(Press-News.org) An international team of mathematicians has proposed a new solution to understanding a biological puzzle that has confounded molecular biologists.
They have applied a mathematical model to work out the functioning of small molecules known as microRNAs – components of the body akin to the electronics in modern airplanes.
For a long time molecular biologists thought that the major role of RNA in living cells was to serve as a copy of a gene and a template for producing proteins, major cell building blocks. This belief had been changed at the end of 90s when it was found that myriads of RNA molecules are involved in regulating speeds of practically all molecular mechanisms in a cell. These abundant molecules are essential in regulating the speed of protein production– a vital function in bodily processes, including development, differentiation and cancer.
The problem to date has been that scientists have differed over interpretations of how the production of the major building blocks of a cell, proteins, is controlled by microRNAs.
Basically, there were different and sometimes conflicting theories about ways in which microRNAs regulate protein production since the results varied depending on only slightly changed experimental conditions.
Professor Alexander Gorban, who holds a Chair in Applied Mathematics at University of Leicester, said: "The old metaphor of an elephant and blind scientists trying to describe it will be always relevant to science. However, often we use it only as a metaphor, as a generic statement. In this project the elephant's metaphor can be applied literally as a working principle.
"Different biological labs or slightly changed experimental conditions meant that results were different for investigators.
"Quite dramatically, there has been a series of reports in top-ranked journals with contradictory results supporting one or another mechanism. Furthermore, researchers are puzzled by the fact that the same couple of protein and microRNA demonstrate different mechanisms of regulation in different biological labs or in slightly changed experimental conditions."
The mathematical model constructed by Professor Gorban from University of Leicester and Andrei Zinovyev from Institut Curie in Paris in collaboration with biologists Nadya Morozova and Annick Harel-Bellan from CNRS in France showed that there might be one simple mechanism which manifests itself differently in different conditions. Their findings are due to be published in the RNA Journal.
Professor Gorban said: "We have shown that what appeared to be very different mechanisms are in fact manifestations of one relatively simple biochemical reaction, but taking place in various contexts.
"Our model proposes that microRNA performs many actions simultaneously to the protein development, basically acting to get the job done (regulating the speed of protein production) in a stable and efficient way, given whatever conditions the experiment is occurring in.
"If this model is accepted, we would be able to take active steps in determining what the main mechanism of microRNA action is, as the model suggests experiments to verify the hypothesis. This in turn should lead to a resolution of a decade long debate to understand the means in which these very important molecules actually work."
Pat Heslop-Harrison, Professor of Cell Biology at the University of Leicester, said: "The discovery of miRNA and its regulatory role has completely changed our view of how genes in cells are controlled.
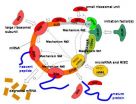
"Understanding all the ways the regulation is happening and interpreting experimental evidence has proved a huge challenge. In this important new paper, Alexander, Andrei, Nadya and colleagues overview the characteristic features of no less than nine different mechanisms, and then generate a unifying model of the whole system integrating the nine mechanisms.
"The multifunctional model gives dynamic predictions of gene control; it can now be tested to understand significance of the various mechanisms coexisiting under different conditions. It will be exciting to link this back the huge range of functions and responses of organisms and understanding miRNA control mechanisms is a systematic and predictive way."
INFORMATION:
The research is due to be published in RNA, Vol. 18, No. 9, September 1st, 2012. Published in Advance July 31, 2012, doi: 10.1261/rna.032284.112
Two relevant preprints are also available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1202.1243 , http://arxiv.org/abs/1204.5941. The general theory of the sensitive places ("dominant systems") of the complex reaction networks was developed recently by Gorban, Zinovyev and Radulescu (A. N. Gorban, O. Radulescu, A. Y. Zinovyev, Asymptotology of chemical reaction networks, Chemical Engineering Science 65 (2010) 2310).
Professor Gorban is Chair in Applied Mathematics, at University of
Leicester, UK and Chief Scientist (on leave), at the Institute of Computational
Modeling, Russian Academy of Sciences, Russia. He is best known for his work on physical and chemical kinetics and data analysis as well as more for his work on how humans adapt to hard living conditions.
