(Press-News.org) Polymer nano-films and nano-composites are used in a wide variety of applications from food packaging to sports equipment to automotive and aerospace applications. Thermal analysis is routinely used to analyze materials for these applications, but the growing trend to use nanostructured materials has made bulk techniques insufficient.
In recent years an atomic force microscope-based technique called nanoscale thermal analysis (nanoTA) has been employed to reveal the temperature-dependent properties of materials at the sub-100 nm scale. Typically, nanothermal analysis works best for soft polymers. Researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Anasys Instruments, Inc. have now shown that they can perform nanoscale thermal analysis on stiff materials like epoxies and filled composites.
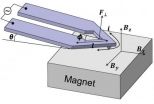
"This new technique lets us measure temperature and frequency-dependent properties of materials rapidly over a wide bandwidth," noted William King, the College of Engineering Bliss Professor in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering at Illinois, who led the research. The technique works by flowing a current around the U-shaped arms of a self-heating atomic force microscope (AFM) cantilever and interacting that current with a magnetic field. The magnetic field allows the tip-sample force to be modulated right near the tip of the AFM.
"We are able to achieve nanometer-scale force control that is independent from the heating temperature," according to Byeonghee Lee, first author of the paper.
"Conventional nanothermal analysis has struggled with highly filled, highly crosslinked materials and sub-100 nm thin films. This new technique has allowed us to reliably measure and map glass transitions and melting transions on classes of materials that were previously very challenging," said Craig Prater, chief technology officer at Anasys Instruments and co-author on the paper.
The paper title is "Magnetic Actuation of a Heated Atomic Force Microscope Cantilever using Lorentz Force," and was published in the journal Nanotechnology (doi:10.1088/0957-4484/23/5/055709).
INFORMATION:
The research was performed in King's Nanoengineering Laboratory and at Anasys Instruments. The research was sponsored by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the National Science Foundation.
Magnetic actuation enables nanoscale thermal analysis
Heated nanoprobes perform thermo-mechanical measurements using magnetic actuation
2012-01-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New 'smart' nanotherapeutics can deliver drugs directly to the pancreas
2012-01-13
BOSTON, January 12, 2012: A research collaboration between the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University and Children's Hospital Boston has developed "smart" injectable nanotherapeutics that can be programmed to selectively deliver drugs to the cells of the pancreas. Although this nanotechnology will need significant additional testing and development before being ready for clinical use, it could potentially improve treatment for Type I diabetes by increasing therapeutic efficacy and reducing side effects.
The approach was found to increase ...
'Open-source' robotic surgery platform going to top medical research labs
2012-01-13
SANTA CRUZ, CA--Robotics experts at the University of California, Santa Cruz and the University of Washington (UW) have completed a set of seven advanced robotic surgery systems for use by major medical research laboratories throughout the United States. After a round of final tests, five of the systems will be shipped to medical robotics researchers at Harvard University, Johns Hopkins University, University of Nebraska, UC Berkeley, and UCLA, while the other two systems will remain at UC Santa Cruz and UW.
"We decided to follow an open-source model, because if all ...
Optical nanoantennas enable efficient multipurpose particle manipulation
2012-01-13
University of Illinois researchers have shown that by tuning the properties of laser light illuminating arrays of metal nanoantennas, these nano-scale structures allow for dexterous optical tweezing as well as size-sorting of particles.
"Nanoantennas are extremely popular right now because they are really good at concentrating optical fields in small areas," explained Kimani Toussaint, Jr., an assistant professor of mechanical science and engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "In this work, we demonstrate for the first time the use of arrays ...
Discrimination may harm your health, according to new Rice study
2012-01-13
Racial discrimination may be harmful to your health, according to new research from Rice University sociologists Jenifer Bratter and Bridget Gorman.
In the study, "Is Discrimination an Equal Opportunity Risk? Racial Experiences, Socio-economic Status and Health Status Among Black and White Adults," the authors examined data containing measures of social class, race and perceived discriminatory behavior and found that approximately 18 percent of blacks and 4 percent of whites reported higher levels of emotional upset and/or physical symptoms due to race-based treatment. ...
A scarcity of women leads men to spend more, save less
2012-01-13
The perception that women are scarce leads men to become impulsive, save less, and increase borrowing, according to new research from the University of Minnesota's Carlson School of Management.
"What we see in other animals is that when females are scarce, males become more competitive. They compete more for access to mates," says Vladas Griskevicius, an assistant professor of marketing at the Carlson School and lead author of the study. "How do humans compete for access to mates? What you find across cultures is that men often do it through money, through status and ...
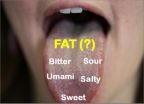
Receptor for tasting fat identified in humans
2012-01-13
Why do we like fatty foods so much? We can blame our taste buds.
Our tongues apparently recognize and have an affinity for fat, according to researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. They have found that variations in a gene can make people more or less sensitive to the taste of fat.
The study is the first to identify a human receptor that can taste fat and suggests that some people may be more sensitive to the presence of fat in foods. The study is available online in the Journal of Lipid Research.
Investigators found that people with ...
Research team discovers genes and disease mechanisms behind a common form of muscular dystrophy
2012-01-13
SEATTLE – Continuing a series of groundbreaking discoveries begun in 2010 about the genetic causes of the third most common form of inherited muscular dystrophy, an international team of researchers led by a scientist at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center has identified the genes and proteins that damage muscle cells, as well as the mechanisms that can cause the disease. The findings are online and will be reported in the Jan. 17 print edition of the journal Developmental Cell.
The discovery could lead to a biomarker-based test for diagnosing facioscapulohumeral muscular ...
Planets around stars are the rule rather than the exception
2012-01-13
LIVERMORE, Calif. --There are more exoplanets further away from their parent stars than originally thought, according to new astrophysics research.
In a new paper appearing in the Jan. 12 edition of the journal, Nature, astrophysicist Kem Cook as part of an international collaboration, analyzed microlensing data that bridges the gap between a recent finding of planets further away from their parent stars and observations of planets extremely close to their parent star. The results point to more planetary systems resembling our solar system rather than being significantly ...
ONR's information discovery and sharing environment undergoes 'Marathon' experiment
2012-01-13
The ability to catch international smugglers and terrorists just got upgraded with a Jan. 12 demonstration of collaborative software funded by the Office of Naval Research (ONR).
The Mission-Focused Autonomy (MFA) program was put into practice for the Joint Interagency Task Force (JIATF) South in Key West, Fla., during an exercise dubbed "Marathon." The collaborative information discovery and knowledge-sharing tools sift through government agency databases to support efforts by federal law enforcement for information on foreign nationals intent on harming national security ...
Largest bird alters its foraging due to climate change
2012-01-13
Paris/ Leipzig. Wandering albatrosses have altered their foraging due to changes in wind fields in the southern hemisphere during the last decades. Since winds have increased in intensity and moved to the south, the flight speed of albatrosses increased and they spend less time foraging. As a consequence, breeding success has improved and birds have gained 1 kilogram. These are the results of the study of an international research team published in the latest issue of the Science journal. However, these positive consequences of climate change may last short if future wind ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
[Press-News.org] Magnetic actuation enables nanoscale thermal analysisHeated nanoprobes perform thermo-mechanical measurements using magnetic actuation