(Press-News.org) As any comic book lover knows, when superheroes band together the bad guys fall harder. The strength that comes in numbers is greater than the sum of its parts.
The same holds true, researchers have recently learned, when different species of crabs (genus Trapezia) and snapping shrimp (Alepheus lottini) in the central Pacific band together to defend their coral homes from hungry seastars. In these frequent conflicts "one-plus-one doesn't always equal two, sometime it is more," explains Seabird McKeon, a marine biologist at the National Museum of Natural History's Smithsonian Marine Station in Fort Pierce, Fla.
The crustaceans are much more effective when they fight together than when they fight alone, a process McKeon calls the Multiple Defender Effect.
"It is a clear example of synergy, and one that underscores the importance of biodiversity in the ocean."
Even in a comic book one would be hard pressed to find an enemy more bizarre than the "cushion" seastar (Culcita novaeguineae), an animal used by McKeon in recent laboratory experiments with living corals (genus Pocillopora) and their defenders. To consume a coral, the seastar pushes its stomach outside its body and lays it over the coral like a cushion. It then hugs the coral close and "eats," letting stomach acids and digestive juices do their work.
The stationary coral is defenseless, yet the tiny crustaceans that live among its branches come to its aid, snipping and prodding an intruding seastar with their claws.
"The coral itself is like a cauliflower head, a main central stem and lots of little branches," McKeon explains. "Crabs gain protection from fish by living inside the coral structure."
Once a mating pair of crabs takes up residence on a coral head they do not tolerate the presence of other crabs of their same species. Crabs of other species, however, are ignored, as are snapping shrimp. As a result, some coral heads may have as many as five different species of defensive crustaceans living on them, all pairs of different species.
In repeated experiments McKeon and colleagues measured the effectiveness of a single crab pair in preventing a seastar from eating their home coral. He found that one pair of crabs reduced the volume of coral eaten by about 19 percent, compared to a coral with no defenders. Two pairs of crustaceans working together, however, were able to reduce the volume of coral eaten by as much as 65 percent—the multiple defender effect.
The take-home lesson here, McKeon says, "is these crabs don't allow others of their same species on their coral, yet the synergy of different pairs fighting together is critical to the defense of the coral. The multiple defender effect is an important new angle on why we must conserve biodiversity in the ocean."
"Multiple defender effects: synergistic coral defense by mutualist crustaceans," by C. Seabird McKeon; Adrian C. Stier of the University of Florida; Shelby McIlroy of the University at Buffalo and Banjamin Bolker of McMaster University; appeared recently in the scientific journal Oecologia.
INFORMATION:
Preventing home invasions means fighting side-by-side for coral-dwelling crabs and shrimp
2012-04-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study supports using virtual environment to teach mind/body techniques
2012-04-02
A small study from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) researchers found that online virtual communities may be an effective way to train patients in meditation and other mind/body techniques. The ability to learn and practice approaches that elicit the relaxation response – a state of deep rest that has been shown to alleviate stress-related symptoms – in a virtual environment could help surmount several barriers that can restrict participation.
"Our finding that a medical intervention – in this case teaching a mind/body approach that includes the relaxation response ...
NASA sees Typhoon Pakhar headed for Vietnam landfall
2012-04-02
The first typhoon of the northern hemisphere 2012 typhoon season is headed for landfall in Vietnam. NASA's Aqua and TRMM satellites have been providing forecasters with valuable data on Typhoon Pakhar, that includes rainfall rates, cloud extent and temperature.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite flew almost directly over Pakhar when it was a newly formed tropical storm in the South China Sea on March 29, 2012 at 1122 UTC/4:22 p.m. Asia local time (or 7:22 a.m. EDT). The intensifying storm had wind speeds of about 45 knots (~52 mph/~83 kph) and was ...
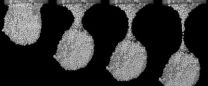
Images capture split personality of dense suspensions
2012-04-02
Stir lots of small particles into water, and the resulting thick mixture appears highly viscous. When this dense suspension slips through a nozzle and forms a droplet, however, its behavior momentarily reveals a decidedly non-viscous side. University of Chicago physicists recorded this surprising behavior in laboratory experiments using high-speed photography that can capture action taking place in one hundred-thousandths of a second or less.