NOTES TO EDITORS
Professor Gorban can be contacted on email: ag153@leicester.ac.uk
Background info:
Molecular biologists had previously thought that the major role of RNA in living cells is to serve as a copy of a gene and a template for producing proteins, the major cell building blocks. This belief was changed at the end of 90s when it was found that myriads of RNA molecules are involved in regulating speeds of practically all molecular mechanisms in cell.
In particular, it was found that there is a class of short RNA molecules which are actively involved in regulating the speed of protein production itself. Since these molecules are very short compared to others (their sequence contains only about 25 genetic "letters"), they were called microRNAs. Recent research showed that practically any protein production can be, and is, controlled by microRNAs. Some researchers say that the role of microRNAs in human cells can be compared to the role of electronics in the modern airplanes. The omnipresent involvement of microRNAs in regulating protein production makes cells of higher organisms more stable, more functional and more efficient compared to the microbes' cells where there are no microRNAs.
MicroRNAs rather slow down protein production than enhance it, but globally this allows more coordinated and equilibrated protein synthesis for various cell's purposes. How exactly microRNAs achieve protein production reduction was a subject of active scientific research for the last decade. Biologists have described nine distinct mechanisms of microRNA action which appeared to be very different one from another. This has led to a hot debate on what is the "main" mechanism of microRNA action?
Professor Gorban added: "MicroRNA's function is to reduce protein production. It seems that it does not matter for a cell how this is achieved, but it should be done stably and efficiently in various conditions. So evolution 'invented' a biochemical mechanism in which a microRNA acts simultaneously at many steps of protein production. But an observer sees only that effect of microRNA which affects the most sensitive place of a protein production in current condition and will completely ignore the others."
If this point of view is accepted by the scientific community, a very hot debate on "which mechanism of microRNA action is the most important?" will become more constructive and less speculative. The model suggests a series of new experiments in order to verify the unifying hypothesis. It advises to biologists which data should be collected to univocally identify the most "visible" (but not the most "important"!) mechanism of microRNA action in their experimental conditions.
Mathematicians find solution to biological building block puzzle
Theory resolves decade-old debate on regulation of protein production by microRNAs in cells
2012-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Low-cost carbon capture gets X-rayed
2012-07-31
Diamond Light Source is being used to improve low cost methods for carbon capture. Scientists from the University of Leeds are using the UK's national synchrotron to investigate the efficiency of calcium oxide (CaO) based materials as carbon dioxide (CO2) sorbents. Their results, published in the journal of Energy & Environmental Science, provide an explanation for one of the key mechanisms involved. This new knowledge will inform efforts to improve the efficiency of this economically viable method of carbon capture and storage.
Current techniques for post-combustion ...
From microns to centimetres
2012-07-31
TORONTO, Ontario (July 31, 2012)– UofT researchers Axel Guenther Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, cross-appointed to the Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering (IBBME), and Milica Radisic, Associate Professor at IBBME and the Department of Chemical Engineering and Applied Chemistry, along with graduate students from their labs—Lian Leng, Boyang Zhang, and Arianna McAllister—have invented a new device that may allow for the uniform, large-scale engineering of tissue.
"There's a lot of interest in soft materials, ...
Childhood obesity may affect timing of puberty, create problems with reproduction
2012-07-31
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A dramatic increase in childhood obesity in recent decades may have impacts that go beyond the usual health concerns – it could be disrupting the timing of puberty and ultimately lead to a diminished ability to reproduce, especially in females.
A body of research suggests that obesity could be related to growing problems with infertility, scientists said in a recent review, in addition to a host of other physical and psycho-social concerns. The analysis was published in Frontiers in Endocrinology.
Human bodies may be scrambling to adjust to a problem ...
Study of zebra fish mouth formation may speak to Fraser syndrome hearing loss
2012-07-31
EUGENE, Ore. -- (July 31, 2012) -- Using mutant zebra fish, researchers studying the earliest formation of cartilage of the mouth believe they may have gotten a look at a mechanism involved in a genetic defect linked to Fraser syndrome deafness in humans.
