(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
The most visible change in the Arctic region in recent years has been the rapid decline of the perennial ice cover. The perennial ice is the portion of the sea...
Click here for more information.
GREENBELT, Md. -- A new NASA study revealed that the oldest and thickest Arctic sea ice is disappearing at a faster rate than the younger and thinner ice at the edges of the Arctic Ocean's floating ice cap.
The thicker ice, known as multi-year ice, survives through the cyclical summer melt season, when young ice that has formed over winter just as quickly melts again. The rapid disappearance of older ice makes Arctic sea ice even more vulnerable to further decline in the summer, said Joey Comiso, senior scientist at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md., and author of the study, which was recently published in Journal of Climate.
The new research takes a closer look at how multi-year ice, ice that has made it through at least two summers, has diminished with each passing winter over the last three decades. Multi-year ice "extent" – which includes all areas of the Arctic Ocean where multi-year ice covers at least 15 percent of the ocean surface – is diminishing at a rate of -15.1 percent per decade, the study found.
There's another measurement that allows researchers to analyze how the ice cap evolves: multi-year ice "area," which discards areas of open water among ice floes and focuses exclusively on the regions of the Arctic Ocean that are completely covered by multi-year ice. Sea ice area is always smaller than sea ice extent, and it gives scientists the information needed to estimate the total volume of ice in the Arctic Ocean. Comiso found that multi-year ice area is shrinking even faster than multi-year ice extent, by -17.2 percent per decade.
"The average thickness of the Arctic sea ice cover is declining because it is rapidly losing its thick component, the multi-year ice. At the same time, the surface temperature in the Arctic is going up, which results in a shorter ice-forming season," Comiso said. "It would take a persistent cold spell for most multi-year sea ice and other ice types to grow thick enough in the winter to survive the summer melt season and reverse the trend."
Scientists differentiate multi-year ice from both seasonal ice, which comes and goes each year, and "perennial" ice, defined as all ice that has survived at least one summer. In other words: all multi-year ice is perennial ice, but not all perennial ice is multi-year ice (it can also be second-year ice).
Comiso found that perennial ice extent is shrinking at a rate of -12.2 percent per decade, while its area is declining at a rate of -13.5 percent per decade. These numbers indicate that the thickest ice, multiyear-ice, is declining faster than the other perennial ice that surrounds it.
As perennial ice retreated in the last three decades, it opened up new areas of the Arctic Ocean that could then be covered by seasonal ice in the winter. A larger volume of younger ice meant that a larger portion of it made it through the summer and was available to form second-year ice. This is likely the reason why the perennial ice cover, which includes second year ice, is not declining as rapidly as the multiyear ice cover, Comiso said.
Multi-year sea ice hit its record minimum extent in the winter of 2008. That is when it was reduced to about 55 percent of its average extent since the late 1970s, when satellite measurements of the ice cap began. Multi-year sea ice then recovered slightly in the three following years, ultimately reaching an extent 34 percent larger than in 2008, but it dipped again in winter of 2012, to its second lowest extent ever.
For this study, Comiso created a time series of multi-year ice using 32 years of passive microwave data from NASA's Nimbus-7 satellite and the U.S. Department of Defense's Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, taken during the winter months from 1978 to 2011. This is the most robust and longest satellite dataset of Arctic sea ice extent data to date, Comiso said.
Younger ice, made from recently frozen ocean waters, is saltier than multi-year ice, which has had more time to drain its salts. The salt content in first- and second-year ice gives them different electrical properties than multi-year ice: In winter, when the surface of the sea ice is cold and dry, the microwave emissivity of multiyear ice is distinctly different from that of first- and second-year ice. Microwave radiometers on satellites pick up these differences in emissivity, which are observed as variations in brightness temperature for the different types of ice. The "brightness" data are used in an algorithm to discriminate multiyear ice from other types of ice.
Comiso compared the evolution of the extent and area of multi-year ice over time, and confirmed that its decline has accelerated during the last decade, in part because of the dramatic decreases of 2008 and 2012. He also detected a periodic nine-year cycle, where sea ice extent would first grow for a few years, and then shrink until the cycle started again. This cycle is reminiscent of one occurring on the opposite pole, known as the Antarctic Circumpolar Wave, which has been related to the El Niño-Southern Oscillation atmospheric pattern. If the nine-year Arctic cycle were to be confirmed, it might explain the slight recovery of the sea ice cover in the three years after it hit its historical minimum in 2008, Comiso said.
###For more information and related images, visit:
http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/thick-melt.html
NASA finds thickest parts of Arctic ice cap melting faster
2012-03-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA satellite sees tropical cyclone Irina headed for Mozambique
2012-03-01
Visible and Infrared satellite imagery together provide a clearer picture of what a tropical cyclone is doing. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over newly strengthened Cyclone Irene and captured both types of images, which showed the extent and power of the storm.
The low pressure area called System 92S that tracked across northern Madagascar this week and brought flooding rains has moved into the Mozambique Channel, strengthen and has been renamed Irina. NASA satellites captured a visible image of Irina as it filled up the northern half of the Mozambique Channel.
