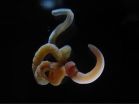
(Press-News.org) WOODS HOLE, MA—The origin of the exquisitely complex vertebrate brain is somewhat mysterious. "In terms of evolution, it basically pops up out of nowhere. You don't see anything anatomically like it in other animals," says Ariel Pani, an investigator at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) in Woods Hole and a graduate student at the University of Chicago.
But this week in the journal Nature, Pani and colleagues report finding some of the genetic processes that regulate vertebrate brain development in (of all places) the acorn worm, a brainless, burrowing marine invertebrate that they collected from Waquoit Bay in Falmouth, Mass.
The scientists were searching for ancestral evidence of three "signaling centers" in the vertebrate embryo that are major components of an "invisible scaffold that sets up the foundation of how the brain develops," Pani says. Diagnostic molecular features of these signaling centers are mostly missing in the sea squirts and the lancelets, the invertebrate chordates that are the closest evolutionary relatives of the vertebrates. This had suggested that these signaling centers are key innovations that arose de novo in the vertebrate lineage.
Yet, surprisingly, the scientists found highly similar signaling centers in the more distantly related acorn worm (Saccoglossus kowalevskii), a hemichordate. Acorn worm embryos lack nervous system structures comparable to vertebrate brains, and their lineages diverged from vertebrates more than 500 million years ago. Pani and colleagues found that, in the acorn worm, the signaling centers direct the formation of the embryonic body plan.
"What this means is the last (common) ancestor of the hemichordates and the vertebrates, even though it presumably did not have a vertebrate-like nervous system, had some very complex and vertebrate-like mechanisms for establishing its body plan," Pani says. "And one of the broad implications is that weird, squishy marine animals can be very informative in terms of understanding the evolution of vertebrate development and genetics in a way that you wouldn't expect."
But the sea squirt shouldn't worry: it has not been usurped by the acorn worm. "The lancelet and ascidians (sea squirts) will still be the first animals we will look at if we want to understand vertebrate evolution. But if we find differences, we now know it is important to look at anatomically divergent animals, where you wouldn't have previously expected to find compelling similarities," Pani says. "I think this principle applies broadly to understanding animal evolution."
The MBL, where more than 200 different types of marine animals are collected and maintained, has long been a center for comparative studies of evolution and development. "It is a valuable perspective that scientists can now implement in a pretty straightforward way," Pani says. "Because of the advances in gene sequencing and developmental techniques, a lot of researchers are now free to pick an animal in an interesting place (in the evolutionary tree) and pursue research on it at a speed that wasn't possible before. I think that is going to have a really big impact."
Christopher Lowe, Pani's Ph.D. advisor, has been working on hemichordates at MBL since 2002, in collaboration with the labs of John Gerhart, Marc Kirschner, Elena Casey, and Mark Terasaki. "The MBL has been a great place for us to work," Pani says. "There is a lot of expertise on the rearing and spawning of the animals, and we have had a ton of help from staff. Zeiss and Nikon have loaned us equipment at the MBL for years. It's just been a really unique and collaborative environment combining organismal knowledge with high-end technical facilities."
INFORMATION:
The MBL is a leading international, independent, nonprofit institution dedicated to discovery and to improving the human condition through creative research and education in the biological, biomedical and environmental sciences. Founded in 1888 as the Marine Biological Laboratory, the MBL is the oldest private marine laboratory in the Americas.
An evolutionary surprise
In a brainless marine worm, MBL researchers find the developmental 'scaffold' for the vertebrate brain
2012-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How cancer cells start new tumor sites
2012-03-15
MAYWOOD, Il. -- A Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine study has revealed details of the complex molecular process involving a protein that enables cancer cells to establish tumors in distant parts of the body.
The finding could lead the way to new drugs to prevent breast cancer and other cancers from spreading to new sites.
The study by Adriano Marchese, PhD and colleagues is published in the March 16 issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, and is now available online.
The study involves a molecule on the surface of cells called CXCR4. There is ...
New labor-tracking tool proposed to reduce C-sections in first-time moms
2012-03-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Researchers have designed a new version of a labor-tracking tool for pregnant women that they predict could reduce the use of hormonal intervention during labor and lower the number of cesarean sections performed on low-risk, first-time mothers.
The tool, called a partograph, takes into account the most recent research findings that suggest labor is not a linear process, but is instead slower during earlier labor and accelerates gradually as labor advances. A diagnosis of abnormally slow labor is the No. 1 reason that C-sections are performed in low-risk ...
I&K International Announces Rise in Sales of Male Grooming Products
2012-03-15
I&K International has announced a significant increase in sales of products from its men's range. The surge in sales is believed to have been a direct result of the addition of new men's products over the last few years, as well as a general increase in the amount of attention men are paying to grooming.
Indeed, the company has saw a 60% rise in the number of men buying these products when compared to the same time last year. These figures would seem to indicate that men are paying more attention to their physical appearance and grooming than ever before, and Kevin ...
Size isn't everything -- it's how sharp you are
2012-03-15
For 300 million years, Earth's oceans teemed with conodonts – early vertebrates that kept their skeleton in their mouth. The elements of this skeleton look uncannily like teeth (see image) and, like teeth, they were often worn and broken during life. This evidence strongly suggests that conodonts evolved the first vertebrate dentitions.