Reporting in the Aug. 1 issue of the journal Development, they identify a potential developmental pathway worthy of more scrutiny in future research into Fraser syndrome, a many-faceted and rare recessive genetic disease. In humans, a mutation in the gene FRAS1, which plays a role in skin epithelial formation during ...
Being paranoid about office politics can make you a target: UBC research
2012-07-31
People who worry about workplace rejection or sabotage can end up bringing it upon themselves, according to University of British Columbia research.
The UBC Sauder School of Business study reveals that paranoia about negative gossip or being snubbed leads people to seek out information to confirm their fears, ultimately annoying colleague and increasing the likelihood they will be rejected or subverted.
"It may be best to ignore impulses that tell you that you're the victim of office politics," says lead author and Sauder Prof. Karl Aquino, whose study was recently ...
Report: Captive lion reintroduction programs in Africa operate under 'conservation myth'
2012-07-31
New York, NY - A new report published in the international conservation journal Oryx concludes that commercial 'wildlife encounter' operations across Africa promoting the reintroduction of captive lions do little to further the conservation of African lions in the wild.
Released 'Early Online' on July 31, 'Walking with lions: Why there is no role for captive-origin lions (Panthera leo) in species restoration,' was authored by a blue-ribbon panel of lion conservationists and wild cat biologists from Panthera, the IUCN Cat Specialist Group and a team of university-based ...
Seniors with serious illness find smoking, drinking tough habits to break
2012-07-31
A recent study of adults age 50 to 85 found that only 19 percent of those diagnosed with lung disease quit smoking within two years. Furthermore, the research showed that the vast majority of older adults who learn they have a chronic condition do not adopt healthier behaviors, according to data presented in the Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences.
The statistics come from the Health and Retirement Study, an ongoing survey of over 11,000 Americans aged 50 or older that began in 1992. For the new journal article, a research team ...
Adaptiva and ProSource Solutions Partner to Deliver World-Class IT Solutions for Microsoft System Center 2012 Configuration Manager
2012-07-31
Adaptiva (http://www.adaptiva.com), an award-winning provider of IT systems management solutions and ProSource Solutions (http://prosurcesolutionsllc.com), a leading IT consulting services and solutions organization, today announced a strategic partnership that will further enhance Microsoft System Center 2012 Configuration Manager for enterprise clients. Through this agreement, ProSource Solutions will offer the Adaptiva IT Systems Management Software Suite as part of its' world-class IT core infrastructure, business productivity and application solution services.
"Adaptiva ...
Trauma Expert, Psychiatrist Richard P. Brown, Talks About Dissolving Psychic Pain on August 1
2012-07-31
Richard P. Brown, MD, a New York psychiatrist who practices integrative medicine, is the guest of Les Fehmi, PhD, and Susan Shor Fehmi, LCSW for an Open Focus Attention Teleseminar entitled "A Safe Harbor" from 1 to 2 p.m. EST, August 1, 2012. Dr. Brown will discuss how trauma and negative experiences can affect the brain and the stress response systems in the body.
Dr. Brown will discuss his experiences, his research, and the practice of Open Focus as they relate to integrative approaches for mental and physical wellness. "Anything worth doing is worth ...
Prominent Adviser Stephen Hogan Launches New Website for Broker Services
2012-07-31
The world of financial markets can be tough and confusing, with risks at every turn. Whether managing private wealth, or contemplating on exchange traded options, success in any financial situation can only be attained through sound, educated advice and guidance that will enable you to dodge the risks and reap the benefits. With Stephen Hogan, you can be assured of expert investment analysis, professional advice and other reliable broker services accessible through his new website, http://www.stephenhogan.com.au.
Stephen Hogan is an experienced client adviser who specialises ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
[Press-News.org] Mathematicians find solution to biological building block puzzleTheory resolves decade-old debate on regulation of protein production by microRNAs in cells