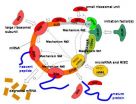
(Press-News.org) Brain-computer interfaces are at the cutting edge for treatment of neurological and psychological disorder, including Parkinson's, epilepsy, and depression. Among the most promising advance is deep brain stimulation (DBS) — a method in which a silicon chip implanted under the skin ejects high frequency currents that are transferred to the brain through implanted electrodes that transmit and receive the signals. These technologies require a seamless interaction between the brain and the hardware.
But there's a catch. Identified as foreign bodies by the immune system, the brain attacks the electrodes and forms a barrier to the brain tissue, making it impossible for the electrodes to communicate with brain activity. So while the initial implantation can diminish symptoms, after a few short years or even months, the efficacy of this therapy begins to wane.
Now Aryeh Taub of Tel Aviv University's School of Psychological Sciences, along with Prof. Matti Mintz, Roni Hogri and Ari Magal of TAU's School of Psychological Sciences and Prof. Yosi Shacham-Diamand of TAU's School of Electrical Engineering, has developed a bioactive coating which not only "camouflages" the electrodes in the brain tissue, but actively suppresses the brain's immune response. By using a protein called an "interleukin (IL)-1 receptor antagonist" to coat the electrodes, the multi-disciplinary team of researchers has found a potential resolution to turn a method for short-term relief into a long-term solution. This development was reported in the Journal of Biomedical Materials Research.
Limiting the immune response
To overcome the creation of the barrier between the tissue and the electrode, the researchers sought to develop a method for placing the electrode in the brain tissue while hiding the electrode from the brain's immune defenses. Previous research groups have coated the electrodes with various proteins, says Taub, but the TAU team decided to take a different approach by using a protein that is active within the brain itself, thereby suppressing the immune reaction against the electrodes.
In the brain, the IL-1 receptor antagonist is crucial for maintaining physical stability by localizing brain damage, Taub explains. For example, if a person is hit on the head, this protein works to create scarring in specific areas instead of allowing global brain scarring. In other words, it stops the immune system from overreacting. The team's coating, the first to be developed from this particular protein, not only integrates the electrodes into the brain tissue, but allows them to contribute to normal brain functioning.
In pre-clinical studies with animal models, the researchers found that their coated electrodes perform better than both non-coated and "naïve protein"-coated electrodes that had previously been examined. Measuring the number of damaged cells at the site of implantation, researchers found no apparent difference between the site of electrode implantation and healthy brain tissue elsewhere, Taub says. In addition, evidence suggests that the coated electrodes will be able to function for long periods of time, providing a more stable and long-term treatment option.
Restoring brain function
Approximately 30,000 people worldwide are currently using deep brain stimulation (DBS) to treat neurological or psychological conditions. And DBS is only the beginning. Taub believes that, in the future, an interface with the ability to restore behavioral or motor function lost due to tissue damage is achievable — especially with the help of their new electrode coating.
"We duplicate the function of brain tissue onto a silicon chip and transfer it back to the brain," Taub says, explaining that the electrodes will pick up brain waves and transfer these directly to the chip. "The chip then does the computation that would have been done in the damaged tissue, and feeds the information back into the brain — prompting functions that would have otherwise gotten lost."
###American Friends of Tel Aviv University (www.aftau.org) supports Israel's leading, most comprehensive and most sought-after center of higher learning. Independently ranked 94th among the world's top universities for the impact of its research, TAU's innovations and discoveries are cited more often by the global scientific community than all but 10 other universities.
Internationally recognized for the scope and groundbreaking nature of its research and scholarship, Tel Aviv University consistently produces work with profound implications for the future.
Protein-based coating could help rehabilitate long-term brain function
Tel Aviv University researchers develop bioactive coating to 'camouflage' neutral electrodes
2012-07-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can herbal products provide sun protection?
2012-07-31
New Rochelle, NY, July 31, 2012—Recent research supports the ability of some herbal agents, taken orally or applied topically, to prevent sunburn and limit the damage caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. Natural products with proven and promising photoprotective properties are highlighted in an article in Alternative and Complementary Therapies, published by Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Alternative and Complementary Therapies website at http://www.liebertpub.com/act.
The article "Herbal Sunscreens and Ultraviolet ...
Computational analysis identifies drugs to treat drug-resistant breast cancer
2012-07-31
HEIDELBERG, 31 July 2012 – Researchers have used computational analysis to identify a new Achilles heel for the treatment of drug-resistant breast cancer. The results, which are published in Molecular Systems Biology, reveal that the disruption of glucose metabolism is an effective therapeutic strategy for the treatment of tumours that have acquired resistance to front-line cancer drugs such as Lapatinib.
