(Press-News.org) BOSTON – There is a long-held concern that youths who eat a lot of fast food are at risk for becoming overweight. New research to be presented Sunday, April 29, at the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) annual meeting in Boston shows that greater familiarity with fast-food restaurant advertising on television is associated with obesity in young people.
"We know that children and adolescents are highly exposed to fast-food restaurant advertising, particularly on television. This study links obesity in young people to familiarity with this advertising, suggesting that youth who are aware of and receptive to televised fast-food marketing may be at risk for health consequences," said lead author Auden C. McClure, MD, MPH, FAAP, assistant professor in the Department of Pediatrics at Children's Hospital at Dartmouth, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center.
Previous research has shown that watching TV is associated with obesity. Dr. McClure and her colleagues sought to determine whether recognition of fast-food ads on TV is associated with obesity in adolescents and young adults.
The researchers surveyed a national sample of 3,342 youths ages 15 to 23 years. Participants were asked about their height, weight, age, gender, race, socioeconomic status, exercise, consumption of soda or sweet drinks, frequency of eating at quick-service restaurants, how many hours they watched TV each day, and whether they snacked while watching TV.
They also were shown 20 still images selected from television ads for top quick-service restaurants that aired in the year before the survey. The images were digitally edited to remove the brands. Individuals were asked if they remembered seeing the ad, if they liked the ad and if they could name the restaurant brand. In addition, they were shown 20 ads for alcohol.
Results showed that about 18 percent of participants surveyed were overweight, and 15 percent were obese. The percentage of youths who were obese was significantly higher among those who recognized more ads than those who recognized few ads (17 percent vs. 8.3 percent). Even after controlling for the variables listed above, youths who recognized many ads were more than twice as likely to be obese compared with those who recognized few ads.
"A similar association with obesity was not found for familiarity with televised alcohol ads, suggesting that the relationship was specific to fast-food advertising content," Dr. McClure said. "After accounting for overall TV time, TV ad familiarity was still linked with obesity suggesting that this finding is not simply due to increased sedentary time or an effect of TV programming."
However, eating more frequently at fast-food restaurants depicted in the ads was not associated with obesity.
"The relation between fast-food marketing and obesity is not simply that it prompts more quick-serve restaurant visits," said study co-author James D. Sargent, MD, FAAP, professor in the Department of Pediatrics at Children's Hospital at Dartmouth. Instead, "individuals who are more familiar with these ads may have food consumption patterns that include many types of high-calorie food brands, or they may be especially sensitive to visual cues to eat while watching TV. More research is necessary to determine how fast-food ad familiarity is linked to obesity," he added.
"Given the broad exposure of youth to advertising, the more we know about how media and marketing affect young people, the better equipped we are as pediatricians and parents to guide them in making healthy diet choices," Dr. McClure concluded.
###
The Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) are four individual pediatric organizations that co-sponsor the PAS Annual Meeting – the American Pediatric Society, the Society for Pediatric Research, the Academic Pediatric Association, and the American Academy of Pediatrics. Members of these organizations are pediatricians and other health care providers who are practicing in the research, academic and clinical arenas. The four sponsoring organizations are leaders in the advancement of pediatric research and child advocacy within pediatrics, and all share a common mission of fostering the health and well-being of children worldwide. For more information, visit www.pas-meeting.org. Follow news of the PAS meeting on Twitter at http://twitter.com/PedAcadSoc.
END
BOSTON – Minors who were familiar with television alcohol advertisements were more likely to have tried alcoholic beverages and binge drink than those who could not recall seeing such ads, according to a study to be presented Sunday, April 29, at the Pediatric Academic Societies (PAS) annual meeting in Boston.
"Underage drinking remains an important health risk in the U.S.," said lead author Susanne E. Tanski, MD, MPH, FAAP, assistant professor in the Department of Pediatrics at Children's Hospital at Dartmouth, Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center. "In this study, we ...
