(Press-News.org) Scientists with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley have directed the first self-assembly of nanoparticles into device-ready materials. Through a relatively easy and inexpensive technique based on blending nanoparticles with block co-polymer supramolecules, the researchers produced multiple-layers of thin films from highly ordered one-, two- and three-dimensional arrays of gold nanoparticles. Thin films such as these have potential applications for a wide range of fields, including computer memory storage, energy harvesting, energy storage, remote-sensing, catalysis, light management and the emerging new field of plasmonics.
"We've demonstrated a simple yet versatile supramolecular approach to control the 3-D spatial organization of nanoparticles with single particle precision over macroscopic distances in thin films," says polymer scientist Ting Xu, who led this research. "While the thin gold films we made were wafer-sized, the technique can easily produce much larger films, and it can be used on nanoparticles of many other materials besides gold."
Xu holds joint appointments with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division and UC Berkeley's Departments of Materials Sciences and Engineering, and Chemistry. She is the corresponding author of a paper describing this research in the journal Nano Letters titled "Nanoparticle Assemblies in Thin Films of Supramolecular Nanocomposites." Co-authoring the paper were Joseph Kao, Peter Bai, Vivian Chuang, Zhang Jiang and Peter Ercius.
Nanoparticles can be thought of as artificial atoms with unique optical, electrical and mechanical properties. If nanoparticles can be coaxed into routinely assembling themselves into complex structures and hierarchical patterns, similar to what nature does with proteins, devices a thousand times smaller than those of today's microtechnologies could be mass-produced.
Xu and her research group have been advancing towards this goal for the past decade. In a study earlier this year, they were able to induce rod-shaped semiconductor nanocrystals to self-assemble into one-, two- and even three-dimensional macroscopic structures. With this latest application of their methods to thin films, they have moved into the realm of material forms that are required for device fabrication and are well-suited for scalable nanomanufacturing.
"This is the first time that 2-D nanoparticle assembly, similar to those obtained using DNA linkers and controlled solvent evaporation, can be clearly achieved in multi-layers in supramolecule-based nanocomposite thin films," Xu says. "Our supramolecular approach does not require chemical modification to any of the components in the composite system and, in addition to providing a means of building nanoparticle-based devices, should also provide a powerful platform for studying nanoparticle structure-property correlations."
The technique developed by Xu and her colleagues uses solutions of block co-polymer supramolecules to direct the self-assembly of nanoparticles. A supramolecule is a group of molecules that act as a single molecule able to perform a specific set of functions. Block copolymers are long sequences or "blocks" of one type of monomer bound to blocks of another type of monomer that have an innate ability to self-assemble into well-defined arrays of nano-sized structures over macroscopic distances.
"Block copolymer supramolecules self-assemble and form a wide range of morphologies that feature microdomains typically a few to tens of nanometers in size," Xu says. "As their size is comparable to that of nanoparticles, the microdomains of block copolymer supramolecules provide an ideal structural framework for the co-self-assembly of nanoparticles."
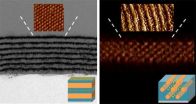
In this latest study, Xu and her colleagues incorporated gold nanoparticles into solutions of block co-polymer supramolecules to form films that ranged in thickness between 100 to 200 nanometers. The nanocomposite films featured microdomains in one of two common morphologies - lamellar or cylindrical. For the lamellar microdomains, the nanoparticles formed hexagonally-packed 2-D sheets that were stacked into multiple layers parallel to the surface. For the cylindrical microdomains, the nanoparticles formed 1-D chains (single particle width) that were packed into distorted hexagonal lattices in parallel orientation with the surface.
"Upon incorporation of nanoparticles, the block co-polymer supramolecules experience conformational changes, resulting in entropy that determines the placement and distribution of the nanoparticles, as well as the overall morphology of the nanocomposite thin films," Xu says. "Our results indicate that it should be possible to generate highly-ordered lattices of nanoparticles within block co-polymer microdomains and obtain 3-D hierarchical assemblies of nanoparticles with precise structural control."
The inter-particle distance between gold nanoparticles in the 1-D chains and the 2-D sheets was 8 to 10 nanometers, which raises intriguing possibilities with regards to plasmonics, the phenomenon by which a beam of light is confined in ultra-cramped spaces. Plasmonic technology holds great promise for superfast computers and optical microscopy, among other applications. However, a major challenge for developing plasmonics has been the difficulty of fabricating metamaterials with noble metal nanoparticles such as gold.
"Our gold thin films display strong plasmonic coupling along the inter-particle spacing in the 1-D chains and 2-D sheets respectively," Xu says. "We should therefore be able to use these films to investigate unique plasmonic properties for next-generation electronic and photonic devices. Our supramolecular technique might also be used to fabricate plasmonic metamaterials."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
Golden potential for gold thin films
Berkeley Lab researchers direct the self-assembly of gold nanoparticles into device-ready thin films
2012-04-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New graphene-based material could revolutionize electronics industry
2012-04-30
The most transparent, lightweight and flexible material ever for conducting electricity has been invented by a team from the University of Exeter. Called GraphExeter, the material could revolutionise the creation of wearable electronic devices, such as clothing containing computers, phones and MP3 players.
GraphExeter could also be used for the creation of 'smart' mirrors or windows, with computerised interactive features. Since this material is also transparent over a wide light spectrum, it could enhance by more than 30% the efficiency of solar panels.
Adapted from ...
lobSTR algorithm rolls DNA fingerprinting into 21st century
2012-04-30
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (April 27, 2012) – As any crime show buff can tell you, DNA evidence identifies a victim's remains, fingers the guilty, and sets the innocent free. But in reality, the processing of forensic DNA evidence takes much longer than a 60-minute primetime slot.
