(Press-News.org) A bioinspired robot has provided the first experimental evidence that live zebrafish can be influenced by engineered robots.
Results published today, 8 June, in IOP Publishing's journal Bioinspiration and Biomimetics, provide a stepping stone on the path to using autonomous robots in an open environment to monitor and control fish behaviour.
In the future, water-based robots could potentially contribute to the protection of endangered animals and the control of pest species.
The robot, created by researchers from Polytechnic Institute of New York University and Instituto Superiore di Sanitá, Italy, was 15 centimetres long and spray-painted with the characteristic blue stripes of the zebrafish. The tail of the robot was mechanically controlled by the researchers to mimic the action of the zebrafish itself.
When placed in a 65 litre fish tank, the movements of the robot's tail attracted both individual and shoals of zebrafish; the researchers believe that such capability was influenced by its bioinspired features which were optimised to increase attraction.
For example, the robot was given a rounder shape to mimic a fertile female, which is preferred by both male and female zebrafish, and its colour pattern – a magnified stripe width and saturated yellow pigment – emphasized distinctive biologically relevant features.
The robot was in a fixed position in the tank so that the tail movements could be controlled, recorded and, most importantly, associated with the behaviour of the zebrafish.
The fish tank where the experiments took place was divided into one large middle section and two smaller sections at either end, separated by transparent Plexiglas. A total of 16 experiments were performed in which individual, and then shoals of, zebrafish were placed in the middle compartment of the tank and two stimuli were placed at either end behind the Plexiglass.
The combinations of stimuli were: one fish versus an empty space; ten fish versus an empty space; ten fish versus one fish; the robot versus an empty space, and the robot versus one fish.
A camera was placed above the tank to monitor the movements of the zebrafish, and statistical tests were performed to calculate whether the robot acted as an attractive, neutral or aversive stimulus and whether this relationship depends on the fish being isolated or in a shoal.
Although the live zebrafish tended to prefer each other to the robot, when given the choice to spend time next to the robotic fish or an empty space, both the individual fish and shoal of fish preferred the robot. While the noise of the robot's motor was shown to decrease its attraction, the actual beating of the tail emphasized its attractiveness.
The corresponding author, Dr Maurizio Porfiri, said: "These findings provide practical evidence that a species' preference for conspecifics may be used to inspire the design of robots which can actively engage their source of inspiration.
"New studies are currently underway in our lab investigating the interactions between fish and robotic fish when they are free to swim together under controlled and ecologically complex conditions."
###
Notes to Editors
Contact
1. For further information, a full draft of the journal paper or contact with one of the researchers, contact IOP Publishing Press Assistant, Michael Bishop:
Tel: 0117 930 1032
E-mail: Michael.Bishop@iop.org
Zebrafish response to robotic fish: preference experiments on isolated individuals and small shoals
2. The published version of the paper "Zebrafish response to robotic fish: preference experiments on isolated individuals and small shoals" (Bioinspir. Biomim. 7 036019) will be freely available online from 8 June.
Bioinspiration & Biomimetics
3. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics publishes research which applies principles abstracted from natural systems to engineering and technological design and applications.
IOP Publishing
4. IOP Publishing provides publications through which leading-edge scientific research is distributed worldwide.
IOP Publishing is part of the Institute of Physics, a leading scientific society promoting physics and bringing physicists together for the benefit of all. Any financial surplus earned by IOP Publishing goes to support science through the activities of the Institute.
Beyond the company's core journals programme, high-value scientific information is made easily accessible through an ever-evolving portfolio of community websites, magazines, conference proceedings and a multitude of electronic services. IOP is focused on making the most of new technologies and continually improving electronic interfaces to make it easier for researchers to find exactly what they need, when they need it, in the format that suits them best. Go to http://publishing.iop.org/.
The Institute of Physics
5. The Institute of Physics is a leading scientific society promoting physics and bringing physicists together for the benefit of all.
It has a worldwide membership of around 40 000 comprising physicists from all sectors, as well as those with an interest in physics. It works to advance physics research, application and education; and engages with policy makers and the public to develop awareness and understanding of physics. Its publishing company, IOP Publishing, is a world leader in professional scientific communications. Go to www.iop.org
Engineered robot interacts with live fish
2012-06-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Manipulating chromatin loops to regulate genes may offer future treatments for blood diseases
2012-06-08
In exploring how proteins interact with crucial DNA sequences to regulate gene activity, researchers have shed light on key biological events that may eventually be manipulated to provide new disease treatments.
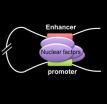
Within a cell's nucleus, regulatory elements in DNA called promoters and enhancers communicate with each other in carrying out gene activity, often over large genomic distances, hundreds of thousands of chemical bases apart from each other in chromosomes. As these elements physically contact each other, the intervening DNA sequences bend into loops made of chromatin ...
