(Press-News.org) Plastic electronics hold the promise of cheap, mass-produced devices. But plastic semiconductors have an important flaw: the electronic current is influenced by "charge traps" in the material. These traps, which have a negative impact on plastic light-emitting diodes and solar cells, are poorly understood.
However, a new study by a team of researchers from the University of Groningen and the Georgia Institute of Technology reveals a common mechanism underlying these traps and provides a theoretical framework to design trap-free plastic electronics. The results are presented in an advance online publication of the journal Nature Materials.
Plastic semiconductors are made from organic, carbon-based polymers, comprising a tunable forbidden energy gap. In a plastic light-emitting diode (LED), an electron current is injected into a higher molecular orbital, situated just above the energy gap. After injection, the electrons move toward the middle of the LED and fall down in energy across the forbidden energy gap, converting the energy loss into photons. As a result, an electrical current is converted into visible light.
However, during their passage through the semiconductor, a lot of electrons get stuck in traps in the material and can no longer be converted into light. In addition, this trapping process greatly reduces the electron current and moves the location where electrons are converted into photons away from the center of the device.
"This reduces the amount of light the diode can produce," explained Herman Nicolai, first author of the Nature Materials paper.
The traps are poorly understood, and it has been suggested that they are caused by kinks in the polymer chains or impurities in the material.
"We've set out to solve this puzzle by comparing the properties of these traps in nine different polymers," Nicolai explained. "The comparison revealed that the traps in all materials had a very similar energy level."
The Georgia Tech group, led by Jean-Luc Bredas, investigated computationally the electronic structure of a wide range of possible traps. "What we found out from the calculations is that the energy level of the traps measured experimentally matches that produced by a water-oxygen complex," said Bredas.
Nicolai explains that "such a complex could easily be introduced during the manufacturing of the semiconductor material, even if this is done under controlled conditions." The devices Nicolai studied were fabricated in a nitrogen atmosphere, "but this cannot prevent contamination with minute quantities of oxygen and water," he noted.
The fact that the traps have a similar energy level means that it is now possible to estimate the expected electron current in different plastic materials. And it also points the way to trap-free materials. "The trap energy lies in the forbidden energy gap," Nicolai explained.
This energy gap represents the difference in energy of the outer shell in which the electrons circle in their ground state and the higher orbital to which they can be moved to become mobile charge carriers. When such a mobile electron runs into a trap that is within the energy gap it will fall in, because the trap has a lower energy level.
"But if chemists could design semiconducting polymers in which the trap energy is above that of the higher orbital in which the electrons move through the material, they couldn't fall in," he suggested. "In this case, the energy level of the trap would be higher than that of the electron."
The results of this study are therefore important for both plastic LEDs and plastic solar cells. "In both cases, the electron current should not be hindered by charge trapping. With our results, more efficient designs can be made," Nicolai concluded.
INFORMATION:
The experimental work for this study was done in the Zernike Institute of Advanced Materials (ZIAM) at the faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, University of Groningen, the Netherlands. The theoretical work to identify the nature of the trap was carried out at the School of Chemistry and Biochemistry and Center for Organic Photonics and Electronics at the Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, USA .
The work at the University of Groningen was supported by the European Commission under contract FP7-13708 (AEVIOM). The work at Georgia Tech was supported by the MRSEC program of the National Science Foundation under award number DMR-0819885.
Citation: H. T. Nicolai1, M. Kuik1, G. A. H.Wetzelaer1, B. de Boer1, C. Campbell2, C. Risko2, J. L. Brédas2,4 and P.W. M. Blom1,3* Unification of trap-limited electron transport in semiconducting polymers. Nature Materials, published online: 29 July 2012 | DOI: 10.1038/NMAT3384
Technical Contacts: Herman Nicolai (hermannicolai@gmail.com) or Jean-Luc Bedas (jean-luc.bredas@chemistry.gatech.edu).
How to avoid traps in plastic electronics
2012-07-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Shared decision-making between doctors and patients can reduce antibiotic use
2012-07-30
A training tool that helps physicians involve patients in decision-making can reduce the use of antibiotics for acute respiratory infections, according to a study published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Antibiotics are prescribed too often for acute respiratory infections, even though many are not bacterial infections and therefore will not respond to antibiotic use. Overuse of antibiotics is a health concern and may be contributing to antibiotic resistance.
Researchers conducted a cluster randomized trial to determine the impact of a shared decision-making ...
Nurse staffing, burnout linked to hospital infections
2012-07-30
Washington, July 30, 2012 -- Nurse burnout leads to higher healthcare-associated infection rates (HAIs) and costs hospitals millions of additional dollars annually, according to a study published in the August issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
Researchers from the Center for Health Outcomes and Policy Research at the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing analyzed data previously collected by the Pennsylvania Health Care Cost Containment ...
