(Press-News.org) New research published today in BioMed Central's open access journal BMC Genomics reveals that the Malaysian parasitic plant Rafflesia cantleyi, with its 50cm diameter flowers, has 'stolen' genes from its host Tetrastigma rafflesiae. Analysis of these genes shows that their functions range from respiration to metabolism, and that some of them have even replaced the parasites own gene activity.
Vertical gene transfer is that between parents and their offspring, while horizontal gene transfer is the movement of genes between two different organisms. Bacteria use horizontal gene transfer to exchange resistance to antibiotics. Recent studies have shown that plants can also use horizontal gene transfer, especially parasitic plants and their hosts due to their intimate physical connections.
Rafflesia cantleyi is an obligate holoparasite (dependent on its host, and only that host, for sustenance), which grows on Tetrastigma rafflesiae, a member of the grape family. Researchers from Singapore, Malaysia and USA collaborated to systematically investigate the possibility of horizontal gene transfer between these two plants. By looking at the transcriptome (the transcribed products of switched on genes) they found 49 genes transcribed by the parasite, accounting for 2% of their total transcriptome, which originally belonged to the host. Three quarters of these transcripts appear to have replaced the parasites own version.
Most of these genes had been integrated into the parasite's nucleus, allowing the researchers to perform genomic analysis. Over time DNA randomly mutates and investigation of genetic drift between the genes for these transcripts, between the parasite and host, showed that some time has passed since the genes were acquired and that they were acquired gradually.
Prof Charles Davis, from the Harvard University Herbaria, who co-led this project with Prof Joshua Rest from Stony Brook University, explained, "The elevated rate of horizontal gene transfer between T. rafflesiae and its parasite R. cantleyi raises the possibility that there is a 'fitness' benefit to the parasite. For example they may improve the parasites ability to extract nutrients from the host, or help it evade the host's defences, as has been seen for a bacterial pathogen of citrus trees."
Prof Davis continued, "Furthermore it appears that about one third of the parasites own genes have evolved to be more like those of T. rafflesia. Finding out how T. rafflesia manages its genomic deception will provide us with real insights into the slow war between plant parasites and their hosts."
INFORMATION:
Media Contact
Dr Hilary Glover
Scientific Press Officer, BioMed Central
Tel: +44 (0) 20 3192 2370
Mob: +44 (0) 778 698 1967
Email: hilary.glover@biomedcentral.com
Notes to Editors
1. Horizontal transfer of expressed genes in a parasitic flowering plant.
Zhenxiang Xi, Robert K Bradley, Kenneth J Wurdack, K.M. Wong, M. Sugumaran, Kirsten Bomblies, Joshua S Rest and Charles C Davis
BMC Genomics (in press)
Please name the journal in any story you write. If you are writing for the web, please link to the article. All articles are available free of charge, according to BioMed Central's open access policy.
Article citation and URL available on request on the day of publication.
2. BMC Genomics is an open access, peer-reviewed journal that considers articles on all aspects of genome-scale analysis, functional genomics, and proteomics.
3. BioMed Central (http://www.biomedcentral.com/) is an STM (Science, Technology and Medicine) publisher which has pioneered the open access publishing model. All peer-reviewed research articles published by BioMed Central are made immediately and freely accessible online, and are licensed to allow redistribution and reuse. BioMed Central is part of Springer Science+Business Media, a leading global publisher in the STM sector.
Parasitic plants 'steal' genes from their hosts
2012-06-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Engineered robot interacts with live fish
2012-06-08
A bioinspired robot has provided the first experimental evidence that live zebrafish can be influenced by engineered robots.
Results published today, 8 June, in IOP Publishing's journal Bioinspiration and Biomimetics, provide a stepping stone on the path to using autonomous robots in an open environment to monitor and control fish behaviour.
In the future, water-based robots could potentially contribute to the protection of endangered animals and the control of pest species.
The robot, created by researchers from Polytechnic Institute of New York University and ...
Manipulating chromatin loops to regulate genes may offer future treatments for blood diseases
2012-06-08
In exploring how proteins interact with crucial DNA sequences to regulate gene activity, researchers have shed light on key biological events that may eventually be manipulated to provide new disease treatments.
