(Press-News.org) Berlin, Germany, June 7 2012: Patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRD) treated with anti-tumour necrosis factor medications (anti-TNFs) have a 75% greater risk of developing herpes zoster, or shingles, than patients treated with traditional disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), according to a meta-analysis presented today at EULAR 2012, the Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism.
"Anti-TNFs, such as infliximab, adalimumab and etanercept have become the treatment of choice for patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases who are uncontrolled on traditional DMARDs, but it is known that a side effect of these drugs is an increased risk of bacterial infections," said Ms. Helene Che, from Lapeyronie Hospital, France and lead author of the study. "This systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrates that careful monitoring of patients treated with anti-TNFs is required for early signs and symptoms of herpes zoster and raises the issue as to when vaccination against the virus should occur."
The study authors conducted a literature search in Medline, Embase, the Cochrane library and abstracts from ACR and EULAR congresses from 2006 to 2010. From the 657 articles, 134 congress abstracts, and 11 national registries included in the literature search, 22 articles and 28 abstracts met eligibility criteria and were included in the study. The meta-analysis included a total follow up of 124,966 patient years (PY) (74,198 PY in the biologics group and 50,768 PY in the DMARD group) across five registries.
Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they reported the respective incidences of herpes infection in anti-TNF and conventional DMARD treated patients. Incidence of severe herpetic infections (multidermatomal lesions, requiring hospitalisation or intravenous treatment) were excluded and reported when available.
Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, is a painful, blistering skin rash due to the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox . People are more likely to develop it if they are older than 60, had chickenpox before the age of one and have a compromised immune system due to medications or diseasei. Symptoms include one-sided pain, tingling or burning followed by a rash of small blisters, which eventually break, ulcer and dry upi. Other symptoms may include fever, chills, abdominal pain, swollen glands, difficulty moving muscles in the face, and drooping eyelidsi. Shingles is usually treated with antiviral medications to reduce pain and complications and corticosteroids to reduce swellingi. Pain from shingles can last for months or years, even though the infection normally lasts only two to three weeks. The virus can also cause temporary or permanent paralysis.*
Abstract Number: THU0368
###
*Netdoctor - Shingles (Herpes zoster). http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/diseases/facts/herpeszoster.htm 2011. Accessed 4 May 2012
NOTES TO EDITORS:
For further information on this study, or to request an interview with the study lead, please do not hesitate to contact the EULAR congress Press Office in Hall 6 on the 3rd floor of the Congress Centre during EULAR 2012 or on:
Email: eularpressoffice@cohnwolfe.com
Candice Debleu:
Onsite tel: +44 7894 386 425
About EULAR
The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) is the organisation which represents the patient, health professional and scientific societies of rheumatology of all the European nations
In line with The European Union of Medical Specialists (UEMS), EULAR defines rheumatology as including rheumatic diseases of the connective tissue, locomotor and musculoskeletal systems
EULAR aims to promote, stimulate and support the research, prevention, treatment and rehabilitation of rheumatic diseases. With 45 scientific member societies, 36 PARE organisations and 10 health professionals associations, EULAR underscores the importance of combating rheumatic diseases not only by medical means, but also through a wider context of care for rheumatic patients and a thorough understanding of their social and other needs
Diseases of the bone and joints such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis cause disability in 4-5% of the adult population and are predicted to rise as people live longer
EULAR 2012 is set to be the biggest rheumatology event in Europe with over 15,000 scientists, physicians, allied health professionals, and related audiences in attendance from over 115 countries. Over the course of the congress, more than 275 oral and 1400 poster abstract presentations will be featured, with 1,010 invited speaker lectures taking place in 190 sessions
To find out more about the activities of EULAR, visit: www.eular.org
END
Berlin, Germany, June 7 2012: Data from one of the few head-to-head trials in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) presented today at EULAR 2012, the Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism, demonstrates that at one year, 64.8% of patients receiving abatacept (Orencia) and 63.4% of patients receiving adalimumab (Humira) achieved ACR20*.
