Stem cell therapy could offer new hope for defects and injuries to head, mouth
2012-07-31
(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich.—In the first human study of its kind, researchers found that using stem cells to re-grow craniofacial tissues—mainly bone—proved quicker, more effective and less invasive than traditional bone regeneration treatments.
Researchers from the University of Michigan School of Dentistry and the Michigan Center for Oral Health Research partnered with Ann Arbor-based Aastrom Biosciences Inc. in the clinical trial, which involved 24 patients who required jawbone reconstruction after tooth removal.
Patients either received experimental tissue repair cells or traditional guided bone regeneration therapy. The tissue repair cells, called ixmyelocel-T, are under development at Aastrom, which is a U-M spinout company.
"In patients with jawbone deficiencies who also have missing teeth, it is very difficult to replace the missing teeth so that they look and function naturally," said Darnell Kaigler, principal investigator and assistant professor at the U-M School of Dentistry. "This technology and approach could potentially be used to restore areas of bone loss so that missing teeth can be replaced with dental implants."
William Giannobile, director of the Michigan Center for Oral Health Research and chair of the U-M Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine, is co-principal investigator on the project.
The treatment is best suited for large defects such as those resulting from trauma, diseases or birth defects, Kaigler said. These defects are very complex because they involve several different tissue types—bone, skin, gum tissue—and are very challenging to treat.
The main advantage to the stem cell therapy is that it uses the patient's own cells to regenerate tissues, rather than introducing man-made, foreign materials, Kaigler said.
The results were promising. At six and 12 weeks following the experimental cell therapy treatment, patients in the study received dental implants. Patients who received tissue repair cells had greater bone density and quicker bone repair than those who received traditional guided bone regeneration therapy.
In addition, the experimental group needed less secondary bone grafting when getting their implants.
The cells used for the therapy were originally extracted from bone marrow taken from the patient's hip. The bone marrow was processed using Aastrom's proprietary system, which allows many different cells to grow, including stem cells. These stem cells were then placed in different areas of the mouth and jaw.
Stem cell therapies are still probably 5-10 years away from being used regularly to treat oral and facial injuries and defects, Kaigler said. The next step is to perform more clinical trials that involve larger craniofacial defects in a larger number of patients.
INFORMATION: The study, "Stem cell therapy for craniofacial bone repair: A randomized, controlled clinical trial," appears this month in the journal Cell Transplantation.
Darnell Kaigler:
www.dent.umich.edu/pom/faculty/links/dkbio
William Giannobile:
www.dent.umich.edu/pom/faculty/links/wgbio
Aastrom Biosciences:
www.aastrom.com
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-07-31
Parents concerned about their children's slothful ways can do something about it, according to research at National Jewish Health. They can increase their own activity. In the July 2012 issue of the Journal of Physical Activity and Health, Kristen Holm, PhD, Assistant Professor of Medicine at National Jewish Health, and her colleagues report that, when parents increase their daily activity, as measured by a pedometer, their children increase theirs as well.
"It has long been known that parent and child activity levels are correlated," said Dr. Holm. "This is the first ...
2012-07-31
Irvine, Calif., July 30, 2012 – UC Irvine scientists have discovered intriguing differences in the brains and mental processes of an extraordinary group of people who can effortlessly recall every moment of their lives since about age 10.
The phenomenon of highly superior autobiographical memory – first documented in 2006 by UCI neurobiologist James McGaugh and colleagues in a woman identified as "AJ" – has been profiled on CBS's "60 Minutes" and in hundreds of other media outlets. But a new paper in the peer-reviewed journal Neurobiology of Learning & Memory's July issue ...
2012-07-31
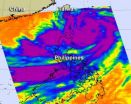
Typhoon Saola looks like a monster tropical cyclone in infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite today, July 30. Although Saola's center is over 300 nautical miles (368 miles/592 km) south-southeast of Taiwan, it stretches over the north and central Philippines and has triggered a number of warnings throughout the country.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured an image of Typhoon Saola approaching Taiwan on July 30 at 0215 UTC (July 29 at 10:15 p.m. EDT). The image showed a ragged eye in the storm's center ...
2012-07-31
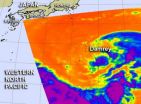
Tropical Storm Damrey appears to be a compact tropical storm on NASA satellite imagery as it heads west. It is expected to pass north of Iwo To, Japan and later south of Kyushu, one of Japan's large islands.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Damrey on July 30 at 03:21 UTC (July 29 at 11:21 p.m. EDT) and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the storm. It showed that strong, high, cold cloud tops of thunderstorms were in a tight circle around the center of circulation. There were bands of thunderstorms mostly north ...
2012-07-31
Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center researchers have identified how one of the genes most commonly mutated in lung cancer may promote such tumors.
The investigators found that the protein encoded by this gene, called EPHA3, normally inhibits tumor formation, and that loss or mutation of the gene – as often happens in lung cancer – diminishes this tumor-suppressive effect, potentially sparking the formation of lung cancer. The findings, published July 24 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, could offer direction for personalizing cancer treatments and development ...
2012-07-31
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Sandia National Laboratories' wind energy researchers are re-evaluating vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs) to help solve some of the problems of generating energy from offshore breezes.
Though VAWTs have been around since the earliest days of wind energy research at Sandia and elsewhere, VAWT architecture could transform offshore wind technology.
The economics of offshore windpower are different from land-based turbines, due to installation and operational challenges. VAWTs offer three big advantages that could reduce the cost of wind energy: a ...
2012-07-31
Montreal, July 30, 2012 – Rows of chip bags in a vending machine, endless bottles of shampoo on pharmacy shelves, long lines of books arranged in the bestsellers section at the bookstore. From supermarket shelves to barroom beer selection, long lines of horizontally arranged products are the norm when it comes to the shopping experience.
But how does where a product is placed on the storeroom shelf influence which option a consumer will ultimately choose? It turns out that the shopper's eye has a very central focus.
"Consumers are more likely to purchase products ...
2012-07-31
Scientists at the University of Liverpool have discovered that variations in the long-term reversal rate of the Earth's magnetic field may be caused by changes in heat flow from the Earth's core into the base of the overlying mantle.
The Earth is made up of a solid inner core, surrounded by a liquid outer core, in turn covered by a thicker or more viscous mantle, and ultimately by the solid crust beneath our feet. The magnetic field is generated by the motions of the liquid iron alloy in the outer core, approximately 3,000 km beneath the Earth's crust. These motions ...
2012-07-31
WASHINGTON, DC, July 25, 2012 — Policies that reward abstinence from terrorism are more successful in reducing such acts of violence than tactics that aim to punish terrorists, suggests a new study in the August issue of the American Sociological Review.
Titled, "Moving Beyond Deterrence: The Effectiveness of Raising the Expected Utility of Abstaining from Terrorism in Israel," the study looked specifically at the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and found that between 1987 and 2004, Israeli policies and actions that encouraged and rewarded refrain from terrorist acts were ...
2012-07-31
A new strain of influenza virus found in harbor seals could represent a threat to wildlife and human health, according to the authors of a study appearing July 31 in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology. It is crucial to monitor viruses like this one, which originated in birds and adapted to infect mammals, the authors say, so that scientists can better predict the emergence of new strains of influenza and prevent pandemics in the future.
"There is a concern that we have a new mammalian-transmissible virus to which humans haven't ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Stem cell therapy could offer new hope for defects and injuries to head, mouth