(Press-News.org) OAKLAND, Calif., May 25, 2012 – Among women with gestational diabetes mellitus, referral to a telephone-based nurse management program was associated with lower risk of high baby birth weight and increased postpartum glucose testing, according to Kaiser Permanente researchers.
Investigators for the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research examined the associations between referral to telephone-based nurse consultation and outcomes in 12 Kaiser Permanente medical centers with variation in the percent of patients referred to telephonic nurse management.
"Compared with women from Kaiser Permanente medical centers where the annual proportions of referral to nurse management at the Kaiser Permanente Regional Perinatal Service Center was less than 30 percent, women who delivered in medical centers with an annual referral proportion of greater than 70 percent were less likely to have a high birth weight infant without increasing the risk or having a low birth weight infant," said Assiamira Ferrara, MD, PhD, a research scientist with the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research and the lead author of the study. "In addition, they were more likely to have postpartum glucose testing, which leads to earlier identification and management of postpartum glucose intolerance or diabetes."
The study appears online in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Investigators used data from the Kaiser Permanente Northern California GDM registry to identify women who had pregnancy complicated by GDM from 1997 through 2006. They restricted their cohort to women with GDM according to the National Diabetes Data Group criteria. During the study period, 96 percent of all pregnant women without preexisting diabetes who delivered an infant were screened for GDM. Researchers excluded women who delivered multiple births due to their increased risk of perinatal complications. Overall, researchers identified 11,435 women with GDM at the 12 medical centers, of whom 44.5 percent were referred to the perinatal service center.
"The Kaiser Permanente Regional Perinatal Service Center is a nurse-based management program for women with GDM that offers supplemental care via telephone counseling to women with high-risk pregnancies, including those complicated by GDM," explained co-author Monique Hedderson, PhD, a research scientist with the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Division of Research.
The program includes a call center with 32 registered nurses and two registered dieticians who offer phone counseling seven days a week and address glucose monitoring and control, diet and physical activity. Nurses are available 24 hours a day, seven days a week, while dieticians are available to patients during the week from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. In addition to care provided by obstetricians, women referred to the center receive one to two counseling calls per week to help them manage their blood glucose levels during pregnancy. The center also sends a laboratory slip for postpartum glucose testing and a reminder telephone call if the screening test was not performed.
The Kaiser Permanente Regional Perinatal Service Center GDM program was first implemented in 1997 in two medical centers and gradually disseminated to 12 more centers. By 2006, the program was implemented in all Kaiser Permanente medical centers.
"Due to the timeline for program implementation, there was some medical-center level variation in the percent of patients referred to the program," said Dr. Ferrara. "This allowed us to develop a quasi-experimental design to examine the association between referral to the program and infant adverse outcomes (infant high and low birth weight) and to measure processes such as patient postpartum glucose testing."
###Additional authors on the study included Jenny Ching, RN, and Yvonne M. Crites, MD, both with the Kaiser Permanente Regional Perinatal Service Center based in Santa Clara, Calif.; Tiffany Peng, MA, with the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research; and Catherine Kim, MD, MPH, with the departments of medicine and obstetrics gynecology at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
The study was supported by funds from the Translating Research into Action for Diabetes study, which was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
About the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research (http://www.dor.kaiser.org/)
The Kaiser Permanente Division of Research conducts, publishes and disseminates epidemiologic and health services research to improve the health and medical care of Kaiser Permanente members and the society at large. It seeks to understand the determinants of illness and well-being and to improve the quality and cost-effectiveness of health care. Currently, DOR's 500-plus staff is working on more than 250 epidemiological and health services research projects.
About Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente is committed to helping shape the future of health care. We are recognized as one of America's leading health care providers and not-for-profit health plans. Founded in 1945, our mission is to provide high-quality, affordable health care services to improve the health of our members and the communities we serve. We currently serve more than 9 million members in nine states and the District of Columbia. Care for members and patients is focused on their total health and guided by their personal physicians, specialists and team of caregivers. Our expert and caring medical teams are empowered and supported by industry-leading technology advances and tools for health promotion, disease prevention, state-of-the art care delivery and world-class chronic disease management. Kaiser Permanente is dedicated to care innovations, clinical research, health education and the support of community health. For more information, go to: http://www.kp.org/newscenter.
http://www.kaiserpermanente.org
Phone contact with nurses linked with better outcomes for women with gestational diabetes
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new invading sea crab reaches the Ebro Delta
2012-05-28
Originally endemic to the Atlantic Coast of North America, over the past 30 years Dyspanopeus sayi has been involuntarily introduced in the UK, France, the Netherlands, the Black Sea and the Adriatic Sea. A study shows that in recent years the sea crab has established itself along the Western Mediterranean Coast.