The Phase IIIb AMPLE study (Abatacept Versus Adalimumab Comparison in Biologic-Naive RA Subjects with Background Methotrexate) was carried out in 646 biologic-naïve patients with active RA and inadequate response to methotrexate. ...
All nuclear energy and weapons programs should be independently regulated and subject to rigorous peer review, according to three experts on nuclear policy. Their comments and recommendations are published in an article entitled, "A Safer Nuclear Enterprise," in the June 8 issue of the journal Science.
The authors noted that, despite international diplomatic efforts to prevent the proliferation of nuclear weapons and ensure that nuclear material is protected against theft, there is growing apprehension about terrorists acquiring weapons or nuclear material.
"There is ...
When you are planning a vacation or a trip and you need to rent a car, one of the most important things that you should consider is whether or not you need to buy rental car insurance. When you search for a car rental company online or in person, most salespeople will tell you that you need insurance, while most web pages will tell you that you do not need it. This couldn't be further from the truth. In reality, purchasing rental car insurance for a few extra dollars per day may be one of the most intelligent things that a person can do for themselves.
CheapCarInsurance.net ...
An international research team led by the University of Colorado Boulder has generated the first laser-like beams of X-rays from a tabletop device, paving the way for major advances in many fields including medicine, biology and nanotechnology development.
For half a century, scientists have been trying to figure out how to build a cost-effective and reasonably sized X-ray laser that could, among other things, provide super-high-resolution imaging, according to Henry Kapteyn, a CU-Boulder physics professor and fellow at JILA, a joint institute of CU-Boulder and the National ...
New York, NY (June 7, 2012) — Researchers at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) have identified a brain receptor that appears to play a central role in regulating appetite. The findings, published today in the online edition of Cell, could lead to new drugs for preventing or treating obesity.
"We've identified a receptor that is intimately involved in regulating food intake," said study leader Domenico Accili, MD, professor of Medicine at CUMC. "What is especially encouraging is that this receptor is belongs to a class of receptors that turn out to be good targets ...
Chemical reactions on the surface of metal oxides, such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, are important for applications such as solar cells that convert the sun's energy to electricity. Now University of Washington scientists have found that a previously unappreciated aspect of those reactions could be key in developing more efficient energy systems.
Such systems could include, for example, solar cells that would produce more electricity from the sun's rays, or hydrogen fuel cells efficient enough for use in automobiles, said James Mayer, a UW chemistry professor.
"As ...
New research published today in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Genomics reveals that the Malaysian parasitic plant Rafflesia cantleyi, with its 50cm diameter flowers, has 'stolen' genes from its host Tetrastigma rafflesiae. Analysis of these genes shows that their functions range from respiration to metabolism, and that some of them have even replaced the parasites own gene activity.
Vertical gene transfer is that between parents and their offspring, while horizontal gene transfer is the movement of genes between two different organisms. Bacteria use horizontal ...
A bioinspired robot has provided the first experimental evidence that live zebrafish can be influenced by engineered robots.
Results published today, 8 June, in IOP Publishing's journal Bioinspiration and Biomimetics, provide a stepping stone on the path to using autonomous robots in an open environment to monitor and control fish behaviour.
In the future, water-based robots could potentially contribute to the protection of endangered animals and the control of pest species.
The robot, created by researchers from Polytechnic Institute of New York University and ...
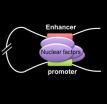
In exploring how proteins interact with crucial DNA sequences to regulate gene activity, researchers have shed light on key biological events that may eventually be manipulated to provide new disease treatments.
Within a cell's nucleus, regulatory elements in DNA called promoters and enhancers communicate with each other in carrying out gene activity, often over large genomic distances, hundreds of thousands of chemical bases apart from each other in chromosomes. As these elements physically contact each other, the intervening DNA sequences bend into loops made of chromatin ...
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute have, for the first time, determined the function of a series proteins within the mosquito that transduce a signal that enables the mosquito to fight off infection from the parasite that causes malaria in humans. Together, these proteins are known as immune deficiency (Imd) pathway signal transducing factors, are analogous to an electrical circuit. As each factor is switched on or off it triggers or inhibits the next, finally leading to the launch of an immune response against the malaria parasite. The study was ...