(Press-News.org) Researchers at Mount Sinai School of Medicine have found that 92 percent of more than 1,000 gastroenterologists responding to a survey believed that pressures to increase the volume of colonoscopies adversely impacted how they performed their procedures, which could potentially affect the quality of colon cancer screening. The findings, based on responses from members of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE), are published in the March 2012 issue of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
"The number of colonoscopies has risen dramatically over the past fifteen years, but it is imperative that an increase in volume not occur at the expense of quality and safety," said Lawrence B. Cohen, MD, lead study author and an Associate Clinical Professor of Gastroenterology at Mount Sinai. "Balancing quantity and quality is an issue that needs to be addressed in order to ensure the continued success of colon cancer prevention programs."
Overall, 92.3 percent of survey respondents indicated that production pressures, such as heightened demand for the procedure, rising overhead or shrinking reimbursement rates, resulted in physicians postponing, aborting or reducing the extent of a colonoscopy procedure. For example, 7.2 percent of participants said production pressures made them reduce the time examining the colon wall, 5.3 percent of participants said these pressures made them abort a difficult colonoscopy, and 69 percent said they performed a colonoscopy on a patient with an unfavorable risk/benefit ratio.
Mount Sinai researchers sent a 40-question survey to the 5,739 members of the ASGE working in the United States and received 1,073 completed responses. The survey focused on three key areas: the respondent's demographic and practice characteristics, the operational characteristics of their facilities and their observations of colleagues.
Additional results of the survey include:
13 percent of respondents indicated that they have insufficient time for a pre-procedure assessment, 7.7 percent believed they routinely had inadequate time to complete an examination and 5.5 percent believed that patients were discharged from the unit prematurely;
47.8 percent of respondents had witnessed a colleague alter their usual practice patterns, within the past three years, as a result of production pressure;
42 percent identified one or more sources of inefficiency in their practice, such as an inadequate number of procedure rooms, insufficient staff, or too few beds in the recovery unit;
77.8 percent believed that their weekly workload was excessive; 97 percent believe the medical care that they provide is equivalent to or better than it was three years ago, but 78.5 percent experienced more work-related stress, compared with three years earlier; and 81 percent indicated they are working harder now to preserve their practice income.
"At Mount Sinai, we have worked diligently to implement continuous quality-improvement programs, offer periodic retraining, and allocate enough time per procedure," said Dr. Cohen. "In fact, we perform colonoscopies in half-day blocks, and emphasize the importance of the quality of bowel cleansing. Ultimately, we all need to confront the issue of production pressure and create these kinds of solutions in order to ensure the delivery of effective colonoscopy screenings."
###
Mount Sinai's Gastroenterology Division is ranked fifth in the country among top hospitals, according to U.S. News and World Report.
About The Mount Sinai Medical Center
The Mount Sinai Medical Center encompasses both The Mount Sinai Hospital and Mount Sinai School of Medicine. Established in 1968, Mount Sinai School of Medicine is one of the leading medical schools in the United States. The Medical School is noted for innovation in education, biomedical research, clinical care delivery, and local and global community service. It has more than 3,400 faculty in 32 departments and 14 research institutes, and ranks among the top 20 medical schools both in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and by US News and World Report.
The Mount Sinai Hospital, founded in 1852, is a 1,171-bed tertiary- and quaternary-care teaching facility and one of the nation's oldest, largest and most-respected voluntary hospitals. In 2011, US News and World Report ranked The Mount Sinai Hospital 16th on its elite Honor Roll of the nation's top hospitals based on reputation, safety, and other patient-care factors. Of the top 20 hospitals in the United States, Mount Sinai is one of 12 integrated academic medical centers whose medical school ranks among the top 20 in NIH funding and US News and World Report and whose hospital is on the US News and World Report Honor Roll. Nearly 60,000 people were treated at Mount Sinai as inpatients last year, and approximately 560,000 outpatient visits took place.
For more information, visit http://www.mountsinai.org/.
Find Mount Sinai on:
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/mountsinainyc
Twitter: @mountsinainyc
YouTube: http://www.youtube.com/mountsinainy
END
For the red pigmentation to develop, blood oranges normally require a period of cold as they ripen. The only place to reliably grow them on a commercial scale is in the Sicilian area of Italy around Mount Etna. Here, the combination of sun and cold/sunny days and warm nights provides ideal growing conditions.
