(Press-News.org) New pictures from the University of Iowa show what it looks like when a person runs out of patience and loses self-control.
A study by University of Iowa neuroscientist and neuro-marketing expert William Hedgcock confirms previous studies that show self-control is a finite commodity that is depleted by use. Once the pool has dried up, we're less likely to keep our cool the next time we're faced with a situation that requires self-control.
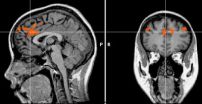
But Hedgcock's study is the first to actually show it happening in the brain using fMRI images that scan people as they perform self-control tasks. The images show the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)—the part of the brain that recognizes a situation in which self-control is needed and says, "Heads up, there are multiple responses to this situation and some might not be good"—fires with equal intensity throughout the task.
However, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC)—the part of the brain that manages self-control and says, "I really want to do the dumb thing, but I should overcome that impulse and do the smart thing"—fires with less intensity after prior exertion of self-control.
He said that loss of activity in the DLPFC might be the person's self-control draining away. The stable activity in the ACC suggests people have no problem recognizing a temptation. Although they keep fighting, they have a harder and harder time not giving in.
Which would explain why someone who works very hard not to take seconds of lasagna at dinner winds up taking two pieces of cake at desert. The study could also modify previous thinking that considered self-control to be like a muscle. Hedgcock says his images seem to suggest that it's like a pool that can be drained by use then replenished through time in a lower conflict environment, away from temptations that require its use.
The researchers gathered their images by placing subjects in an MRI scanner and then had them perform two self-control tasks—the first involved ignoring words that flashed on a computer screen, while the second involved choosing preferred options. The study found the subjects had a harder time exerting self-control on the second task, a phenomenon called "regulatory depletion." Hedgcock says that the subjects' DLPFCs were less active during the second self-control task, suggesting it was harder for the subjects to overcome their initial response.
Hedgcock says the study is an important step in trying to determine a clearer definition of self-control and to figure out why people do things they know aren't good for them. One possible implication is crafting better programs to help people who are trying to break addictions to things like food, shopping, drugs, or alcohol. Some therapies now help people break addictions by focusing at the conflict recognition stage and encouraging the person to avoid situations where that conflict arises. For instance, an alcoholic should stay away from places where alcohol is served.
But Hedgcock says his study suggests new therapies might be designed by focusing on the implementation stage instead. For instance, he says dieters sometimes offer to pay a friend if they fail to implement control by eating too much food, or the wrong kind of food. That penalty adds a real consequence to their failure to implement control and increases their odds of choosing a healthier alternative.
The study might also help people who suffer from a loss of self-control due to birth defect or brain injury.
"If we know why people are losing self-control, it helps us design better interventions to help them maintain control," says Hedgcock, an assistant professor in the Tippie College of Business marketing department and the UI Graduate College's Interdisciplinary Graduate Program in Neuroscience.
INFORMATION:
Hedgcock's paper, "Reducing self-control depletion effects through enhanced sensitivity to implementation: Evidence from fMRI and behavioral studies," was co-authored by Kathleen Vohs and Akshay Rao of the University of Minnesota. It will be published in January 2013 in the Journal of Consumer Psychology.
This is your brain on no self-control
MRI images show what the brain looks like when you do something you know you shouldn't
2012-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Million year old groundwater in Maryland water supply
2012-06-19
A portion of the groundwater in the upper Patapsco aquifer underlying Maryland is over a million years old. A new study suggests that this ancient groundwater, a vital source of freshwater supplies for the region east of Washington, D.C. and Baltimore, was recharged over periods of time much greater than human timescales.
"Understanding the average age of groundwater allows scientists to estimate at what rate water is re-entering the aquifer to replace the water we are currently extracting for human use," explained USGS Director Marcia McNutt. "This is the first step ...
Anti-cocaine vaccine described in Human Gene Therapy Journal
2012-06-19
New Rochelle, NY, June 18, 2012—A single-dose vaccine capable of providing immunity against the effects of cocaine offers a novel and groundbreaking strategy for treating cocaine addiction is described in an article published Instant Online in Human Gene Therapy, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. (http://www.liebertpub.com) The article is available free online at the Human Gene Therapy website (http://www.liebertpub.com/hum).
"This is a very novel approach for addressing the huge medical problem of cocaine addiction," says James M. Wilson, MD, PhD, Editor-in-Chief, ...
Doctors cite concern for patients, colleagues top motives for working sick
2012-06-19
An unwavering work ethic is a hallmark of many health professionals. But a new survey finds that when a doctor is sick, staunch dedication can have unintended consequences.
A poll of 150 attendees of an American College of Physicians meeting in 2010 revealed that more than half of resident physicians had worked with flu-like symptoms at least once in the last year. One in six reported working sick on three or more occasions during the year, according to the survey conducted by researchers at the University of Chicago Medicine and Massachusetts General Hospital. Notably, ...
Canadian teen moms run higher risk of abuse, depression than older mothers
2012-06-19
(Edmonton) Teen mothers are far more likely to suffer abuse and postpartum depression than older moms, according to a study of Canadian women's maternity experiences by a University of Alberta researcher.
Dawn Kingston, an assistant professor in the Faculty of Nursing, analyzed data from the Maternity Experiences Survey, which asked more than 6,400 new mothers about their experiences with stress, violence, pre- and postnatal care, breastfeeding and risky behaviour like smoking and drug use before, during and after pregnancy.
