Gold nanoantennas detect proteins
New method of monitoring protein molecules using gold nanoparticles
2012-03-15
(Press-News.org) Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany have developed a new method of observing individual proteins. Detailed knowledge of the dynamics of proteins is necessary in order to understand the related biological processes that occur on the molecular level. To date, this information has been obtained by means of labeling proteins with fluorescent substances, but unfortunately this changes the proteins under investigation and thus influences the biological processes that are to be observed. "Our method allows live tracking of individual proteins without having to label them first," explains Professor Dr. Carsten Sönnichsen of the Institute of Physical Chemistry at JGU. "We are now gaining entirely new insights into molecular processes and can see, for example, how things are constantly in motion even on the very smallest scale."
The method developed by the group of Mainz chemists led by Carsten Sönnichsen is based on the use of gold nanoparticles. These serve as glistening nanoantennas that, when they detect individual unlabeled proteins, slightly change their frequency or, in other words, their color. These tiny color changes can be observed using the technique developed in Mainz. "This is an enormous leap forward technologically: We have managed to achieve a very high time resolution for the observation of individual molecules," says Sönnichsen. It is thus now possible to precisely observe the dynamics of a protein molecule down to the millisecond.
The opportunity to detect individual protein molecules also opens up completely new horizons. It has thus become practicable to track the fluctuation of protein population densities and observe protein adsorption processes in real time, among other things. "We can see how molecules move, how they dock at particular locations, and how they fold – this has given us a window into the molecular world," explains Dr. Irene Ament, a member of Sönnichsen's group. This new technology may prove to be useful not only in chemistry but also in medicine and biology.
The work is an important element in research into non-equilibrium phenomena at the molecular level and thus provides a solid foundation for the planned Cluster of Excellence Molecularly Controlled Non-Equilibrium (MCNE), which has been selected to enter the final round of the Excellence Initiative by the German federal and state governments to promote top-level research at German universities. Among other sources, the project received financial support in the form of an ERC Starting Grant for the project "Single metal nanoparticles as molecular sensors" (SINGLESENS).
INFORMATION:
Publication:
I. Ament et al., Single Unlabeled Protein Detection on Individual Plasmonic Nanoparticles, Nano Letters, 12:2, 1092-1095, 23 January 2012
doi:10.1021/nl204496g
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-03-15
The reputation developed by Jamaica Blue Mountain Coffee has made it one of the most desirable and expensive coffees in the world. Blue Mountain coffee from Jamaica is known to have a mild and balanced flavor and lack the bitterness often found in lesser coffees. J. Martinez & Company is one of few companies given the right to import Jamaica Blue Mountain coffee.
Blue Mountain Coffee is protected by a global certification mark, meaning that steps have been taken to ensure that only authentic Blue Mountain coffee, grown in a specific region of the Blue Mountains of ...
2012-03-15
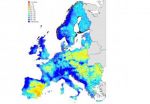
A new assessment of available water resources, published today by the Joint Research Centre (JRC), reveals that large areas in Spain and Eastern Europe have on average less than 200 mm freshwater available every year while the demand for water is three to ten times higher. The report 'Current Water Resources in Europe and Africa' shows variations in yearly freshwater generation from 10 mm to over 500 mm for Europe and from less than 0.1 mm to over 500 mm for Africa. The report outlines existing uncertainties and points to further research efforts needed for improved water ...
2012-03-15
CORAL GABLES, FL (March 14, 2012)--Convincing speeches are central to campaigning for elected office, but do our voices affect how we select our leaders? A newly-published paper in Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences shows that men and women vote for male and female candidates with lower-pitched voices. Men and women with lower voices were also found to be perceived as more competent, stronger, and more trustworthy. Each of these attributes is known to influence voters.
"Our study asks how voice pitch influences electability, and to my knowledge is ...
2012-03-15
NEW YORK (March 14, 2012) -- Nationwide ambulance use by patients suffering from a stroke has not changed since the mid-1990s, even though effective stroke treatments are now available. In a study published in this week's Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), researchers at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Weill Cornell Medical Center found that the number of stroke victims transported via ambulance has remained relatively static over the years, highlighting the need for more education about stroke symptoms and the importance of early intervention.
The study, ...
2012-03-15
WOODS HOLE, MA—The origin of the exquisitely complex vertebrate brain is somewhat mysterious. "In terms of evolution, it basically pops up out of nowhere. You don't see anything anatomically like it in other animals," says Ariel Pani, an investigator at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) in Woods Hole and a graduate student at the University of Chicago.
But this week in the journal Nature, Pani and colleagues report finding some of the genetic processes that regulate vertebrate brain development in (of all places) the acorn worm, a brainless, burrowing marine invertebrate ...
2012-03-15
MAYWOOD, Il. -- A Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine study has revealed details of the complex molecular process involving a protein that enables cancer cells to establish tumors in distant parts of the body.
The finding could lead the way to new drugs to prevent breast cancer and other cancers from spreading to new sites.
The study by Adriano Marchese, PhD and colleagues is published in the March 16 issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, and is now available online.
The study involves a molecule on the surface of cells called CXCR4. There is ...
2012-03-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers have designed a new version of a labor-tracking tool for pregnant women that they predict could reduce the use of hormonal intervention during labor and lower the number of cesarean sections performed on low-risk, first-time mothers.
The tool, called a partograph, takes into account the most recent research findings that suggest labor is not a linear process, but is instead slower during earlier labor and accelerates gradually as labor advances. A diagnosis of abnormally slow labor is the No. 1 reason that C-sections are performed in low-risk ...
2012-03-15
I&K International has announced a significant increase in sales of products from its men's range. The surge in sales is believed to have been a direct result of the addition of new men's products over the last few years, as well as a general increase in the amount of attention men are paying to grooming.
Indeed, the company has saw a 60% rise in the number of men buying these products when compared to the same time last year. These figures would seem to indicate that men are paying more attention to their physical appearance and grooming than ever before, and Kevin ...
2012-03-15
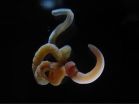
For 300 million years, Earth's oceans teemed with conodonts – early vertebrates that kept their skeleton in their mouth. The elements of this skeleton look uncannily like teeth (see image) and, like teeth, they were often worn and broken during life. This evidence strongly suggests that conodonts evolved the first vertebrate dentitions.
Scientists know that conodont elements worked differently from the teeth of other animals: they are microscopic – about 2 to 0.2 mm long – and must have had paltry muscles to move them, with no jaws to which they could attach. So how ...
2012-03-15
Irvine, Calif., March 14, 2012 — UC Irvine researchers have discovered how Salmonella, a bacterium found in contaminated raw foods that causes major gastrointestinal distress in humans, thrives in the digestive tract despite the immune system's best efforts to destroy it.
Their findings help explain why Salmonella is difficult to eradicate and point to new approaches for possible treatments. Most people infected with Salmonella suffer from diarrhea, fever and abdominal cramps for up to seven days before the infection resolves.
Lead researcher Manuela Raffatellu, a UCI ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Gold nanoantennas detect proteins
New method of monitoring protein molecules using gold nanoparticles