(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, PA, June 14, 2012 – Regenerative medicine, or the use of specially grown tissues and cells to treat injuries and diseases, has been successful in treating disorders of a number of organs, including heart, pancreas, and cartilage. However, efforts to treat disorders of the corneal endothelium, a single cell layer on the inner surface of the cornea, with regenerative techniques have been less effective. Now, a group of scientists has developed a method that enhances the adhesion of injected corneal endothelial cells (CECs), allowing for successful corneal transplantation to repair pathological dysfunctions. Their results are published online today in advance, in the July issue of The American Journal of Pathology.
"Corneal endothelial dysfunction is a major cause of severe visual impairment, since the cells maintain the transparency of the cornea," explains lead investigator Noriko Koizumi, MD, PhD, of the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Life and Medical Sciences, Doshisha University, Kyotanabe, Japan. "Injected cultured CECs can be washed off by aqueous humor flow, resulting in poor adhesion of the cells injected onto the corneal tissue. Previous studies demonstrated that Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) signaling interferes with adhesion. We found that transplanting cultivated CECs in combination with a low-molecular weight compound that inhibits ROCK (ROCK inhibitor Y-27632), successfully achieved the recovery of corneal transparency."
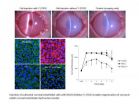
Using rabbit cells, researchers cultivated CECs in the lab and injected them into the anterior chamber of rabbit eyes with damaged corneal endothelia. Based on the recovery of the corneal endothelial function, they found that when the cultivated cells were injected along with Y-27632, the rabbit corneas regained complete transparency 48 hours after injection. In contrast, rabbit CECs injected without Y-27632 resulted in hazy and severely swollen corneas. No complications related to cell injection therapy were observed and reconstructed corneal endothelium with Y-27632 exhibited normal hexagonal cell shape.
Since rabbit CECs are highly prolific in vivo, the scientists performed another round of experiments with monkey CECs, which are more similar to those in humans. The transplantation of CECs in these primates also achieved the recovery of long-term corneal transparency with a monolayer of hexagonal cells, suggesting that cell adhesion modified by ROCK inhibitor may be an effective treatment for human corneal endothelial disorders.
Although surgical techniques to replace the injured corneal endothelium have been developed, these procedures are technically difficult and challenging due to a shortage of donor corneas. "The novel strategy of using a cell-based therapy combined with a ROCK inhibitor may ultimately provide clinicians with a new therapeutic modality in regenerative medicine, not only for treatment of corneal endothelial dysfunctions, but also for a variety of pathological diseases," Dr. Koizumi concludes.
INFORMATION:
Regenerated cells may restore vision after corneal dysfunction
New method reported in the American Journal of Pathology
2012-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Total Family Dental Group Welcomes Torrance Dentist Dr. Remy Rogers Back to its Torrance Dental Practice
2012-06-14
The Total Family Dental Group is delighted to welcome Dr. Remy Rogers back to its Torrance dental office, following her recent maternity leave, and congratulates her on the birth of a healthy baby girl.
Torrance dentist Dr. Rogers is a general and cosmetic dentist who enjoys treating both adults and children. For her younger patients (up to 18 months of age) and their parents, she offers baby dental wellness checks. During this time she checks the infant's oral health, while educating parents on all aspects of their child's oral health care and any other topics relevant ...
Childhood virus infection linked to prolonged seizures with fever
2012-06-14
New research shows that human herpesviruses (HHV)-6B and HHV-7, commonly know as roseola virus), account for one third of febrile status epilepticus (FSE) cases. Results of the FEBSTAT prospective study now available in Epilepsia, a journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE), suggest that HHV-6B may be involved in the development of epilepsy and further research is urgently needed.
FEBSTAT is a multi-center study of the consequences of FSE, designed to identify the factors that increase the risk of injury to the ...
Cougars are re-populating their historical range, new study confirms
2012-06-14
American mountain lions, or cougars, are re-emerging in areas of the United States, reversing 100 years of decline. The evidence, published in The Journal of Wildlife Management, raises new conservation questions, such as how humans can live alongside the returning predators.