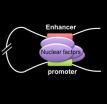
Within a cell's nucleus, regulatory elements in DNA called promoters and enhancers communicate with each other in carrying out gene activity, often over large genomic distances, hundreds of thousands of chemical bases apart from each other in chromosomes. As these elements physically contact each other, the intervening DNA sequences bend into loops made of chromatin ...
Immune system 'circuitry' that kills malaria in mosquitoes identified
2012-06-08
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Malaria Research Institute have, for the first time, determined the function of a series proteins within the mosquito that transduce a signal that enables the mosquito to fight off infection from the parasite that causes malaria in humans. Together, these proteins are known as immune deficiency (Imd) pathway signal transducing factors, are analogous to an electrical circuit. As each factor is switched on or off it triggers or inhibits the next, finally leading to the launch of an immune response against the malaria parasite. The study was ...
Pre-existing problems
2012-06-08
In a critical step that may lead to more effective HIV treatments, Harvard scientists have found that, in a small number of HIV patients, pre-existing mutations in the virus can cause it to develop resistance to the drugs used to slow the progression of the disease.
The finding is particularly important because, while researchers have long known HIV can develop resistance to some drugs, it wasn't understood whether the virus relied on pre-existing mutations to develop the resistance, or if it has to wait for those mutations to occur. By shedding new light on how resistance ...
Should spinal manipulation for neck pain be abandoned?
2012-06-08
The effectiveness of spinal manipulation divides medical opinion. On bmj.com today, experts debate whether spinal manipulation for neck pain should be abandoned.
Spinal manipulation is a technique that involves the application of various types of thrusts to the lumbar spine (lower back) or cervical spine (neck) to reduce back pain, neck pain and other musculoskeletal conditions.
Neil O'Connell and colleagues argue that cervical spine manipulation "may carry the potential for serious neurovascular complications" and that the technique is "unnecessary and inadvisable." ...
Patients suffering from pre-diabetes at potential future risk of stroke
2012-06-08
Millions of people suffering from pre-diabetes may be at a higher risk of stroke, a study published on bmj.com today suggests.
Pre-diabetes is characterised by higher than normal blood glucose levels that, if left untreated, develops into type 2 diabetes. The scale of the problem is enormous and growing, with an estimated 79 million people in the US and 7 million people in the UK affected.
People with pre-diabetes also harbour the same vascular risk factors as people with type 2 diabetes, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol and obesity, but its effect on ...
By adding VSL#3 probiotic to traditional therapies UC patients can improve remission rates
2012-06-08
GAITHERSBURG, MD, June 7 – As one of the few probiotics with medical food designation for specific illnesses, VSL#3® has been the subject of a collection of more than 80 studies that have demonstrated its use in the dietary management of IBS, ulcerative colitis, and an ileal pouch. Ulcerative colitis patients, in particular, have been shown to benefit from adding VSL#3 medical food to their prescription drug regimen. One particular study shows that the combination of VSL#3 and traditional drug therapy can improve remission rates over drug therapy alone by 10 to 17 percent, ...
Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation increases survival in systemic sclerosis patients
2012-06-08
Berlin, Germany, June 7 2012: Initial results from an international, investigator-initiated, open label phase III trial were presented at EULAR 2012, the Annual Congress of the European League Against Rheumatism. Data indicate that haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) results in better long term survival than conventional treatment for patients with poor prognosis early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis.
The ASTIS (Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation International Scleroderma) trial enrolled more than 150 patients between 2001 and 2009, and randomised ...
Mapping genes: Mayo Clinic finds new risk factors for neurodegenerative diseases
2012-06-08
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — Using a new and powerful approach to understand the origins of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, researchers at Mayo Clinic in Florida are building the case that these diseases are primarily caused by genes that are too active or not active enough, rather than by harmful gene mutations.
In the June 7 online issue of PLoS Genetics, they report that several hundred genes within almost 800 brain samples of patients with Alzheimer's disease or other disorders had altered expression levels that did not result from neurodegeneration. ...
Surgeon experience affects complication rate of spinal stenosis surgery
2012-06-08
Philadelphia, Pa. (June 7, 2012) - For patients undergoing surgery for spinal stenosis, the risk of complications is higher when the surgeon performs very few such procedures—less than four per year, suggests a study in the June issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
In contrast, the complication rate is not significantly affected by the volume of spinal stenosis surgeries performed at the hospital, according to the new research. The senior ...