Berkeley-Haas study identifies success factors of extraordinary CIOs
2012-07-30
University of California, Berkeley, Haas School of Business -- A just completed multi-year research project by the Fisher CIO Leadership Program at UC Berkeley's Haas School of Business has uncovered the most important, role specific career success factors of chief information officers.
The study was initiated by Max Hopper, the iconic author of American Airlines industry-changing SABRE system and conducted by the Fisher CIO Leadership Program. Hopper was concerned that so many companies were failing to achieve much if any benefit from their expensive IT organizations, ...
Fruit flies light the way for A*STAR scientists to pinpoint genetic changes that spell cancer
2012-07-30
By studying fruit flies, scientists at A*STAR's Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology (IMCB) have successfully devised a fast and cost-saving way to uncover genetic changes that have a higher potential to cause cancer. With this new approach, researchers will now be able to rapidly distinguish the range of genetic changes that are causally linked to cancer (i.e. "driver" mutations) versus those with limited impact on cancer progression. This research paves the way for doctors to design more targeted treatment against the different cancer types, based on the specific ...
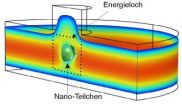
A giant step in a miniature world: UZH researcher measures the electrical charge of nano particles
2012-07-30
In order to observe the individual particles in a solution, Prof. Madhavi Krishnan and her co-workers «entice» each particle into an «electrostatic trap». It works like this: between two glass plates the size of a chip, the researchers create thousands of round energy holes. The trick is that these holes have just a weak electrostatic charge. The scientists than add a drop of the solution to the plates, whereupon each particle falls into an energy hole and remains trapped there. But the particles do not remain motionless in their trap. Instead, molecules in the solution ...
Archaeologists from Bonn discover in Mexico the tomb of a Maya prince
2012-07-30
Archaeologists from the Department of Anthropology of the Americas at the University of Bonn have been excavating for the past four years together with the Mexican National Institute of Anthropology and History in the Maya city of Uxul in Campeche, Mexico. The aim of the excavation project under the direction of Prof. Dr. Nikolai Grube and Dr. Kai Delvendahl is to investigate the process of centralization and collapse of hegemonic state structures in the Maya Lowlands using the example of a mid-sized classic Maya city (Uxul) and its ties to a supra-regional center (Calakmul). ...
Telling the tale of the wealth tail
2012-07-30
A mathematical physicist and her colleague, both from the Free University of Bozen-Bolzano, Italy, are about to publish a study in EPJ B¹ on a family of taxation and wealth redistribution models. The findings could lead to numerical simulations of potential wealth distribution scenarios playing out over the long term and could be used for policy decision making.
Maria Letizia Bertotti and Giovanni Modanese propose a mechanism of individual interaction of economic agents involved in wealth redistribution on a one-to-one level as a means of understanding their collective ...
Brain development is delayed in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
2012-07-30
Philadelphia, PA, July 30, 2012 – Is attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) due to a delay in brain development or the result of complete deviation from typical development? In the current issue of Biological Psychiatry, Dr. Philip Shaw and colleagues present evidence for delay based on a study by the National Institutes of Health.
The cerebral cortex is the folded gray tissue that makes up the outermost portion of the brain, covering the brain's inner structures. This tissue has left and right hemispheres and is divided into lobes. Each lobe performs specific ...
Archeologists unearth extraordinary human sculpture in Turkey
2012-07-30
A beautiful and colossal human sculpture is one of the latest cultural treasures unearthed by an international team at the Tayinat Archaeological Project (TAP) excavation site in southeastern Turkey. A large semi-circular column base, ornately decorated on one side, was also discovered. Both pieces are from a monumental gate complex that provided access to the upper citadel of Kunulua, capital of the Neo-Hittite Kingdom of Patina (ca. 1000-738 BC).
"These newly discovered Tayinat sculptures are the product of a vibrant local Neo-Hittite sculptural tradition," said Professor ...
In Massachusetts, 'individual mandate' led to decreased hospital productivity
2012-07-30
Philadelphia, Pa. (July 30, 2012) - As the "individual mandate" of the Affordable Care Act moves forward, debate and speculation continue as to whether universal health insurance coverage will lead to significant cost savings for hospitals. The assumption is that providing appropriate primary care will improve the overall health of the population, resulting in less need for hospital services and less severe illness among hospitalized patients. Findings from a recent study published in Health Care Management Review challenge that assumption. Health Care Management Review ...