"The growth and survival of cancer cells can often be impaired by treatment with drugs that interfere with the actions of one or more oncogenes," said Prahlad Ram, the ...
Economic recession leads to increased entrepreneurship, MU study finds
2012-07-31
COLUMBIA, Mo. — The recent economic recession has caused many changes in the business landscape across the country, including high unemployment rates. Due to these high rates and the struggling economy, University of Missouri researchers have found that in recent years the number of Americans engaging in entrepreneurship has risen significantly. Maria Figueroa-Armijos, a doctoral candidate in the University of Missouri Truman School of Public Affairs, says that this trend could be positive for the future.
"We've seen similar trends occur in past economically slow periods ...
Chemistry on Mars video with Curiosity Rover from the American Chemical Society
2012-07-31
WASHINGTON, July 31, 2012 - After an epic 354-million-mile trek through space, the Mars Curiosity Rover is zooming along at 13,000 miles per hour toward a scheduled August 6 landing on the Red Planet to search for evidence of extraterrestrial life. The newest episode of the American Chemical Society's (ACS') award-winning Bytesize Science video series highlights Curiosity Rover's mission, scientific instrumentation and the role that chemistry plays in the search for life on other planets. The video, produced by the ACS Office of Public Affairs, is available at www.BytesizeScience.com. ...
Adding a '3D print' button to animation software
2012-07-31
Cambridge, Mass. - July 31, 2012 - Watch out, Barbie: omnivorous beasts are assembling in a 3D printer near you.
A group of graphics experts led by computer scientists at Harvard have created an add-on software tool that translates video game characters -- or any other three-dimensional animations -- into fully articulated action figures, with the help of a 3D printer.
The project is described in detail in the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Transactions on Graphics and will be presented at the ACM SIGGRAPH conference on August 7.
Besides its obvious consumer ...
Camouflage of moths: Secrets to invisibility revealed
2012-07-31
Moths are iconic examples of camouflage. Their wing coloration and patterns are shaped by natural selection to match the patterns of natural substrates, such as a tree bark or leaves, on which the moths rest. But, according to recent findings, the match in the appearance was not all in their invisibility.
Despite a long history of research on these iconic insects, whether moths behave in a way to increase their invisibility has not been determined. A research team from the Laboratory of Behavioral Ecology and Evolution at the Seoul National University has conducted an ...
Critically endangered whales sing like birds; New recordings hint at rebound
2012-07-31
When a University of Washington researcher listened to the audio picked up by a recording device that spent a year in the icy waters off the east coast of Greenland, she was stunned at what she heard: whales singing a remarkable variety of songs nearly constantly for five wintertime months.
Kate Stafford, an oceanographer with UW's Applied Physics Lab, set out to find if any endangered bowhead whales passed through the Fram Strait, an inhospitable, ice-covered stretch of sea between Greenland and the northern islands of Norway. Only around 40 sightings of bowhead whales, ...
Mathematicians find solution to biological building block puzzle
2012-07-31
An international team of mathematicians has proposed a new solution to understanding a biological puzzle that has confounded molecular biologists.
They have applied a mathematical model to work out the functioning of small molecules known as microRNAs – components of the body akin to the electronics in modern airplanes.
For a long time molecular biologists thought that the major role of RNA in living cells was to serve as a copy of a gene and a template for producing proteins, major cell building blocks. This belief had been changed at the end of 90s when it was found ...
Low-cost carbon capture gets X-rayed
2012-07-31
Diamond Light Source is being used to improve low cost methods for carbon capture. Scientists from the University of Leeds are using the UK's national synchrotron to investigate the efficiency of calcium oxide (CaO) based materials as carbon dioxide (CO2) sorbents. Their results, published in the journal of Energy & Environmental Science, provide an explanation for one of the key mechanisms involved. This new knowledge will inform efforts to improve the efficiency of this economically viable method of carbon capture and storage.
Current techniques for post-combustion ...
From microns to centimetres
2012-07-31
TORONTO, Ontario (July 31, 2012)– UofT researchers Axel Guenther Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, cross-appointed to the Institute of Biomaterials and Biomedical Engineering (IBBME), and Milica Radisic, Associate Professor at IBBME and the Department of Chemical Engineering and Applied Chemistry, along with graduate students from their labs—Lian Leng, Boyang Zhang, and Arianna McAllister—have invented a new device that may allow for the uniform, large-scale engineering of tissue.
"There's a lot of interest in soft materials, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
[Press-News.org] Protein-based coating could help rehabilitate long-term brain functionTel Aviv University researchers develop bioactive coating to 'camouflage' neutral electrodes