Immune system 'circuitry' that kills malaria in mosquitoes identified
2012-06-08
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute have, for the first time, determined the function of a series proteins within the mosquito that transduce a signal that enables the mosquito to fight off infection from the parasite that causes malaria in humans. Together, these proteins are known as immune deficiency (Imd) pathway signal transducing factors, are analogous to an electrical circuit. As each factor is switched on or off it triggers or inhibits the next, finally leading to the launch of an immune response against the malaria parasite. The study was ...
Pre-existing problems
2012-06-08
In a critical step that may lead to more effective HIV treatments, Harvard scientists have found that, in a small number of HIV patients, pre-existing mutations in the virus can cause it to develop resistance to the drugs used to slow the progression of the disease.
The finding is particularly important because, while researchers have long known HIV can develop resistance to some drugs, it wasn't understood whether the virus relied on pre-existing mutations to develop the resistance, or if it has to wait for those mutations to occur. By shedding new light on how resistance ...
Should spinal manipulation for neck pain be abandoned?
2012-06-08
The effectiveness of spinal manipulation divides medical opinion. On bmj.com today, experts debate whether spinal manipulation for neck pain should be abandoned.
Spinal manipulation is a technique that involves the application of various types of thrusts to the lumbar spine (lower back) or cervical spine (neck) to reduce back pain, neck pain and other musculoskeletal conditions.
Neil O'Connell and colleagues argue that cervical spine manipulation "may carry the potential for serious neurovascular complications" and that the technique is "unnecessary and inadvisable." ...
Patients suffering from pre-diabetes at potential future risk of stroke
2012-06-08
Millions of people suffering from pre-diabetes may be at a higher risk of stroke, a study published on bmj.com today suggests.
Pre-diabetes is characterised by higher than normal blood glucose levels that, if left untreated, develops into type 2 diabetes. The scale of the problem is enormous and growing, with an estimated 79 million people in the US and 7 million people in the UK affected.
People with pre-diabetes also harbour the same vascular risk factors as people with type 2 diabetes, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol and obesity, but its effect on ...
By adding VSL#3 probiotic to traditional therapies UC patients can improve remission rates
2012-06-08
GAITHERSBURG, MD, June 7 – As one of the few probiotics with medical food designation for specific illnesses, VSL#3® has been the subject of a collection of more than 80 studies that have demonstrated its use in the dietary management of IBS, ulcerative colitis, and an ileal pouch. Ulcerative colitis patients, in particular, have been shown to benefit from adding VSL#3 medical food to their prescription drug regimen. One particular study shows that the combination of VSL#3 and traditional drug therapy can improve remission rates over drug therapy alone by 10 to 17 percent, ...
Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation increases survival in systemic sclerosis patients
2012-06-08
Berlin, Germany, June 7 2012: Initial results from an international, investigator-initiated, open label phase III trial were presented at EULAR 2012, the Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism. Data indicate that haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) results in better long term survival than conventional treatment for patients with poor prognosis early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis.
The ASTIS (Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation International Scleroderma) trial enrolled more than 150 patients between 2001 and 2009, and randomised ...
Mapping genes: Mayo Clinic finds new risk factors for neurodegenerative diseases
2012-06-08
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — Using a new and powerful approach to understand the origins of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, researchers at Mayo Clinic in Florida are building the case that these diseases are primarily caused by genes that are too active or not active enough, rather than by harmful gene mutations.
In the June 7 online issue of PLoS Genetics, they report that several hundred genes within almost 800 brain samples of patients with Alzheimer's disease or other disorders had altered expression levels that did not result from neurodegeneration. ...
Surgeon experience affects complication rate of spinal stenosis surgery
2012-06-08
Philadelphia, Pa. (June 7, 2012) - For patients undergoing surgery for spinal stenosis, the risk of complications is higher when the surgeon performs very few such procedures—less than four per year, suggests a study in the June issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
In contrast, the complication rate is not significantly affected by the volume of spinal stenosis surgeries performed at the hospital, according to the new research. The senior ...
Meditation practice may decrease risk for cardiovascular disease in teens
2012-06-08
AUGUSTA, Ga. – Regular meditation could decrease the risk of developing cardiovascular disease in teens who are most at risk, according to Georgia Health Sciences University researchers.
In a study of 62 black teens with high blood pressure, those who meditated twice a day for 15 minutes had lower left ventricular mass, an indicator of future cardiovascular disease, than a control group, said Dr. Vernon Barnes, a physiologist in the Medical College of Georgia and the Georgia Health Sciences University Institute of Public and Preventive Health.
Barnes, Dr. Gaston Kapuku, ...