Kingston said the survey offers the first ...
Understanding faults and volcanics, plus life inside a rock
2012-06-19
Boulder, Colo., USA – This posting: Orange-like rocks in Utah with iron-oxide rinds and fossilized bacteria inside that are believed to have eaten the interior rock material, plus noted similarities to "bacterial meal" ingredients and rock types on Mars; fine-tuning the prediction of volcanic hazards and warning systems for both high population zones and at Tristan da Cunha, home to the most remote population on Earth; news from SAFOD; and discovery in Germany of the world's oldest known mosses.
Biosignatures link microorganisms to iron mineralization in a paleoaquifer
Karrie ...
Psoriasis increases risk of diabetes, Penn study shows
2012-06-19
PHILADELPHIA - Psoriasis is an independent risk for Type 2 Diabetes, according to a new study by researchers with the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, with the greatest risk seen in patients with severe psoriasis. Researchers estimate that an additional 115,500 people will develop diabetes each year due to the risk posed by psoriasis above and beyond conventional risk factors. The research is published in the latest issue of the Archives of Dermatology, a JAMA Network publication.
"These data suggest that patients with psoriasis are at increased ...
Cheaper drug could lead to serious eye issues
2012-06-19
A Queen's University study of two eye drugs used to treat wet Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) has determined the cheaper of the two could lead to eye inflammation, a potentially blinding adverse effect.
"This is a very important finding," says Sanjay Sharma (Ophthalmology and Epidemiology), a noted AMD and health policy researcher who also practices at Hotel Dieu Hospital. "It is particularly important because many seniors need numerous injections so the risk is cumulative."
AMD is the leading cause of severe visual loss and blindness in Canada. It is linked to ...
Brothers in arms: Commensal bacteria help fight viruses
2012-06-19
PHILADELPHIA – Healthy humans harbor an enormous and diverse group of bacteria and other bugs that live within their intestines. These microbial partners provide beneficial aid in multiple ways – from helping digest food to the development of a healthy immune system. In a new study published online in the journal Immunity, David Artis, PhD, associate professor of Microbiology, and Michael Abt, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the Artis lab, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, show that commensal bacteria are also essential to fight off viral infections. ...
Discovery helps mice beat urinary tract infections
2012-06-19
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found new clues to why some urinary tract infections recur persistently after multiple rounds of treatment.
Their research, conducted in mice, suggests that the bacteria that cause urinary tract infections take advantage of a cellular waste disposal system that normally helps fight invaders. In a counterintuitive finding, they learned that when the disposal system was disabled, the mice cleared urinary tract infections much more quickly and thoroughly.
"This could be the beginning of a paradigm ...
Social-class discrimination contributes to poorer health
2012-06-19
Discrimination felt by teenagers based on their social class background can contribute to physiologic changes associated with poorer health, according to a new study published online in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Lead author Dr. Thomas Fuller-Rowell, a researcher at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and a Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Health & Society Scholar, says that while the link between poverty and poor health has long been known, this is one of the first studies to consider the impact of class discrimination.
"The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Research advances in porous materials, as highlighted in the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Sally C. Morton, executive vice president of ASU Knowledge Enterprise, presents a bold and practical framework for moving research from discovery to real-world impact
Biochemical parameters in patients with diabetic nephropathy versus individuals with diabetes alone, non-diabetic nephropathy, and healthy controls
Muscular strength and mortality in women ages 63 to 99
Adolescent and young adult requests for medication abortion through online telemedicine
Researchers want a better whiff of plant-based proteins
Pioneering a new generation of lithium battery cathode materials
A Pitt-Johnstown professor found syntax in the warbling duets of wild parrots
Cleaner solar manufacturing could cut global emissions by eight billion tonnes
Safety and efficacy of stereoelectroencephalography-guided resection and responsive neurostimulation in drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy
Assessing safety and gender-based variations in cardiac pacemakers and related devices
New study reveals how a key receptor tells apart two nearly identical drug molecules
Parkinson’s disease triggers a hidden shift in how the body produces energy
Eleven genetic variants affect gut microbiome
Study creates most precise map yet of agricultural emissions, charts path to reduce hotspots
When heat flows like water
Study confirms Arctic peatlands are expanding
KRICT develops microfluidic chip for one-step detection of PFAs and other pollutants
How much can an autonomous robotic arm feel like part of the body
Cell and gene therapy across 35 years
Rapid microwave method creates high performance carbon material for carbon dioxide capture
New fluorescent strategy could unlock the hidden life cycle of microplastics inside living organisms
HKUST develops novel calcium-ion battery technology enhancing energy storage efficiency and sustainability
High-risk pregnancy specialists present research on AI models that could predict pregnancy complications
Academic pressure linked to increased risk of depression risk in teens
Beyond the Fitbit: Why your next health tracker might be a button on your shirt
UCSB scientists bottle the sun with liquid battery
Lung cancer drug offers a surprising new treatment against ovarian cancer
When consent meets reality: How young men navigate intimacy
Siemens Healthineers and Mayo Clinic expand strategic collaboration to enhance patient care through advanced technology
[Press-News.org] This is your brain on no self-controlMRI images show what the brain looks like when you do something you know you shouldn't