(Press-News.org) Couples who are married or living together will probably have more trouble parenting as a team if they have been violent toward one another during pregnancy, according to a team of psychologists.
"This finding is helpful because working as a parenting team, in what we call the co-parenting relationship, is a key influence on everything from mothers' postpartum depression to sensitive parenting to the children's emotional and social adjustment," said Mark E. Feinberg, research professor, Prevention Research Center for the Promotion of Human Development at Penn State.
Researchers interviewed 156 expectant couples at three different times -- once before the baby was born, again about six months after the birth of the child and a final time, when the baby was approximately 13 months old. The interviews determined the degree of physical violence between couples prior to the birth of the baby and how well couples were able to act as a team while parenting, after the baby was born.
"The results suggest that working with couples to curtail or prevent violence in their relationships before the birth of their child may have positive implications for the development of co-parenting relationships after the child is born," said the researchers.
The researchers reported in the current issue of the Journal of Family Issues that 29.8 percent of mothers acted violently at least once in the past year, while 17.3 percent of fathers acted violently. Finding mothers to be more violent than fathers is not an uncommon discovery in average community samples, according to the researchers.
"In our sample it seemed to be the 'common couple' type of violence that occurred, not the controlling and severe abuse that people think of when they think of domestic violence," said Marni L. Kan, Ph.D. recipient in human development and family studies at Penn State, now a research psychologist with RTI International in Research Triangle Park, N.C.
Common couple violence incidents are fairly high, especially for couples with young children, Feinberg said. This type of violence is characterized by actions like shoving, slapping and hitting and is usually not intended to control the partner but occurs out of frustration in the middle of an argument. Both partners are equally likely to participate in common couple violence.
"It is important to pay attention to prenatal violence and risk, because low levels of violence among couples may get worse with the stress of parenting small children," said Feinberg. "And there's a lot of overlap between couple violence and child maltreatment."
Only expectant couples were eligible to enroll in the study. Each individual completed a form that asked a series of questions about physical aggression and behavior in the couple's relationship -- such as, did you push or shove your partner? Did you choke your partner? Did you twist your partner's arm?
Questions were each answered with a frequency measure -- did this behavior happen zero times in the past year? Five times in the past year? More than 20 times in the past year?
The participants answered questions pertaining to both their own behavior and their partner's behavior.
After the child was born, participants filled out another survey that looked at the co-parental alliance. Participants were asked to rate whether statements were true for their relationship, such as, "My partner and I have the same goals for our child," "My relationship with my partner is stronger now than before we had a child," and "My partner does not trust my parenting abilities." The higher the score a couple received, the better they were determined to be at parenting as a team.
"A unique element of our research is that we included couples," said Kan. "A lot of research on violence focuses on female victims. Also, having both parents followed after the birth of the child is unique. Often the moms are reporting, but the dads don't have a say."
Anna R. Solmeyer, doctoral student in human development and family studies, Penn State, also worked on this research.
INFORMATION:
The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institute of Mental Health supported this research.
END
CHICAGO --- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle from young adulthood into your 40s is strongly associated with low cardiovascular disease risk in middle age, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study.
"The problem is few adults can maintain ideal cardiovascular health factors as they age," said Kiang Liu, first author of the study. "Many middle-aged adults develop unhealthy diets, gain weight and aren't as physically active. Such lifestyles, of course, lead to high blood pressure and cholesterol, diabetes and elevated cardiovascular risk."
Liu is a professor and the ...
Batavia, Ill. -- The world's most precise measurement of the mass of the W boson, one of nature's elementary particles, has been achieved by scientists from the CDF and DZero collaborations at the Department of Energy's Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory.
The new measurement is an important, independent constraint of the mass of the theorized Higgs boson. It also provides a rigorous test of the Standard Model that serves as the blueprint for our world, detailing the properties of the building blocks of matter and how they interact.
The Higgs boson is the last ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers have discovered critical new details about the structure of a virus that causes potentially fatal brain swelling and paralysis in children, pointing toward designs for antiviral drugs to treat the disease.
The virus, called enterovirus 71, causes hand, foot and mouth disease, and is common throughout the world. Although that disease usually is not fatal, the virus has been reported to cause encephalitis, a potentially fatal illness found primarily in the Asia-Pacific region.
Now, two research teams are reporting new findings about ...
A deterioration of working memory is observed in people who consume drugs containing cannabinoid compounds found in cannabis leaves and buds. A team led by Giovanni Marsicano (Inserm Research Unit 862) in collaboration with a team led by Xia Zhang, has recently identified the mechanism by which these substances affect working memory. These researchers have demonstrated for the first time that the adverse effect of cannabinoids on working memory is exerted via receptors located in the glial cells (brain cells present in large numbers and scarcely studied). This effect is ...
Do you want to achieve your business goals in the next five years? Your personal goals in three years or so? How about achieving them now?
Anyone interested in rapid results for achieving business or life goals can benefit from a free online training video, "6 Steps for Your Rapid Results in Business and Life." The free online video was developed by personal development and fitness guru John Spencer Ellis and Jairek Robbins, the world's foremost authority at developing creative solutions for achieving results; it is now available online at John Spencer Ellis' ...
ATLANTA – The American College of Rheumatology has released the first classification criteria for polymyalgia rheumatica – aimed at helping physicians identify patients with this condition, which occurs in persons aged 50 years or older who have recent onset of pain in the shoulders, neck and hips along with other inflammatory symptoms not explained by an alternate diagnosis.
Polymyalgia rheumatica is a relatively common cause of widespread aching and stiffness in older adults. It can be difficult to diagnose because it rarely causes swollen joints or other abnormalities ...
A small clinical trial led by researchers at UC San Diego School of Medicine and VA San Diego Healthcare System (VASDHS) found that patients with advanced heart failure and type 2 diabetes showed improved mitochondrial structure after three months of treatment with epicatechin-enriched cocoa. Epicatechin is a flavonoid found in dark chocolate.
The results of this initial study has led to the implementation of larger, placebo-controlled clinical trial at UC San Diego School of Medicine and VASDHS to assess if patients with heart failure and diabetes show improvement ...
Emotion-sensing computer software that models and responds to students' cognitive and emotional states – including frustration and boredom – has been developed by University of Notre Dame Assistant Professor of Psychology Sidney D'Mello and colleagues from the University of Memphis and Massachusetts Institute of Technology. D'Mello also is a concurrent assistant professor of computer science and engineering.
The new technology, which matches the interaction of human tutors, not only offers tremendous learning possibilities for students, but also redefines human-computer ...
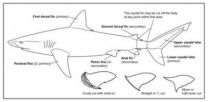
Shark fins are worth more than other parts of the shark and are often removed from the body, which gets thrown back into the sea. To curtail this wasteful practice, many countries allow the fins to be landed detached from shark bodies, as long as their weight does not exceed five per cent of the total shark catch. New University of British Columbia research shows that this kind of legislation is too liberal.
A study published this week in the journal Fish Biology analyzes the fin to body weight ratios for 50 different shark species. The authors find the average fin ...
DestinationPro.com is a solution allowing independent execution of events and incentive programs. If anyone needed to organize a corporate meeting, business trip, training, bonus (incentive) trip for employees, conference, etc., he/she usually took advantage of services provided by one of the specialized agencies (DMCs - Destination Management Company). Based on the client's specification, such agency proposed agenda and individual suppliers (accommodation, restaurants, venues, transportation, logistic, etc.), subsequently ensuring and executing the whole event.
We ...