(Press-News.org) CINCINNATI - New research in Nature Medicine shows that boosting a protein pathway in the body's blood making system protects mice from otherwise fatal radiation poisoning.
Scientists in the multi-institutional study – posted online by the journal on June 24 – say their findings open the potential for new treatments against radiation toxicity during cancer treatment or environmental exposures – such as in a nuclear explosion or accident.
By identifying a target-specific intervention to protect the hematopoietic system against radiation toxicity, the study addresses a largely unmet challenge, according to the researchers.
"These findings suggest that pharmacologic augmentation of the activity of the Thbd-aPC pathway by recombinant Thbd (thrombomodulin) or aPC (activated protein C) might offer a rational approach to the mitigation of tissue injury and lethality caused by ionizing radiation," the scientists write in their manuscript. "Recombinant human aPC has undergone extensive clinical testing in patients, and recombinant soluble human Thbd is currently being investigated for efficacy in antithrombotic therapy in humans. Our data encourage the further evaluation of these proteins for their radio-mitigating activities."
The study reveals a previously unknown function of the Thbd-aPC pathway in radiation mitigation. The pathway is normally known for its ability to prevent the formation of blood clots and help the body fight infections. The researchers found the pathway helps blood cells in the bone marrow recover from injury caused by radiation exposure. They demonstrated that pharmacologic boosting of this pathway with two drugs tested for the treatment of thrombosis or infection (recombinant Thbd and aPC respectively) can be used in mice to prevent death caused by exposure to lethal doses of radiation.
In all instances of treatment with recombinant soluble Thbd or aPC, the result was accelerated recovery of hematopoietic progenitor cell activity in bone marrow and a reduction in the harmful effects of lethal total body irradiation. When treatment was with aPC, these benefits occurred even when treatment was delayed for 24 hours.
The scientists caution their study involves early laboratory research in mice, so it remains to be tested how the findings may translate to human treatment. Researchers also need to determine exactly why the protective function of the targeted Thbd-aPC protein pathway seems to work so well in mice.
Researchers noted that the protective benefits of Thbd-aPC occurred only in vivo in irradiated mouse models. The researchers reported that overexpressed Thbd in irradiated laboratory cell cultures did not offer the same protective benefits, as the cells did not survive. This indicates the protective benefits of Thbd on blood making cells in irradiated mouse models depends on the help of additional cells or molecules in the body, which the researchers are trying to identify in a follow-up study.
The study involves extensive multi-scientist collaborations that combined previously independent lines of research by groups at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and the University of Ulm, Germany (led by Hartmut Geiger, PhD, Division of Experimental Hematology/Cancer Biology and the Department of Dermatology/Allergic Diseases); the University of Arkansas, Little Rock (led by Martin Hauer-Jensen, MD, PhD, Division of Radiation Health, the College of Pharmacy and the Central Arkansas Veterans Healthcare System); the Blood Research Institute in Milwaukee, Wis. (led by Hartmut Weiler, PhD); and The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif. (led by John H. Griffin, PhD, Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine).
The research team said the current study exemplifies a global shift to multi-investigator projects that allow a combination of varied expertise by scientists tackling complex problems from the perspective of their respective fields. This approach requires the willingness of investigators to share unpublished data and engage in an open collaboration. The researchers also said the study underscores the importance of continued federal funding for leading edge basic research that can benefit human health.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by funding from The National Institutes of Health, as well as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and the Edward P. Evans Foundation.
Additional co-authors on the study include Snehalata A. Pawar, Edward J. Kerschen, Kalpana J. Nattamai, Irene Hernandez, Hai-Po Liang, Jose A. Fernandez, Jose A. Cancelas, Marnie A. Ryan, Olga Kustikova, Axel Schambach, Qiang Fu, Junru Wang, Louis M. Fink, Karl-Uwe Petersen, Daohong Zhou and Christopher Baum, and the following institutions: Department of Experimental Hematology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany; the Desert Research Institute, Las Vegas, Nev.; PAION Deutschland GmbH, Aachen, Germany.
About Cincinnati Children's:
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center ranks third in the nation among all Honor Roll hospitals in U.S. News and World Report's 2012 Best Children's Hospitals ranking. It is ranked #1 for neonatology and in the top 10 for all pediatric specialties. Cincinnati Children's is one of the top two recipients of pediatric research grants from the National Institutes of Health. It is internationally recognized for improving child health and transforming delivery of care through fully integrated, globally recognized research, education and innovation. Additional information can be found at www.cincinnatichildrens.org.
