(Press-News.org) MIT researchers have engineered a device that delivers a tiny, high-pressure jet of medicine through the skin without the use of a hypodermic needle. The device can be programmed to deliver a range of doses to various depths — an improvement over similar jet-injection systems that are now commercially available.
The researchers say that among other benefits, the technology may help reduce the potential for needle-stick injuries; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that hospital-based health care workers accidentally prick themselves with needles 385,000 times each year. A needleless device may also help improve compliance among patients who might otherwise avoid the discomfort of regularly injecting themselves with drugs such as insulin.
"If you are afraid of needles and have to frequently self-inject, compliance can be an issue," says Catherine Hogan, a research scientist in MIT's Department of Mechanical Engineering and a member of the research team. "We think this kind of technology … gets around some of the phobias that people may have about needles."
The team reports on the development of this technology in the journal Medical Engineering & Physics.
Pushing past the needle
In the past few decades, scientists have developed various alternatives to hypodermic needles. For example, nicotine patches slowly release drugs through the skin. But these patches can only release drug molecules small enough to pass through the skin's pores, limiting the type of medicine that can be delivered.
With the delivery of larger protein-based drugs on the rise, researchers have been developing new technologies capable of delivering them — including jet injectors, which produce a high-velocity jet of drugs that penetrate the skin. While there are several jet-based devices on the market today, Hogan notes that there are drawbacks to these commercially available devices. The mechanisms they use, particularly in spring-loaded designs, are essentially "bang or nothing," releasing a coil that ejects the same amount of drug to the same depth every time.
Breaching the skin
Now the MIT team, led by Ian Hunter, the George N. Hatsopoulos Professor of Mechanical Engineering, has engineered a jet-injection system that delivers a range of doses to variable depths in a highly controlled manner. The design is built around a mechanism called a Lorentz-force actuator — a small, powerful magnet surrounded by a coil of wire that's attached to a piston inside a drug ampoule. When current is applied, it interacts with the magnetic field to produce a force that pushes the piston forward, ejecting the drug at very high pressure and velocity (almost the speed of sound in air) out through the ampoule's nozzle — an opening as wide as a mosquito's proboscis.
The speed of the coil and the velocity imparted to the drug can be controlled by the amount of current applied; the MIT team generated pressure profiles that modulate the current. The resulting waveforms generally consist of two distinct phases: an initial high-pressure phase in which the device ejects drug at a high-enough velocity to "breach" the skin and reach the desired depth, then a lower-pressure phase where drug is delivered in a slower stream that can easily be absorbed by the surrounding tissue.
Through testing, the group found that various skin types may require different waveforms to deliver adequate volumes of drugs to the desired depth.
"If I'm breaching a baby's skin to deliver vaccine, I won't need as much pressure as I would need to breach my skin," Hogan says. "We can tailor the pressure profile to be able to do that, and that's the beauty of this device."
The team is also developing a version of the device for transdermal delivery of drugs ordinarily found in powdered form by programming the device to vibrate, turning powder into a "fluidized" form that can be delivered through the skin much like a liquid. Hunter says that such a powder-delivery vehicle may help solve what's known as the "cold-chain" problem: Vaccines delivered to developing countries need to be refrigerated if they are in liquid form. Often, coolers break down, spoiling whole batches of vaccines. Instead, Hunter says a vaccine that can be administered in powder form requires no cooling, avoiding the cold-chain problem.
###Written by Jennifer Chu, MIT News Office
Device may inject a variety of drugs without using needles
Jet-injected drugs could improve patient compliance, reduce accidental needle sticks
2012-05-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Positive words: The glue to social interaction
2012-05-28
Scientists at ETH Zurich have studied the use of language, finding that words with a positive emotional content are more frequently used in written communication. This result supports the theory that social relations are enhanced by a positive bias in human communication. The study by David Garcia and his colleagues from the Chair of Systems Design is published in the first issue of the new SpringerOpen journal EPJ Data Science, and is freely available to the general public as an Open Access article.
Previous studies focused on word lengths and frequency. They demonstrated ...
University of Florida physicists set new record for graphene solar cell efficiency
2012-05-28
GAINESVILLE, Fla. — Doping may be a no-no for athletes, but researchers in the University of Florida's physics department say it was key in getting unprecedented power conversion efficiency from a new graphene solar cell created in their lab.
Graphene solar cells are one of industry's great hopes for cheaper, durable solar power cells in the future. But previous attempts to use graphene, a single-atom-thick honeycomb lattice of carbon atoms, in solar cells have only managed power conversion efficiencies ranging up to 2.9 percent. The UF team was able to achieve a record ...
