(Press-News.org) CHICAGO--- Scars left behind by childhood cancer treatments are more than skin-deep. The increased risk of disfigurement and persistent hair loss caused by childhood cancer and treatment are associated with emotional distress and reduced quality of life in adulthood, according to a new study led by a Northwestern Medicine advanced practice nurse, Karen Kinahan, and based on data from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS).
The largest study of its kind, published May 21 in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, compared scarring, disfigurement and persistent hair loss reported by adult survivors of childhood cancer to their siblings, who were not childhood cancer survivors.
Here are some of the study's findings, controlling for cranial radiation, which has been linked to psychosocial distress in the past:
Survivors with persistent hair loss were found to have increased risk of anxiety
Female survivors with persistent hair loss had increased risk of depressive symptoms
Survivors with a head or neck, arm or leg disfigurement had increased risk of depression
"The results show that cancer treatments can affect childhood cancer survivors' physical appearances and their quality of life long after they turn 18," said Kinahan, RN, APN,P-CNS and first author of the study. "I have patients who are asymmetrical because of radiation treatments, others with scars on their faces and necks from biopsies and surgeries and some who've had the amputation of a limb."
As a clinical nurse specialist specializing in pediatric oncology at the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University, Kinahan helped start the STAR Program (Survivors Taking Action & Responsibility) at the Lurie Cancer Center in 2001. It is a comprehensive long-term follow-up program for adult survivors of pediatric cancer that follows these patients for their chronic medical and psychological conditions into adulthood.
For this study, more than 14,000 childhood cancer survivors, all participants in the national CCSS, were surveyed with two questionnaires. The baseline was administered in 1992 and another in 2003. Information related to cancer treatment was abstracted from the survivors' medical records. Half of the survivors were asked to nominate their nearest age sibling for the comparison group. More than 4,000 siblings participated in the study.
The survivors, all of whom were treated between 1970 and 1986, filled out self-reported questionnaires about head/neck, arm/leg and chest/abdomen scarring, disfigurement and persistent hair loss they have suffered.
Psychological distress and quality of life data were taken from the 2003 survey. Distress was evaluated using an 18 item self-report measure of symptoms over the prior seven days. Quality of life data was evaluated using a 36-item self-reported measure of general health over the prior four weeks.
Surrogates completed the baseline questionnaire for survivor participants who had either cognitive limitation, were deceased or were younger than 18 years of age.
"The results of this study help illustrate the complex chain of events childhood cancer can have on quality of life as an adult," said senior author Kevin Krull, Ph.D., an associate member in the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital departments of epidemiology and cancer control and psychology "We have long been aware that radiation therapy is associated with increased risk for emotional distress and social problems, though we did not fully understand the process this involves. The current study begins to map this process."
Future studies are needed to more clearly understand the impact of scarring, disfigurement, and persistent hair loss upon body image, emotional health, and the quality of life of childhood cancer survivors, Kinahan said. However, the results of this first-of-a-kind study are important for practitioners in the field of pediatric cancer care, she said.
"We need to be more aware, so that interventions facilitating coping skills, emotional adjustment and management strategies can be implemented for patients at highest risk," Kinahan said. "A natural next step would be to make efforts to minimize alterations to the physical appearance of pediatric cancer patients during diagnosis and treatment."
INFORMATION: END
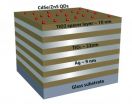
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers are edging toward the creation of new optical technologies using "nanostructured metamaterials" capable of ultra-efficient transmission of light, with potential applications including advanced solar cells and quantum computing.
The metamaterial - layers of silver and titanium oxide and tiny components called quantum dots - dramatically changes the properties of light. The light becomes "hyperbolic," which increases the output of light from the quantum dots.
Such materials could find applications in solar cells, light emitting diodes ...
Tropical Storm Sanvu strengthened overnight as forecast and is now a Typhoon in the western North Pacific Ocean. NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite observed that most of the rainfall is falling in the eastern half of the storm.