To create a victim or perpetrator's DNA profile, the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) scans a DNA sample for at least 13 short tandem repeats (STRs). STRs are collections of repeated two to six nucleotide-long sequences, such as CTGCTGCTG, which are scattered around the genome. Because the ...
New avocado rootstocks are high-performing and disease-tolerant
2012-04-30
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Avocado, a significant fruit crop grown in many tropical and subtropical parts of the world, is threatened by Phytophthora root rot (PRR), a disease that has already eliminated commercial avocado production in many areas in Latin America and crippled production in Australia and South Africa. Just in California the disease is estimated to cost avocado growers approximately $30-40 million a year in production losses.
Research on developing PRR-tolerant rootstocks to manage the disease has been a major focus of avocado research at the University of California, ...
Big girls don't cry
2012-04-30
A study to be published in the June 2012 issue of Journal of Adolescent Health looking at the relationships between body satisfaction and healthy psychological functioning in overweight adolescents has found that young women who are happy with the size and shape of their bodies report higher levels of self-esteem. They may also be protected against the negative behavioral and psychological factors sometimes associated with being overweight.
A group of 103 overweight adolescents were surveyed between 2004 and 2006, assessing body satisfaction, weight-control behavior, ...
Notre Dame paper examines nanotechnology-related safety and ethics problem
2012-04-30
A recent paper by Kathleen Eggleson, a research scientist in the Center for Nano Science and Technology (NDnano) at the University of Notre Dame, provides an example of a nanotechnology-related safety and ethics problem that is unfolding right now.
The world of nanotechnology, which involves science and engineering down at billionths-of-a-meter scales, might seem remote.
But like most new advances, the application of that technology to everyday experience has implications that can affect people in real ways.
If not anticipated, discussed or planned for, some of those ...
NASA's Landsat satellites see Texas crop circles
2012-04-30
VIDEO:
In this time series animation, vegetation appears red and the bare soil of fallow fields or sparsely vegetated grasslands appear white to green. The blue-gray X near the center of...
Click here for more information.
A water-rich polka dot pattern takes over the traditional rectangular patchwork of fields in this time series animation of 40 years of Landsat images. In the dry Texas panhandle near the town of Dalhart, this transformation is due to center-pivot irrigation, ...
Moffitt researchers find adolescents with cancer concerned about their future reproductive health
2012-04-30
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center and colleagues have found that adolescents newly diagnosed with cancer have strong concerns about their ability to have children as cancer survivors. They also found that standard health-related quality-of-life survey tools used to elicit answers from teens with cancer did not accurately reflect these concerns. Parents, who often answer survey questions as proxies, often inaccurately relayed their child's reproductive concerns.
The study, carried out by Moffitt researchers and colleagues from the University of South Florida, the University ...
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers working at frontiers of melanoma research
2012-04-30
At Moffitt Cancer Center, patients with stage III and IV unresectable melanoma are now routinely genetically profiled for several gene mutations, including the BRAF gene, a known driver oncogene for melanoma. Research has shown that mutations in the BRAF gene determine sensitivity or resistance to a class of drugs that are BRAF inhibitors.
"We have found that a large number of patients with melanoma who have the BRAF gene mutation quickly develop resistance to drugs that are BRAF inhibitors," said Jeffrey S. Weber, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Donald A. Adam Comprehensive ...
Moffitt Cancer Center researchers: Quality of life as important as quantity of life
2012-04-30
Researchers at Moffitt Cancer Center have placed new emphasis on gathering data on cancer patient quality of life during both treatment and survivorship. Their focus is on gathering and using that data to develop interventions to improve the quality of life for patients in treatment and for cancer survivors.
Much of the quality of life and survivorship research is carried out by researchers in Moffitt's Department of Health Outcomes & Behavior.
"Among the several research goals of the Department of Health Outcomes & Behaviors is the evaluation and improvement of quality ...
Automated breast volume sonography improves screening and diagnosis of breast cancer for Asian women
2012-04-30
A new study from researchers at the Bangkok Breast Center shows significant improvement in the detection of breast cancer in Asian women using automated breast volume sonography (ABVS) as compared to hand-held ultrasound (HHUS).
In their study on 504 findings in 212 patients at the Bangkok Breast Center, researchers found that ABVS agreed with HHUS in detecting 15 suspicious lesions, uncovered 12 additional suspicious lesions, and excluded 3 suspicious lesions in these cases. A coordinating five-year retrospective study on 26,741 mammograms with ultrasound also revealed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
How studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
Chemists thought phosphorus had shown all its cards. It surprised them with a new move
A feedback loop of rising submissions and overburdened peer reviewers threatens the peer review system of the scientific literature
Rediscovered music may never sound the same twice, according to new Surrey study
Ochsner Baton Rouge expands specialty physicians and providers at area clinics and O’Neal hospital
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
Ambitious climate policy ensures reduction of CO2 emissions
Frontiers in Science Deep Dive webinar series: How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
UMaine researcher develops model to protect freshwater fish worldwide from extinction
Illinois and UChicago physicists develop a new method to measure the expansion rate of the universe
Pathway to residency program helps kids and the pediatrician shortage
How the color of a theater affects sound perception
Ensuring smartphones have not been tampered with
Overdiagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer
Association of dual eligibility and medicare type with quality of postacute care after stroke
Shine a light, build a crystal
AI-powered platform accelerates discovery of new mRNA delivery materials
Quantum effect could power the next generation of battery-free devices
[Press-News.org] Golden potential for gold thin filmsBerkeley Lab researchers direct the self-assembly of gold nanoparticles into device-ready thin films