key West, Fla., during an exercise dubbed "Marathon." The collaborative information discovery and knowledge-sharing tools sift through government agency databases to support efforts by federal law enforcement for information on foreign nationals intent on harming national security ...
Largest bird alters its foraging due to climate change
2012-01-13
Paris/ Leipzig. Wandering albatrosses have altered their foraging due to changes in wind fields in the southern hemisphere during the last decades. Since winds have increased in intensity and moved to the south, the flight speed of albatrosses increased and they spend less time foraging. As a consequence, breeding success has improved and birds have gained 1 kilogram. These are the results of the study of an international research team published in the latest issue of the Science journal. However, these positive consequences of climate change may last short if future wind ...
Graphene quantum dots: The next big small thing
2012-01-13
A Rice University laboratory has found a way to turn common carbon fiber into graphene quantum dots, tiny specks of matter with properties expected to prove useful in electronic, optical and biomedical applications.
The Rice lab of materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan, in collaboration with colleagues in China, India, Japan and the Texas Medical Center, discovered a one-step chemical process that is markedly simpler than established techniques for making graphene quantum dots. The results were published online this month in the American Chemical Society's journal Nano ...
Deaf sign language users pick up faster on body language
2012-01-13
Deaf people who use sign language are quicker at recognizing and interpreting body language than hearing non-signers, according to new research from investigators at UC Davis and UC Irvine.
The work suggests that deaf people may be especially adept at picking up on subtle visual traits in the actions of others, an ability that could be useful for some sensitive jobs, such as airport screening.
"There are a lot of anecdotes about deaf people being better able to pick up on body language, but this is the first evidence of that," said David Corina, professor in the UC ...
How the brain routes traffic for maximum alertness
2012-01-13
A new UC Davis study shows how the brain reconfigures its connections to minimize distractions and take best advantage of our knowledge of situations.
"In order to behave efficiently, you want to process relevant sensory information as fast as possible, but relevance is determined by your current situation," said Joy Geng, assistant professor of psychology at the UC Davis Center for Mind and Brain.
For example, a flashing road sign alerts us to traffic merging ahead; or a startled animal might cue you to look out for a hidden predator.
When concentrating on a specific ...