A team of Spanish and German researchers have recorded the first American Dyspanopeus sayi sea crab in the bay of Els Alfacs in the Ebro Delta (Spain). Both sexes were captured along with many ovigerous females (carrying eggs) in different areas and different ...
First study to suggest that the immune system may protect against Alzheimer's changes in humans
2012-05-28
Recent work in mice suggested that the immune system is involved in removing beta-amyloid, the main Alzheimer's-causing substance in the brain. Researchers have now shown for the first time that this may apply in humans.
Researchers at the Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Exeter with colleagues in the National Institute on Aging in the USA and in Italy screened the expression levels of thousands of genes in blood samples from nearly 700 people. The telltale marker of immune system activity against beta-amyloid, a gene called CCR2, emerged as ...
Autopsy of an eruption: Linking crystal growth to volcano seismicity
2012-05-28
How processes below a volcano are linked to seismic signals at the surface is described by scientists from the petrology group of the Ruhr-Universität Bochum and their colleagues from Bristol in a paper published today in Science. They analyzed the growth of crystals in the magma chamber and used results obtained from the monitoring of seismic signals. The research could ultimately help to predict future volcanic eruptions with greater accuracy.
Like tree rings: Crystals in a magma chamber
A few kilometers below the volcano a liquid reservoir exists, the magma chamber, ...
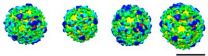
Picture release: More than meets the eye
2012-05-28
VIDEO:
Depicting each copy of COPI as a triangle, the different arrangements of these building blocks become easier to spot.
Click here for more information.
These spheres may look almost identical, but subtle differences between them revealed a molecular version of the robots from Transformers. Each sphere is a vesicle, a pod that cells use to transport materials between different compartments. The images, produced by Marco Faini from John Briggs' lab at the European Molecular ...
Oldest Jewish archaeological evidence on the Iberian Peninsula
2012-05-28
On a marble plate, measuring 40 by 60 centimetres, the name "Yehiel" can be read, followed by further letters which have not yet been deciphered. The Jena Archaeologists believe that the new discovery might be a tomb slab. Antlers, which were found very close to the tomb slab in the rubble gave a clue to the age determination. "The organic material of the antlers could be dated by radiocarbon analysis with certainty to about 390 AD," excavation leader Dr. Dennis Graen of the Jena University explains. "Therefore we have a so-called 'terminus ante quem' for the inscription, ...
70 percent of women use contraceptives during their first sexual encounter
2012-05-28
VIDEO:
Contraceptive use in Spain during the first sexual encounter is similar to other European countries. However, there are some geographical differences between Spanish regions: women in Murcia use contraceptives less...
Click here for more information.
Contraceptive use in Spain during the first sexual encounter is similar to other European countries. However, there are some geographical differences between Spanish regions: women in Murcia use contraceptives less (55.8%) ...
Copy of the genetic makeup travels in a protein suitcase
2012-05-28
The blueprint of all living beings is stored in their genetic material. In higher organisms this is stored in the well-protected cell nucleus. "Here a kind of copier works around the clock to make copies of the information needed at the time," says first author Jan Peter Siebrasse from the Institute for Physical and Theoretical Chemistry at the University of Bonn. The copies contain the information which the cells need to produce vital enzymes or other cell building materials. These copies consist of messenger RNA which travels on random paths to the membrane of the cell ...
Inherited DNA change explains overactive leukemia gene
2012-05-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A small inherited change in DNA is largely responsible for overactivating a gene linked to poor treatment response in people with acute leukemia.
The study by researchers at the Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James) focused on a gene called BAALC. This gene is often overactive, or overexpressed, in people with acute myeloid or acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and it indicates that the disease is likely to respond poorly to standard therapy.
This study ...
World Health Assembly endorses new plan to increase global access to vaccines
2012-05-28
Geneva, Switzerland – May 25, 2012 – Ministers of Health from 194 countries at the Sixty-fifth World Health Assembly today endorsed a landmark Global Vaccine Action Plan (GVAP), a roadmap to prevent millions of deaths by 2020 through more equitable access to existing vaccines for people in all communities.
The GVAP was coordinated by the Decade of Vaccines Collaboration, a group of leading international vaccine experts, and represents the collective vision of hundreds of global health stakeholders to extend the full benefits of immunization to all people, regardless of ...
Cancer may require simpler genetic mutations than previously thought
2012-05-28
Chromosomal deletions in DNA often involve just one of two gene copies inherited from either parent. But scientists haven't known how a deletion in one gene from one parent, called a "hemizygous" deletion, can contribute to cancer.
A research team led by Stephen Elledge, a professor in the Department of Genetics at Harvard Medical School, and his post-doctoral fellow Nicole Solimini, has now provided an answer. The most common hemizygous deletions in cancer, their research shows, involve a variety of tumor suppressing genes called STOP genes (suppressors of tumorigenesis ...