Childhood cancer scars survivors later in life
2012-05-28
CHICAGO--- Scars left behind by childhood cancer treatments are more than skin-deep. The increased risk of disfigurement and persistent hair loss caused by childhood cancer and treatment are associated with emotional distress and reduced quality of life in adulthood, according to a new study led by a Northwestern Medicine advanced practice nurse, Karen Kinahan, and based on data from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS).
The largest study of its kind, published May 21 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, compared scarring, disfigurement and persistent hair loss ...
'Metamaterials,' quantum dots show promise for new technologies
2012-05-28
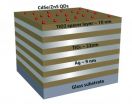
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers are edging toward the creation of new optical technologies using "nanostructured metamaterials" capable of ultra-efficient transmission of light, with potential applications including advanced solar cells and quantum computing.
The metamaterial - layers of silver and titanium oxide and tiny components called quantum dots - dramatically changes the properties of light. The light becomes "hyperbolic," which increases the output of light from the quantum dots.
Such materials could find applications in solar cells, light emitting diodes ...
NASA's TRMM satellite sees some heavy rainfall in Typhoon Sanvu
2012-05-28
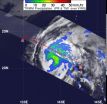
Tropical Storm Sanvu strengthened overnight as forecast and is now a Typhoon in the western North Pacific Ocean. NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite observed that most of the rainfall is falling in the eastern half of the storm.
The TRMM satellite measured the rainfall from Typhoon Sanvu on May 24, 2012.TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data shows that Sanvu's heaviest rainfall was occurring in its northeastern quadrant where some intense storms were dropping rainfall at a rate greater than 50mm/hr (~2 inches/hr). TRMM ...
NASA satellites feed forecasters information as Bud becomes a hurricane
2012-05-28
Bud has now become the first hurricane of the eastern Pacific Hurricane Season, as NASA visible and infrared satellite imagery revealed an organized structure of spiraling thunderstorms around the eye. Watches and warnings are already in effect for southwestern Mexico as Bud nears.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument onboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Hurricane Bud off the southwestern coast of Mexico on May 23 at 2035 UTC (1:35 PDT) before it reached hurricane status. The image showed the outer fringes of Bud's ...
Cyber exercise partners help you go the distance
2012-05-28
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A new study testing the benefits of a virtual exercise partner shows the presence of a moderately more capable cycling partner can significantly boost the motivation – by as much as 100 percent – to stick to an exercise program.
The research out of Michigan State University's Department of Kinesiology shows women taking part in cycling exercises exercised twice as long when working with a virtual partner, results the authors said can be used to help people meet physical activity recommendations.
The work by Brandon Irwin and colleagues is published ...
Stanford psychologists examine how race affects juvenile sentencing
2012-05-28
When it comes to holding children accountable for crimes they commit, race matters.
According to a new study by Stanford psychologists, if people imagine a juvenile offender to be black, they are more willing to hand down harsher sentences to all juveniles.
"These results highlight the fragility of protections for juveniles when race is in play," said Aneeta Rattan, lead author of the study, which appears this week in the journal PLoS ONE.
Historically, the courts have protected juveniles from the most severe sentences. It has been recognized that children are different ...
A nanoclutch for nanobots
2012-05-28
Chinese researchers have designed and tested simulations of a "nanoclutch," a speed regulation tool for nanomotors. The nanoclutch consists of two carbon nanotubes (CNTs), one inside the other, separated by a film of water. Electrowetting forces control the friction between the water and the inner and outer walls of the CNTs. When the two tubes are electrically charged, the water confined between them can transmit the torque from the inner tube to the outer tube, and the device is said to be in the engaged state. When the CNTs are uncharged, the device is in the disengaged ...
Sound increases the efficiency of boiling
2012-05-28
Scientists at the Georgia Institute of Technology achieved a 17-percent increase in boiling efficiency by using an acoustic field to enhance heat transfer. The acoustic field does this by efficiently removing vapor bubbles from the heated surface and suppressing the formation of an insulating vapor film. As reported in the American Institute of Physics' (AIP) journal the Physics of Fluids, bubble removal was enhanced because the acoustic field induces capillary waves on the bubble, causing its contact line to contract and detach the bubble from the surface. The mechanisms ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Device may inject a variety of drugs without using needlesJet-injected drugs could improve patient compliance, reduce accidental needle sticks