Scientists have identified the gene responsible for blood orange pigmentation, naming it Ruby, and have discovered how it is controlled.
"Blood oranges contain naturally-occurring pigments associated with improved cardiovascular health, controlling diabetes and ...
A recent study led by Gergely Lukacs, a professor at McGill University's Faculty of Medicine, Department of Physiology, and published in the January issue of Cell, has shown that restoring normal function to the mutant gene product responsible for cystic fibrosis (CF) requires correcting two distinct structural defects. This finding could point to more effective therapeutic strategies for CF in the future.
CF, a fatal genetic disease that affects about 60,000 people worldwide, is caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), a ...
A novel study of honey bee genetic diversity co-authored by an Indiana University biologist has for the first time found that greater diversity in worker bees leads to colonies with fewer pathogens and more abundant helpful bacteria like probiotic species.
Led by IU Bloomington assistant professor Irene L.G. Newton and Wellesley College assistant professor Heather Mattila, and co-authors from Wellesley College and the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research, the new work describes the communities of active bacteria harbored by honey bee colonies. The ...
A study of cervical cancer incidence and mortality in North Carolina has revealed areas where rates are unusually high.
The findings indicate that education, screening, and vaccination programs in those places could be particularly useful, according to public health researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who authored the report.
"In general the rates of incidence and mortality in North Carolina are consistent with national averages," said Jennifer S. Smith, Ph.D., associate professor of epidemiology at the UNC Gillings School of Global Public ...
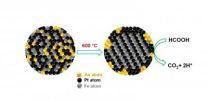
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Advances in fuel-cell technology have been stymied by the inadequacy of metals studied as catalysts. The drawback to platinum, other than cost, is that it absorbs carbon monoxide in reactions involving fuel cells powered by organic materials like formic acid. A more recently tested metal, palladium, breaks down over time.
Now chemists at Brown University have created a triple-headed metallic nanoparticle that they say outperforms and outlasts all others at the anode end in formic-acid fuel-cell reactions. In a paper published in the ...
Could parental exposure to solvents at work be linked to autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in their children? According to an exploratory study by Erin McCanlies, a research epidemiologist from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), and colleagues, such exposures could play a role, but more research would be needed to confirm an association. Their pilot study is published online in Springer's Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders.
The experts' assessment indicated that exposures to lacquer, varnish and xylene occurred more often in the ...
A program that helps obese patients improve healthy behaviors is associated with modest weight loss and improved blood pressure control in a high-risk, low-income group, according to researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Duke University, Harvard University and other institutions.
The research is published March 12 in Archives of Internal Medicine.
Obesity treatments are not widely available in the U.S. primary care setting, particularly for low-income patients who seek care at community health centers, according to the study's authors. ...
A study by the Children's Oncology Group (COG) reported that five-year survival for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL, the most common type of pediatric cancer) among children treated through COG clinical trials increased from 83.7 percent during the period 1990-1994 to 90.4 percent in the period 2000-2005. The improvements in survival were observed among all children over age 1 regardless of age, sex, ethnicity, or subtype of ALL. This analysis, which is the largest study to date of ALL survival, showed similar gains in 10-year survival. The findings are published March ...
Kandy Magazine announced today that it is now available as a FREE iPad App in Apple's Newsstand and in less than a week has attained a top 100 ranking. To commemorate the release of the Kandy Magazine iPad app in the App Store, the first 100,000 downloads of the newest iPad edition featuring the World's Sexiest DJ Colleen Shannon are complimentary.
The Kandy App features in-app social media integration, in-app media libraries, notes, pinch-to-zoom, vertical scroll and easy navigation menus.
"As an independent publisher we took a look at the different options ...
For children aged 14 and under, delaying reconstructive surgery for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries may raise their risk of further injury, according to a new study by pediatric orthopaedic surgeons. If surgery occurs later than 12 weeks after the injury, the injury may even be irreparable.
"Treating ACL injuries in these children is controversial, because they are still growing and the surgery has a small risk of causing a growth disturbance," said study leader J. Todd Lawrence, M.D., Ph.D., an orthopaedic surgeon at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. ...