Scientists have predicted that ocean temperatures will rise in the equatorial Pacific by the end of the century, wreaking havoc on coral reef ecosystems. But a new study shows that climate change could cause ocean currents to operate in a surprising way and mitigate the warming near a handful of islands right on the equator. As a result these Pacific islands may become isolated refuges for corals and fish.
Here's how it would happen, according to the study by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution scientists Kristopher Karnauskas and Anne Cohen, published April 29 in the ...
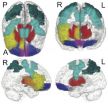
Why do some teenagers start smoking or experimenting with drugs—while others don't?
In the largest imaging study of the human brain ever conducted—involving 1,896 14-year-olds—scientists have discovered a number of previously unknown networks that go a long way toward an answer.
Robert Whelan and Hugh Garavan of the University of Vermont, along with a large group of international colleagues, report that differences in these networks provide strong evidence that some teenagers are at higher risk for drug and alcohol experimentation—simply because their brains work differently, ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Red, green, and blue lasers have become small and cheap enough to find their way into products ranging from BluRay DVD players to fancy pens, but each color is made with different semiconductor materials and by elaborate crystal growth processes. A new prototype technology demonstrates all three of those colors coming from one material. That could open the door to making products, such as high-performance digital displays, that employ a variety of laser colors all at once.
"Today in order to create a laser display with arbitrary colors, ...
A combination of two diabetes drugs, metformin and rosiglitazone, was more effective in treating youth with recent-onset type 2 diabetes than metformin alone, a study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has found. Adding an intensive lifestyle intervention to metformin provided no more benefit than metformin therapy alone.
The study also found that metformin therapy alone was not an effective treatment for many of these youth. In fact, metformin had a much higher failure rate in study participants than has been reported in studies of adults treated with ...
It is important to be able to monitor genetically modified (GM) crops, not only in the field but also during the food processing chain. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Biotechnology shows that products from genetically modified crops can be identified at low concentration, using bioluminescent real time reporter (BART) technology and loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). The combination of these techniques was able to recognise 0.1% GM contamination of maize, far below the current EU limit of 0.9%.
In agriculture GM crops have ...
Alu elements infiltrated the ancestral primate genome about 65 million years ago. Once gained an Alu element is rarely lost so comparison of Alu between species can be used to map primate evolution and diversity. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal Mobile DNA has found a single Alu, which appears to be an ancestral great ape Alu, that has uniquely multiplied within the orangutan genome.
Analysis of DNA sequences has found over a million Alu elements within each primate genome, many of which are species specific: 5,000 are unique to humans, ...
Early colonization of the gut by microbes in infants is critical for development of their intestinal tract and in immune development. A new study, published in BioMed Central's open access journal Genome Biology, shows that differences in bacterial colonization of formula-fed and breast-fed babies leads to changes in the infant's expression of genes involved in the immune system, and in defense against pathogens.
The health of individuals can be influenced by the diversity of microbes colonizing the gut, and microbial colonization can be especially important in regulating ...
SALT LAKE CITY, April 30, 2012 – Cochlear implants have restored basic hearing to some 220,000 deaf people, yet a microphone and related electronics must be worn outside the head, raising reliability issues, preventing patients from swimming and creating social stigma.
Now, a University of Utah engineer and colleagues in Ohio have developed a tiny prototype microphone that can be implanted in the middle ear to avoid such problems.
The proof-of-concept device has been successfully tested in the ear canals of four cadavers, the researchers report in a study just published ...
PULLMAN, Wash.— The Yellowstone "super-volcano" is a little less super—but more active—than previously thought.
Researchers at Washington State University and the Scottish Universities Environmental Research Centre say the biggest Yellowstone eruption, which created the 2 million year old Huckleberry Ridge deposit, was actually two different eruptions at least 6,000 years apart.
Their results paint a new picture of a more active volcano than previously thought and can help recalibrate the likelihood of another big eruption in the future. Before the researchers split ...