Loyola study debunks common myth that urine is sterile
Research challenges misconception among doctors
2012-04-10
(Press-News.org) MAYWOOD, Ill. -- Researchers have determined that bacteria are present in the bladders of some healthy women, which discredits the common belief that normal urine is sterile. These findings were published in the April issue of the Journal of Clinical Microbiology by researchers at Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine (SSOM).
"Doctors have been trained to believe that urine is germ-free," said Linda Brubaker, MD, MS, dean, SSOM. "However, these findings challenge this notion, so this research may have positive implications for how we treat patients with urinary tract conditions in the future."
This study evaluated urine specimens of women who had symptoms consistent with a urinary tract infection (UTI), but were free of known UTIs. Urine samples were collected from standard urination, through a catheter, or from a thin needle inserted into the abdomen while the women were under anesthesia for gynecologic surgery. The urine was analyzed using advanced DNA-based detection methods. These tests determined that the adult female bladder can contain certain forms of bacteria that are not identified by urine culture techniques that are typically used to diagnose UTIs.
"While urine cultures have been the gold standard to identify UTIs in the past, they have limited utility," said Alan Wolfe, PhD, co-author and professor of Microbiology and Immunology, SSOM. "They are not as effective as the DNA-based detection measures used in this study."
This study also looked at collection methods to test urine for bacteria. The results revealed that the standard method to catch urine in a cup poses problems, because bacteria from the vagina often contaminate these specimens. In contrast, urine collection using a catheter or a needle was effective and comparable between tests.
Loyola researchers now plan to determine which bacteria in the bladder are helpful and which are harmful. They also will look at how these bacteria interact with each other and with their host, and how we can use this information to help patients. This research is in line with a larger international effort that is underway to identify the core bacterial composition of a healthy human body. Researchers strive to correlate changes in the composition of bacterial communities in and on the body with certain diseases.
"Further studies are needed to determine if the bacteria found in the bladders of women in this study are relevant to urinary tract conditions," Dr. Brubaker said. "If that is the case, these studies could make it possible to identify women who are at-risk for these conditions, which may change how we manage patients."
INFORMATION: END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-04-10
PINC Solutions, the leading provider of advanced yard management systems (YMS) today announced that the company has been included in the list of "Cool Vendors" in the Supply Chain Management report by Gartner, Inc.
According to the March 26, 2012 report, this year's "Cool Vendors" prove once again that, although aspects of the SCM technology market are mature, innovation continues as companies look for capabilities that make them more competitive or improve their operating metrics.
Traditionally, yard management has been looked at as a means to ...
2012-04-10
Money doesn't buy happiness. Neither does materialism: Research shows that people who place a high value on wealth, status, and stuff are more depressed and anxious and less sociable than those who do not. Now new research shows that materialism is not just a personal problem. It's also environmental. "We found that irrespective of personality, in situations that activate a consumer mindset, people show the same sorts of problematic patterns in wellbeing, including negative affect and social disengagement," says Northwestern University psychologist Galen V. Bodenhausen. ...
2012-04-10
A new analysis provides a closer look at how much cancer patients value hope — with important implications for how insurers value treatment, particularly in end-of-life care.
The analysis led by Darius Lakdawalla, director of research at the Schaeffer Center at USC and associate professor in the USC Price School of Public Policy, surveyed 150 cancer patients currently undergoing treatment, and is part of a special issue on cancer spending from the journal Health Affairs.
Lakdawalla and his co-authors found the overwhelming majority of cancer patients prefer riskier ...
2012-04-10
In the face of mass deforestation of the Amazon, recent findings indicate that we could learn from its earliest inhabitants who managed their farmland sustainably. An international team of archaeologists and paleoecologists, including Dr. Mitchell Power, curator of the Garrett Herbarium at the Natural History Museum of Utah and assistant professor in the Department of Geography at the University of Utah, report for the first time that indigenous people, living in the savannas around the Amazonian forest, farmed without using fire. These findings are published today, April ...
2012-04-10
BOSTON – Contrary to popular perception, a large proportion of obese Americans can and do lose weight, say researchers at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. What's more, they say, the old tried and true methods of eating less fat and exercising are some of the most effective paths to weight loss success.
The research results appear in the April 10 online issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
"This is great news because studies have shown that even a 5 percent reduction in weight can lead to improved health," says lead author Jacinda M. Nicklas, MD, ...
2012-04-10
San Diego, CA, April 10, 2012 – A third of Americans are now obese, and up to 70% of them are trying to lose weight. In a new study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, researchers from Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston have found in a nationally representative sample that obese dieters who said they ate less fat, exercised more, and used prescription weight loss medications were more likely to lose weight. Diet foods and products, nonprescription diet pills, and popular diets were less successful, according ...
2012-04-10
People who received frequent dental x-rays in the past have an increased risk of developing the most commonly diagnosed primary brain tumor in the United States. That is the finding of a study published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. Although dental x-rays are necessary in many cases, these findings suggest that moderate use of this form of imaging may be of benefit to some patients.
Ionizing radiation is the primary environmental risk factor for developing meningioma, which is the most frequently diagnosed primary brain ...
2012-04-10
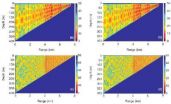
The coupled normal mode method is a powerful approach for solving range-dependent propagation problems in underwater acoustics. An important area of study is to improve stability and efficiency so as to be able to deal with complex scenarios in a realistic environment. Professor LUO Wenyu and his group from the State Key Laboratory of Acoustics, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, set out to tackle this problem. After several years of innovative research, they have developed an accurate, efficient, and numerically stable coupled normal mode method to solve ...
2012-04-10
The Pharmaceutical Education and Research Institute (PERI) and PeerParty are pleased to announce the inaugural CME National Championship for the healthcare community. The Championship introduces a new approach to continuing education for healthcare practitioners - a fun, collaborative approach that rewards participants for learning and building their professional networks. This innovative approach employs a number of new techniques to challenge and reward participants, with the goal of positively affecting knowledge-sharing, learning and most importantly, improving patient ...
2012-04-10
The bio-mechanisms of the woodpecker's resistance to head impact injury are an interesting scientific question. Professor FAN Yubo and his group from the Key Laboratory for Biomechanics and Mechanobiology of the Ministry of Education, School of Biological Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, and the School of Materials Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, set out to study this problem. After 3 years of innovative research, they are making progress in uncovering the explanation for the avoidance of head impact injury by woodpeckers. Their ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Loyola study debunks common myth that urine is sterile
Research challenges misconception among doctors