END
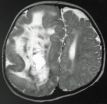
Hemimegalencephaly is a rare but dramatic condition in which the brain grows asymmetrically, with one hemisphere becoming massively enlarged. Though frequently diagnosed in children with severe epilepsy, the cause of hemimegalencephaly is unknown and current treatment is radical: surgical removal of some or all of the diseased half of the brain.
In a paper published in the June 24, 2012 online issue of Nature Genetics, a team of doctors and scientists, led by researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, ...
The vagaries of South Asian summer monsoon rainfall impact the lives of more than one billion people. A review in Nature Climate Change (June 24 online issue) of over 100 recent research articles concludes that with continuing rise in CO2 and global warming, the region can expect generally more rainfall, due to the expected increase in atmospheric moisture, as well as more variability in rainfall.
In spite of the rise in atmospheric CO2 concentration of about 70 parts per million by volume and in global temperatures of about 0.50°C over the last 6 decades, the All India ...
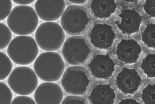
Kyoto, Japan -- In what may prove to be a significant boon for industry, separating mixtures of liquids or gasses has just become considerably easier.
Using a new process they describe as "reverse fossilization," scientists at Kyoto University's WPI Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) have succeeded in creating custom designed porous substances capable of low cost, high efficiency separation.
The process takes place in the mesoscopic realm, between the nano- and the macroscopic, beginning with the creation of a shaped mineral template, in this case ...
The study is the first to give a comprehensive projection for this long perspective, based on observed sea-level rise over the past millennium, as well as on scenarios for future greenhouse-gas emissions.
"Sea-level rise is a hard to quantify, yet critical risk of climate change," says Michiel Schaeffer of Climate Analytics and Wageningen University, lead author of the study. "Due to the long time it takes for the world's ice and water masses to react to global warming, our emissions today determine sea levels for centuries to come."
Limiting global warming could considerably ...
CHICAGO – Federally funded community health centers with higher patient-centered medical home ratings on measures such as quality improvement had higher operating costs, according to a study appearing in JAMA. This study is being published early online to coincide with its presentation at the Annual Research Meeting of AcademyHealth.
"The patient-centered medical home (PCMH) is a model of care characterized by comprehensive primary care, quality improvement, care management, and enhanced access in a patient-centered environment. The PCMH is intuitively appealing and has ...
In choosing a mate both males and females rely on visual cues to determine which potential partner will supply the best genes, best nesting site, best territory, and best parenting skills. New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal Frontiers in Zoology shows that male blue tits' (Cyanistes caeruleus) parental behavior is determined by female ornamentation (ultraviolet coloration of the crown), as predicted by the differential allocation hypothesis (DAH).
DAH makes the assumption that aesthetic traits indicate quality and arises from the needs of a ...
Offenders with mental health problems need improved and on-going access to health care, according to the first study to systematically examine healthcare received by offenders across the criminal justice system.
A new report from Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth University, and the Centre for Mental Health, suggests that prison and community sentences offer the best opportunities to provide this. If improvements to mental health are to contribute to breaking the cycle of repeat offending, unemployment and ill-health, advantage should be taken of ...
EVANSTON, Ill. – Want to nail that tune that you've practiced and practiced? Maybe you should take a nap with the same melody playing during your sleep, new provocative Northwestern University research suggests.
The research grows out of exciting existing evidence that suggests that memories can be reactivated during sleep and storage of them can be strengthened in the process.
In the Northwestern study, research participants learned how to play two artificially generated musical tunes with well-timed key presses. Then while the participants took a 90-minute nap, the ...
A new study shows that although gastric bypass surgery reverses Type 2 diabetes in a large percentage of obese patients, the disease recurs in about 21 percent of them within three to five years. The study results will be presented Saturday at The Endocrine Society's 94th Annual Meeting in Houston.
"The recurrence rate was mainly influenced by a longstanding history of Type 2 diabetes before the surgery," said the study's lead author, Yessica Ramos, MD, an internal medicine resident at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale. "This suggests that early surgical intervention ...
A team of researchers from Mount Sinai School of Medicine and four other institutions have found that young children with documented or likely allergies to milk and/or eggs, whose families were instructed on how to avoid these and other foods, still experienced allergic reactions at a rate of almost once per year. Of severe cases, less than a third received epinephrine, a medication used to counter anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic condition.
The findings are from an ongoing Consortium of Food Allergy Research (CoFAR) study that has been following more than 500 ...