(Press-News.org) A new genre of medical tests – which determine whether a medicine is right for a patient's genes – are paving the way for increased use of personalized medicine, according to the cover story in the current edition of Chemical & Engineering News. C&EN is the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific society.
Celia Henry Arnaud, C&EN senior editor, points out that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved several precedent-setting cancer drugs that provide a glimpse of the "personalized" medical care that awaits patients with cancer and other diseases in the future. Personalized medicine involves selecting treatments that work best with the set of genes present in each individual person. Such treatments work only for patients with conditions related to mutations, or alterations, in certain genes.
The article describes new "companion diagnostics," or diagnostic tests that already have gone into use, with more on the horizon, to identify patients most likely to benefit from a medication. Doctors must perform these tests before starting treatment. Arnaud describes how pharmaceutical companies are embracing an approach that involves co-development of drugs and companion diagnostics that can be used in clinical trials and later when a medication goes into general use.
###
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 164,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
A new genre of diagnostic tests for the era of personalized medicine
2012-07-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The first robot that mimics the water striders' jumping abilities
2012-07-27
The first bio-inspired microrobot capable of not just walking on water like the water strider – but continuously jumping up and down like a real water strider – now is a reality. Scientists reported development of the agile microrobot, which could use its jumping ability to avoid obstacles on reconnaissance or other missions, in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Qinmin Pan and colleagues explain that scientists have reported a number of advances toward tiny robots that can walk on water. Such robots could skim across lakes and other bodies of water to monitor water ...
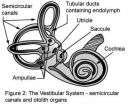
Decoding the secrets of balance
2012-07-27
If you have ever looked over the edge of a cliff and felt dizzy, you understand the challenges faced by people who suffer from symptoms of vestibular dysfunction such as vertigo and dizziness. There are over 70 million of them in North America. For people with vestibular loss, performing basic daily living activities that we take for granted (e.g. dressing, eating, getting in and out of bed, getting around inside as well as outside the home) becomes difficult since even small head movements are accompanied by dizziness and the risk of falling.
We've known for a while ...
Big horns trump smooth pickup lines every time
2012-07-27
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Elk and rhinoceros beetles aren't diabetic, but to grow big horns and attract mates it appears that the males are insulin-dependent.
Ian Dworkin, Michigan State University zoologist, was part of a team that for the first time ever showed why horns – from elk to rhinoceros beetles – and other decorative, mate-attracting structures are sensitive to changes in nutrition. As reported in the current issue of Science, the key ingredient for this growth is insulin, Dworkin said.
"Clearly elk antlers, peacock tail feathers and beetle horns are very different, ...
Rivers flowing into the sea offer vast potential as electricity source
2012-07-27
WASHINGTON, July 25, 2012 — The latest episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions podcast series describes a process that could pave the way for a new genre of electric power-generating stations. These stations could supply electricity for more than a half billion people by tapping just one-tenth of the global potential of a little-known energy source that exists where rivers flow into the ocean.
Based on a report by Menachem Elimelech, Ph.D., and Ngai Yin Yip in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology, ...
New research confirms efficacy of transcranial magnetic stimulation for depression
2012-07-27
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – In one of the first studies to look at transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) in real-world clinical practice settings, researchers at Butler Hospital, along with colleagues across the U.S., confirmed that TMS is an effective treatment for patients with depression who are unable to find symptom relief through antidepressant medications. The study findings are published online in the June 11, 2012 edition of Depression and Anxiety in the Wiley Online Library.
Previous analysis of the efficacy of TMS has been provided through more than 30 published ...
Photovoltaics from any semiconductor
2012-07-27
A technology that would enable low-cost, high efficiency solar cells to be made from virtually any semiconductor material has been developed by researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley. This technology opens the door to the use of plentiful, relatively inexpensive semiconductors, such as the promising metal oxides, sulfides and phosphides, that have been considered unsuitable for solar cells because it is so difficult to taylor their properties by chemical means.
"It's ...
MRSA cases in academic hospitals double in 5 years: study
2012-07-27
CHICAGO (July 26, 2012) -- Infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) doubled at academic medical centers in the U.S. between 2003 and 2008, according to a report published in the August issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America.
Researchers from the University of Chicago Medicine and the University HealthSystem Consortium (UHC) estimate hospitalizations increased from about 21 out of every 1,000 patients hospitalized in 2003 to about 42 out of every 1,000 in 2008, ...
NASA X-ray concept inspired from a roll of Scotch® tape
2012-07-27
The inspiration behind NASA scientist Maxim Markevitch's quest to build a highly specialized X-ray mirror using a never-before-tried technique comes from an unusual source: a roll of Scotch® tape.
Markevitch and a team of X-ray optics experts at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., have begun investigating the feasibility of fashioning a low-cost mirror from plastic tape and tightly rolling it like the sticky adhesive commonly found in most homes and offices.
"I remember looking at a roll of Scotch tape and thinking, 'was it possible to use the same ...
Maric Industries MarVac Achieves Title of UL Recognized Supplier
2012-07-27
Maric Industries'MarVac division is proud to inform you that we are now a UL Recognized supplier of wire and cable assemblies. This means that you can be confident that MarVac is building exactly to the customers specifications spelled out on their print. It also means we are using the exact components called out on the print or BOM and no deviation will be made.
Visit
http://maricindustries.com/press-release/
Maric Industries Signifies Quality
Maric Industries solutions serve broadband operators, telecommunication system contractors and many other markets. ...
Boeing Performance Excellence Award Issued to Pasternack
2012-07-27
Pasternack Enterprises, Inc., a leading ISO 9001:2008 manufacturer and International supplier of custom and standard RF, microwave and fiber optic products, today announced that it has received the 2011 Boeing Performance Excellence Award.
The Boeing Company issues the award annually to recognize suppliers who have achieved superior performance. Pasternack maintained a Silver composite performance rating for each month of the 12-month performance period, from Oct. 1, 2010, to Sept. 30, 2011. This year, Boeing recognized 407 suppliers who achieved a Silver level Boeing ...