Scientists know that conodont elements worked differently from the teeth of other animals: they are microscopic – about 2 to 0.2 mm long – and must have had paltry muscles to move them, with no jaws to which they could attach. So how ...
UCI-led study uncovers how Salmonella avoids the body's immune response
2012-03-15
Irvine, Calif., March 14, 2012 — UC Irvine researchers have discovered how Salmonella, a bacterium found in contaminated raw foods that causes major gastrointestinal distress in humans, thrives in the digestive tract despite the immune system's best efforts to destroy it.
Their findings help explain why Salmonella is difficult to eradicate and point to new approaches for possible treatments. Most people infected with Salmonella suffer from diarrhea, fever and abdominal cramps for up to seven days before the infection resolves.
Lead researcher Manuela Raffatellu, a UCI ...
The Brazilian Navy faces its worst enemy in WWI: The Spanish flu
2012-03-15
Few people know about the participation of Brazil in Word War I. Although Brazil remained neutral during most of the conflict, it eventually sent a fleet to support the war effort against the central powers. It was the only Latin-American country to do so. But the Brazilian expedition encountered an unexpected and treacherous enemy in the African coast against which -like all other Armies- it was not prepared for: the Spanish flu.
The Spanish flu swept the globe in 1918-1919 and in a few months made more victims than the total number of battlefield deaths during the ...
Study suggests link between H. pylori bacteria and blood sugar control in adult Type 2 diabetes
2012-03-15
NEW YORK, March 14, 2012 – A new study by researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center reveals that the presence of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria is associated with elevated levels of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), an important biomarker for blood glucose levels and diabetes. The association was even stronger in obese individuals with a higher Body Mass Index (BMI). The results, which suggest the bacteria may play a role in the development of diabetes in adults, are available online in The Journal of Infectious Diseases.
There have been several studies evaluating ...
Getting a full picture of an elusive subject
2012-03-15
Two teams of astronomers have used data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and other telescopes to map the distribution of dark matter in a galaxy cluster known as Abell 383, which is located about 2.3 billion light years from Earth. Not only were the researchers able to find where the dark matter lies in the two dimensions across the sky, they were also able to determine how the dark matter is distributed along the line of sight.
Dark matter is invisible material that does not emit or absorb any type of light, but is detectable through its gravitational effects. ...
Epigenetic signatures direct the repair potential of reprogrammed cells
2012-03-15
BOSTON (March 14, 2012) — A research team has identified epigenetic signatures, markers on DNA that control transient changes in gene expression, within reprogrammed skin cells. These signatures can predict the expression of a wound-healing protein in reprogrammed skin cells or induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), cells that take on embryonic stem cell properties. Understanding how the expression of the protein is controlled brings us one step closer to developing personalized tissue regeneration strategies using stem cells from a patient, instead of using human embryonic ...
What does delaying childbearing cost?
2012-03-15
Freezing eggs or ovarian tissue for the sole purpose of delaying childbearing for social reasons may prove too costly for society, according to a recent analysis by a University of Illinois at Chicago researcher.
Fertility preservation -- freezing eggs or ovarian tissue -- was originally intended for women undergoing medical treatments that could affect their fertility.
But now, fertility centers around the country are offering these technologies to women who are not undergoing treatment, but who are "trying to create a backup plan for delaying pregnancy," says Dr. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain cells drive endurance gains after exercise
Same-day hospital discharge is safe in selected patients after TAVI
Why do people living at high altitudes have better glucose control? The answer was in plain sight
Red blood cells soak up sugar at high altitude, protecting against diabetes
A new electrolyte points to stronger, safer batteries
Environment: Atmospheric pollution directly linked to rocket re-entry
Targeted radiation therapy improves quality of life outcomes for patients with multiple brain metastases
Cardiovascular events in women with prior cervical high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
Transplantation and employment earnings in kidney transplant recipients
Brain organoids can be trained to solve a goal-directed task
Treatment can protect extremely premature babies from lung disease
Roberto Morandotti wins prestigious Max Born Award for pioneering research in quantum photonics
Scientists map brain's blood pressure control center
Acute coronary events registry provides insights into sex-specific differences
Bar-Ilan University and NVIDIA researchers improve AI’s ability to understand spatial instructions
New single-cell transcriptomic clock reveals intrinsic and systemic T cell aging in COVID-19 and HIV
Smaller fish and changing food webs – even where species numbers stay the same
Missed opportunity to protect pregnant women and newborns: Study shows low vaccination rates among expectant mothers in Norway against COVID-19 and influenza
Emotional memory region of aged brain is sensitive to processed foods
Neighborhood factors may lead to increased COPD-related emergency department visits, hospitalizations
Food insecurity impacts employees’ productivity
Prenatal infection increases risk of heavy drinking later in life
‘The munchies’ are real and could benefit those with no appetite
FAU researchers discover novel bacteria in Florida’s stranded pygmy sperm whales
DEGU debuts with better AI predictions and explanations
‘Giant superatoms’ unlock a new toolbox for quantum computers
Jeonbuk National University researchers explore metal oxide electrodes as a new frontier in electrochemical microplastic detection
Cannabis: What is the profile of adults at low risk of dependence?
Medical and materials innovations of two women engineers recognized by Sony and Nature
Blood test “clocks” predict when Alzheimer’s symptoms will start
[Press-News.org] An evolutionary surpriseIn a brainless marine worm, MBL researchers find the developmental 'scaffold' for the vertebrate brain