"The cougar population declined dramatically from 1900, due to both hunting, and a lack of prey, leaving the remaining population isolated to the American west," said Michelle LaRue from the University of Minnesota. "Here we present the hard evidence that the western population has spread, with cougar ...
Interactive iBooks: the Next Generation of Learning and Training
2012-06-14
This series of 9 interactive iBooks are great tools to suppport the blended and digital learning methods that schools are adopting.
The interactive iBooks are available for the iPad and contain interactive elements, tutorials, educational resources, web 2.0 tools, lesson suggestions and tips for integrating blended learning into any learning management system or educational portal.
Author: Ryan Macdonald is a trainer, online course developer and ePublisher.
www.mmcid.com
iBook Titles:
1. Itslearning Teacher Training
2. Blended Learning: Tricks and Tips ...
Childhood obesity linked to math performance, MU researcher says
2012-06-14
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Childhood obesity has increased dramatically throughout the past 40 years and has been tied to many health problems. Now, a University of Missouri researcher has found that children's weight is associated with their math performance.
"The findings illustrate the complex relationships among children's weight, social and emotional well-being, academics and time," said Sara Gable, associate professor in the MU Department of Nutrition and Exercise Physiology, who led the study.
Gable looked at more than 6,250 children from the Early Childhood Longitudinal ...
Elemental and magnetic imaging using X-rays and a microscope
2012-06-14
A team of researchers has developed a new microscope that can image the elemental and magnetic properties of a wide range of energy-important materials that are used in devices such as solar cells and solid-state lighting. The imager is based on a technique known as X-ray excited luminescence microscopy (XELM). It was created by hitching a standard optical microscope to a synchrotron X-ray source. Synchrotrons produce X-rays and other forms of electromagnetic radiation by sending electrons on a curved path at nearly the speed of light. When the X-rays strike the material ...
Flood Wood Care to Provide One Lucky Homeowner with a Deck Staining and a Backyard Party
2012-06-14
With Flood wood care, staining a deck is always easy, but for one lucky homeowner there's only one step: enjoy!
Flood wood care, a leading brand of specialty wood stains, is giving away the product and labor for a deck staining, as well as a backyard party.
The giveaway is part of the Take-It-Easy Sweepstakes, and homeowners can enter online through July 15 at www.Flood.com.
"The Take-It-Easy Sweepstakes emphasizes our commitment to helping homeowners enhance and enjoy their outdoor space," said Nathalie Lambert, brand manager for AkzoNobel's portfolio ...
Relocating LEDs from silicon to copper enhances efficiency
2012-06-14
Chinese researchers have succeeded in transferring gallium nitride (GaN) light-emitting diodes (LEDs) grown on a layer of silicon to a layer of copper. The new copper substrate enabled the GaN crystals to release some of the internal stresses generated when they originally formed. This relaxation helped minimize the so-called "quantum confined stark effect," a vexing problem for LEDs that reduces their efficiency. In comparison with LEDs on silicon substrates, the light output of LEDs on copper was enhanced by 122 percent. The relocation of the LEDs produced no obvious ...
Researchers 'heal' plasma-damaged semiconductor with treatment of hydrogen radicals
2012-06-14
Gallium nitride (GaN) is a highly promising material for a wide range of optical and high-power electronic devices, which can be fabricated by dry etching with plasmas. However, the plasma-induced defects and surface residues that remain after such processes tend to degrade the optical and electrical properties of the devices. A team of Japanese researchers has developed and tested a new way to "heal" such defects. The team exposed plasma-damaged GaN to hydrogen (H) radicals at room temperature. After testing various doses of H radicals, the researchers evaluated the optical ...
Tracking breast cancer cells on the move
2012-06-14
Breast cancer cells frequently move from their primary site and invade bone, decreasing a patient's chance of survival. This process of metastasis is complex, and factors both within the breast cancer cells and within the new bone environment play a role. In next week's Journal of Biological Chemistry "Paper of the Week," Roger Gomis and colleagues at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine in Spain investigated how breast cancer cells migrate to bone.
In particular, they examined the role of NOG, a gene important to proper bone development. Previously, NOG was associated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
[Press-News.org] Regenerated cells may restore vision after corneal dysfunctionNew method reported in the American Journal of Pathology