The TRMM satellite measured the rainfall from Typhoon Sanvu on May 24, 2012.TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data shows that Sanvu's heaviest rainfall was occurring in its northeastern quadrant where some intense storms were dropping rainfall at a rate greater than 50mm/hr (~2 inches/hr). TRMM ...
Bud has now become the first hurricane of the eastern Pacific Hurricane Season, as NASA visible and infrared satellite imagery revealed an organized structure of spiraling thunderstorms around the eye. Watches and warnings are already in effect for southwestern Mexico as Bud nears.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument onboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Hurricane Bud off the southwestern coast of Mexico on May 23 at 2035 UTC (1:35 PDT) before it reached hurricane status. The image showed the outer fringes of Bud's ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. — A new study testing the benefits of a virtual exercise partner shows the presence of a moderately more capable cycling partner can significantly boost the motivation – by as much as 100 percent – to stick to an exercise program.
The research out of Michigan State University's Department of Kinesiology shows women taking part in cycling exercises exercised twice as long when working with a virtual partner, results the authors said can be used to help people meet physical activity recommendations.
The work by Brandon Irwin and colleagues is published ...
When it comes to holding children accountable for crimes they commit, race matters.
According to a new study by Stanford psychologists, if people imagine a juvenile offender to be black, they are more willing to hand down harsher sentences to all juveniles.
"These results highlight the fragility of protections for juveniles when race is in play," said Aneeta Rattan, lead author of the study, which appears this week in the journal PLoS ONE.
Historically, the courts have protected juveniles from the most severe sentences. It has been recognized that children are different ...
Chinese researchers have designed and tested simulations of a "nanoclutch," a speed regulation tool for nanomotors. The nanoclutch consists of two carbon nanotubes (CNTs), one inside the other, separated by a film of water. Electrowetting forces control the friction between the water and the inner and outer walls of the CNTs. When the two tubes are electrically charged, the water confined between them can transmit the torque from the inner tube to the outer tube, and the device is said to be in the engaged state. When the CNTs are uncharged, the device is in the disengaged ...
Scientists at the Georgia Institute of Technology achieved a 17-percent increase in boiling efficiency by using an acoustic field to enhance heat transfer. The acoustic field does this by efficiently removing vapor bubbles from the heated surface and suppressing the formation of an insulating vapor film. As reported in the American Institute of Physics' (AIP) journal the Physics of Fluids, bubble removal was enhanced because the acoustic field induces capillary waves on the bubble, causing its contact line to contract and detach the bubble from the surface. The mechanisms ...
Researchers from Vestfold University College in Norway have created a simple, efficient energy harvesting device that uses the motion of a single droplet to generate electrical power. The new technology could be used as a power source for low-power portable devices, and would be especially suitable for harvesting energy from low frequency sources such as human body motion, write the authors in a paper accepted to the American Institute of Physics' (AIP) journal Applied Physics Letters. The harvester produces power when an electrically conductive droplet (mercury or an ionic ...
NASA's next flagship mission — the James Webb Space Telescope — will carry the largest primary mirror ever deployed. This segmented behemoth will unfold to 21.3 feet in diameter once the observatory reaches its orbit in 2018.
A team of scientists at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., now is developing an instrument that would image and characterize planets beyond the solar system possibly from a high-altitude balloon has borrowed a page from the Webb telescope's playbook. It has created an infinitely smaller segmented mirror that currently measures ...
Porous ceramic water filters are often coated with colloidal silver, which prevents the growth of microbes trapped in the micro- and nano-scale pores of the filter. Other metals such as copper and zinc have also been shown to exhibit anti-microbial activity. Researchers from Princeton University in New Jersey used atomic force microscopy (AFM) measurements to study the adhesion interaction between Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacteria and colloidal silver, silver nanoparticles, and copper nanoparticles, as well as the interactions of the bacteria and the three different types ...