System ...
Jackson Grills Inc. Now Under New Ownership, Reflecting a Strong Commitment to Quality With a Fresh New Website
2012-03-01
Jackson Grills, a leading specialty grill manufacturer, is announcing a new ownership structure and website to support their corporate mandate of offering "Premium Quality."
"We believe that the Jackson Grills product lineup fills a unique niche in the barbeque market - one that masterfully balances value with style and performance," says Ken Friesen, Owner of Jackson Grills. Initiated by the new ownership, Jackson Grills has undergone a complete brand makeover, featuring a new refined logo, tagline, website and social media initiatives.
"All ...
Can industrial parks be more environmentally friendly?
2012-03-01
New Rochelle, NY, February 29, 2012—Although industrial parks are often considered major economic engines for the communities in which they reside, they can also consume environmental resources and produce significant pollution that can negatively affect human health and quality of life. A case study published in Environmental Engineering Science (http://www.liebertpub.com/ees), a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. (http://www.liebertpub.com), describes a systems-based approach to assess and reduce the negative societal and economic impact of industrial parks. ...
Fitness programs for minority adults lack cultural relevance, MU study finds
2012-03-01
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Many leading causes of death are linked to unhealthy lifestyle behaviors, including inadequate physical activity. Adults in minority populations have lower levels of physical activity and higher rates of preventable deaths, according to the Department of Health & Human Services. In a new study, University of Missouri researchers found that minority adults who received exercise interventions increased their physical activity levels. However, these interventions are not culturally tailored to best assist minority populations in improving overall health.
Conn ...
Postmenopausal women at greater risk of stroke from high trans fat intake
2012-03-01
New research shows an increased risk of ischemic stroke in postmenopausal women who consume higher amounts of trans fatty acids, commonly found in baked goods, fried foods, and packaged products. Study findings now available in Annals of Neurology, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the American Neurological Association and Child Neurology Society, suggest aspirin use may moderate the stroke risk caused by a diet high in trans fats.
Ischemic stroke is a result of a blockage in an artery leading to the brain. According to the American Heart Association ...
Study: Sleep gets better with age, not worse
2012-03-01
DARIEN, IL – Aging does not appear to be a factor in poor sleep, a new survey of more than 150,000 Americans shows. In fact, subjective sleep quality seems to improve over a lifetime, with the fewest complaints coming from people in their 80s.
"This flies in the face of popular belief," said Michael Grandner, PhD, lead author of the study. "These results force us to re-think what we know about sleep in older people – men and women."
The study, appearing in the March edition of the journal Sleep, examined rates of sleep disturbance and daytime fatigue reported by 155,877 ...
Medical School implements successful radiation protection program for undergraduate medical students
2012-03-01
Reston, VA -- A medical school in Ireland has successfully implemented a radiation protection program, improving knowledge of radiation protection among medical undergraduates, according to a study in the March issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology.
Although the increased use of diagnostic imaging has resulted in faster, more accurate diagnosis, better assessment of therapy response, and early detection of complications, there has been a great deal of scrutiny of its increasing use. As a result, there is a growing need for medical professionals to ...
Radiation, business and health care policy curricula for US radiation residents show need for improvement
2012-03-01
Reston, VA -- Residency training requirements in competencies related to radiology business practice and health care policy have been in place for more than a decade. However, a recent study, published in the March issue of the Journal of the American College of Radiology, suggests curricula addressing these items still seem to be in a stage of acceptance and development.
"The United States has been experiencing a period of rapid changes in health care delivery and financing. Institutions and individuals have been repeatedly challenged to successfully adapt to the accelerating ...
New function of a bacterial photoresponsive protein: Resisting adhesion of mammalian cells
2012-03-01
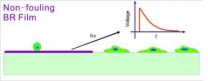
Non-fouling materials that resist cell adhesion are very important in fundamental research on cell–biomaterial interactions and for practical applications. Thus, they have been extensively investigated during the last decade. Natural biomacromolecules such as bovine serum albumin (BSA) have conventionally been used to block cell adhesion. Zhao and Ding (Fudan University, Shanghai, China) recently reported that the purple membrane (PM) containing a natural photoresponsive protein, bacteriorhodopsin (BR), can serve as a new basic substance that resists adhesion of mammalian ...
Titanic Disaster Centenary Inspires Publication by the Darwin Press of the Authentic Love Story of Two Survivors: Starboard at Midnight by Helen Behr Sanford
2012-03-01
Although the Titanic disaster is widely known, the authentic story of the lovers, tennis star Karl H. Behr and Helen Newsom, is little known...until now. This new, definitive biography, Starboard at Midnight, written by their granddaughter, brings to light the long-buried secrets of these two survivors, breathing new life into legend.
Based on Karl Behr's unpublished autobiography (now in the Tennis Hall of Fame, Newport, RI) along with family scrapbooks and more than ten years of research into the historical background of this period, the full story of this epic romance ...