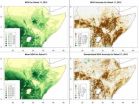
(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– What might happen if droughts were predicted months ahead of time? Food aid and other humanitarian efforts could be put together sooner and executed better, say UC Santa Barbara geographers Chris Funk, Greg Husak, and Joel Michaelsen. After over a decade of gathering and analyzing climate and vegetation data from East Africa, the researchers, who are part of the U.S. Agency for International Development's Famine Early Warning System Network (FEWS NET), say there is enough evidence to associate climate conditions in the region with projected rainfall deficits that could lead to food shortages.
"We've been looking at climate in East Africa and trying to relate that back to patterns in sea surface temperatures, rainfall, and winds over the Indian and Pacific oceans," said Funk, who analyzes and predicts large-scale climate anomalies in Africa. Results show that over the last 14 years, the number of droughts has doubled in East Africa. Roughly half of the last 14 years have been drought years.
"We've been worried about these trends for a long time," said Michaelsen, who studies the patterns of vegetation greening and browning in the area. "This year marks a bit of a watershed because we're starting to understand more the specific structure of these droughts, which is what underlay our early warning projections this year."
Through the climate data, coupled with satellite data that has recorded the patterns of vegetation greening and browning over the last decade, the researchers have detected a pattern that points to the likelihood of water shortages months ahead of time –– a pattern the U.S. government is taking seriously. A recent alert from the government-run USAID agency has taken into account FEWS NET's projection of the likelihood of low rainfall this March-May rainy season in East Africa, as USAID prepares its outreach efforts.
"It's already a billion-dollar problem that they're thinking needs $50 million more; they're already anticipating a 5 percent increase in the need for aid," said Husak, who specializes in analyzing remote sensing data and rainfall. The area, which includes chronically food-insecure countries like Ethiopia and Somalia, is still recovering from last year's famine.
The U.S. government spends more than a billion dollars in food aid every year. FEWS NET was created after the 1984-1985 Ethiopian famine, an event that killed over a million people before sufficient food aid could be airlifted into the country. FEWS NET has since become a leader in integrating monitoring, forecasting, and climate trends analysis.
Famine, say the researchers, is the result of more than severe climate: Conflict, political unrest, corruption, and other human factors are also major contributors to the crisis. Additionally, relief is not just a matter of putting food on a boat and distributing it among the locals. If food aid is sent to a place that doesn't need it, the surplus could distort the local market by devaluing the prices of local products. Conversely, not providing food aid quickly enough distorts the market in the other direction, limiting access to available resources.
"Prices of food have gone up," said Michaelsen. "It's not the brownness (of the vegetation) that causes food insecurity; it's the price of food." The challenge, say the geographers, will be for aid agencies to determine where their finite resources will go.
In the long term, and with more information, Michaelsen, Husak, and Funk, along with the extensive network of colleagues in FEWS NET, hope to gain a better understanding of the effects the changing climate will have on the abilities of a region –– and the agencies that support it –– to prevent future crises.
"There are going to be a lot of surprises, and how agile we are at responding to those surprises is going to make a big difference," said Michaelsen.
INFORMATION:
With climate and vegetation data, UCSB geographers closer to predicting droughts in Africa
2012-05-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Thwarting the cleverest attackers
2012-05-02
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. — In the last 10 years, cryptography researchers have demonstrated that even the most secure-seeming computer is shockingly vulnerable to attack. The time it takes a computer to store data in memory, fluctuations in its power consumption and even the noises it emits can betray information to a savvy assailant.
Attacks that use such indirect sources of information are called side-channel attacks, and the increasing popularity of cloud computing makes them an even greater threat. An attacker would have to be pretty motivated to install a device in your ...
Interpreting the Avastin-Lucentis study for persons with macular degeneration
2012-05-02
Clarksburg, MD—This week, the second-year results of an important clinical trial on age-related macular degeneration (AMD), known as the Comparison of AMD Treatments Trials (or CATT), were published in the journal Ophthalmology. Researchers found that two drugs known as Avastin (bevacizumab) and Lucentis (ranibizumab), commonly used to treat the wet form of AMD, were similarly effective in maintaining vision.
In this clinical trial funded by the National Eye Institute (NEI) of the National Institutes of Health, CATT researchers found that two years into the study, ...