UChicago graduate student Marc Miskin and Heinrich Jaeger, the William J. Friedman and Alicia Townsend Friedman Professor in Physics, ...
Tokai Pharmaceuticals' galeterone well-tolerated in patients with advanced prostate cancer
2012-04-02
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. and CHICAGO, Ill. -- Tokai Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a biopharmaceutical company focused on developing new treatments for prostate cancer, today announced that its lead candidate galeterone (TOK-001) was well-tolerated with minimal side effects and demonstrated efficacy in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) in a Phase 1 study. The data will be presented in an oral presentation titled, "ARMOR1: Safety of galeterone (TOK-001) in a Phase 1 clinical trial in chemotherapy naïve patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC)," abstract ...
Early clinical data show galeterone safe, effective against prostate cancer
2012-04-02
CHICAGO — Patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer had limited side effects and in many cases a drop in prostate-specific antigen expression with galeterone (TOK-001), a small-molecule oral drug, according to phase I data presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2012, held here March 31 - April 4.
Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) is an advanced form of prostate cancer that occurs when the disease progresses after treatment with androgen deprivation therapy. Galeterone works against CRPC by blocking the androgen receptor, reducing levels of the ligand ...
Metformin appeared to slow prostate cancer growth
2012-04-02
CHICAGO — The use of metformin in men with prostate cancer before prostatectomy helped to reduce certain metabolic parameters and slow the growth rate of the cancer, according to the results of a phase II study.
Anthony M. Joshua, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., staff medical oncologist at the Princess Margaret Hospital, University Health Network in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, presented the data at the AACR Annual Meeting 2012, held here March 31 - April 4.
Metformin is the most commonly prescribed medication for diabetes. Prior laboratory research has suggested that metformin may ...
Biomarker identified in relation to drug response in refractory urothelial cancer
2012-04-02
CHICAGO — The antiangiogenic drug pazopanib has demonstrated clinically meaningful activity in patients with refractory urothelial cancer, according to results presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2012, held here March 31 - April 4. The results also revealed that increases in interleukin-8 levels early after treatment with pazopanib may predict a lack of tumor response to the therapy.
"Historically, prognosis of patients with relapsed or refractory urothelial cancer is quite dismal," said Andrea Necchi, M.D., faculty member in the department of medicine at Fondazione ...
Towards TB elimination: ECDC and ERS introduce new guidelines on tuberculosis care in Europe
2012-04-02
Today, the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) publish their jointly developed European Union Standards for Tuberculosis Care (ESTC). The 21 patient-centred standards aim to guide clinicians and public health workers to ensure optimal diagnosis, treatment and prevention of tuberculosis (TB) in Europe – with nearly 74,000 reported TB cases in the EU/EEA in 2010 clearly showing that TB remains a public health challenge across the region.
The new EU-specific guidelines were developed by a panel of 30 experts ...
Oxygen in tumors predicts prostate cancer recurrence
2012-04-02
TORONTO -- Low oxygen levels in tumors can be used to predict cancer recurrence in men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer even before they receive radiation therapy.
The clinical research, led by radiation oncologists at the Princess Margaret Hospital (PMH) Cancer Program, University Health Network (UHN) is published online today in Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2711).
"We've not only shown that men do worse if they have low oxygen levels (hypoxia) in their prostate cancer, but ...
2 targeted therapies act against Ewing's sarcoma tumors
2012-04-02
CHICAGO - A pair of targeted therapies shrank tumors in some patients with treatment-resistant Ewing's sarcoma or desmoplastic small-round-cell tumors, according to research led by investigators from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center reported at the AACR Annual Meeting 2012.
Five of 17 Ewing's sarcoma patients responded to the combination, with two achieving complete responses, one for 27 weeks. The researchers noted that the ability to manage patients' treatment-related side effects is vital to maintaining the therapy and slowing disease progression. ...