Researchers find potential 'dark side' to diets high in beta-carotene
2012-05-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio - New research suggests that there could be health hazards associated with consuming excessive amounts of beta-carotene.
This antioxidant is a naturally occurring pigment that gives color to foods such as carrots, sweet potatoes and certain greens. It also converts to vitamin A, and foods and supplements are the only sources for this essential nutrient.
But scientists at Ohio State University have found that certain molecules that derive from beta-carotene have an opposite effect in the body: They actually block some actions of vitamin A, which is critical ...
Atlanta Family Dentist Makes Access to Practice Information Easier for Smartphone Users
2012-05-02
To further increase patients' awareness of dental health care and his practice, Dr. Donald Rozema, Atlanta family dentist, is happy to announce the launch of a mobile website for his practice. The new mobile website was created to offer smartphone and tablet users a quick, and easy way to access important information about Dr. Rozema, his practice and dental health care information.
"More and more people are using smartphones and tablet devices to look up information they need. From restaurants to daily news articles, we are always on the go," said Dr. Donald ...
Woodbridge Best Pediatrician Offers Free Prenatal Consultations for Expectant Mothers
2012-05-02
Expecting parents are encouraged to visit Dr. Nimisha Shukla, Woodbridge best pediatrician, for a free prenatal consultation. With free prenatal consultations, Dr. Shukla gives expecting parents the opportunity to meet with the doctor who will be caring for their child over the next 20 years in order to establish a child's medical home.
Dr. Shukla, best pediatrician in Edison, offers in-office and telephonic prenatal consultations. At the prenatal visit a mother's obstetric history, prenatal history, and ultrasound results are discussed, in addition to identifying high-risk ...
Gastroenterologist in Philadelphia Releases Mobile Website for Faster Loading Times
2012-05-02
Board certified gastroenterologists in Philadelphia, Bala Cynwyd and Langhorne, PA, G.I. Specialists, invite patients that are constantly on-the-go to visit their technologically advanced mobile website. With the recent launch of their mobile website, patients can now gain easy access to G.I. Specialists, gastroenterologists in Langhorne, without the complications of slow loading, difficult to navigate webpages.
"Today, a host of people are accessing the Internet from their smartphones and tablet devices, but many websites are still stuck in the age of computer-only ...
Montreal Dentist Receives Fellowship From the Academy of General Dentistry
2012-05-02
By maintaining the highest level of continuing education standards, Dr. John Petruccelli, Montreal dentist, has received a Fellowship from the Academy of General Dentistry. With less than 2% of dentists in Canada holding this Fellowship status, Dr. Petruccelli is honored to receive this.
"It is a great honor to receive a Fellowship from the Academy of General Dentistry. I look forward to continuing to maintain the highest level of continuing education, while providing my patients with quality dental care they deserve and trust," said Dr. John Petruccelli, ...
Greater numbers of highly educated women are having children, bucking recent history
2012-05-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio - A national study suggests that a significantly greater number of highly educated women in their late 30s and 40s are deciding to have children - a dramatic turnaround from recent history.
Among college-educated women, childlessness peaked in the late 1990s, when about 30 percent had no children, according to the new analysis of U.S. data. But childlessness declined about 5 percentage points between 1998 and 2008.
"We may be seeing the beginning of a new trend," said Bruce Weinberg, co-author of the study and professor of economics at Ohio State University.
"One ...
Ajax Dentist Creates Social Network for Increased Interaction
2012-05-02
Dr. Zina Shoaib, an experienced Ajax dentist, has recently announced the launch of her practice's Facebook, Twitter, and blog. The practice's new presence on these leading social media platforms has enabled the practice to communicate with existing and prospective patients more effectively and efficiently.
Patients can now read Dr. Shoaib's blog for informal dental information or become a "fan" or "friend" of the practice's Facebook, and Twitter pages for updates on office happenings. To access and join Dr. Shoaib's social network, patients can visit ...
Bigger gorillas better at attracting mates and raising young
2012-05-02
Conservationists with the Wildlife Conservation Society and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology have found that larger male gorillas living in the rainforests of Congo seem to be more successful than smaller ones at attracting mates and even raising young.
The study—conducted over a 12-year period in Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park in the Republic of Congo—helps to illuminate the selective pressures that influence the evolution of great apes.
The study appears in a recent edition of Journal of Human Evolution. The authors of the study include: Thomas ...