(Press-News.org) ZURICH — Though sophisticated three-dimensional imagery is abundant in computer-generated games and movies, a group of researchers from Disney Research, Zürich, University of California, San Diego, Limbic Software, and RWTH Aachen University say they have gained insights to improve the rendering of those images by envisioning a flat, two-dimensional world.
The fundamental physics of light is easier to understand in that 2D world than in a 3D environment, they said, and enabled them to develop simplified equations for governing the behavior of light. This in turn allowed the team of researchers to find practical improvements to 3D photorealistic rendering techniques which improved their speed and quality.
"Rendering techniques have become so incredibly sophisticated and complex that skilled artists can now easily create photorealistic depictions of synthetic worlds and are limited only by their imaginations," said Dr. Wojciech Jarosz, research scientist at Disney Research, Zürich and coauthor of the work. Ultimately, all of these rendering techniques simulate how light would bounce around in a virtual environment. This physical lighting simulation is what allows these computer-generated images to look so convincingly photorealistic. "Unfortunately, these methods can often be incredibly slow, taking hours to simulate a single frame of a movie, and the physical processes they try to mimic are incredibly complex," he added.
This increased complexity not only limits artists, but hampers researchers such as Jarosz who pursue improved approaches and can make it more difficult to discuss and teach the underlying concepts. To address this ever increasing complexity, the team of researchers decided to go back to basics. They imagined how light would behave in a fictional two-dimensional world to avoid dealing with the harsh complexities of how light behaves in our physical 3D world.
"It turns out that we can define a 2D world where light behaves much the same way as it does in our 3D reality — however, all the fundamental equations governing the physics of light become significantly simpler," Jarosz explained. This seemingly frivolous exercise actually provides tangible benefits for developing better 3D rendering techniques. All the common rendering techniques can be analyzed in this simplified 2D setting and their weaknesses and strengths can be more easily discovered.
In addition to improving 3D rendering techniques, Jarosz, who is also an adjunct lecturer at ETH, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, speculates that the simplified view of the physics of light could also serve as a good teaching tool within computer graphics curricula at universities.
These ideas will be presented Aug. 7 in the "Sampling, Reconstructing, and Filtering Light" session at SIGGRAPH 2012, the International Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques at the Los Angeles Convention Center. For a copy of the research paper, please visit the project website at http://zurich.disneyresearch.com/~wjarosz/publications/jarosz12theory.html.
INFORMATION:
About Disney Research
Disney Research is a network of research laboratories supporting The Walt Disney Company. Its purpose is to pursue scientific and technological innovation to advance the company's broad media and entertainment efforts. Disney Research is managed by an internal Disney Research Council co-chaired by Disney-Pixar's Ed Catmull and Walt Disney Imagineering's Bruce Vaughn, and including the directors of the individual labs. It has facilities in Los Angeles, San Francisco, Pittsburgh, Boston and Zurich. Research topics include computer graphics, video processing, computer vision, robotics, radio and antennas, wireless communications, human-computer interaction, displays, data mining, machine learning and behavioral sciences.
END
VIDEO:
An animation of satellite observations shows the progression of Tropical Storm Ernesto from Aug. 4-6, 2012. The animation begins when Ernesto was south of Jamaica and ends when the storm...
Click here for more information.
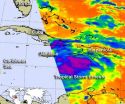
Tropical Storm Ernesto continues to track through the Caribbean and satellite data and NOAA hurricane hunter aircraft revealed a strengthening storm mid-day on Monday, August 6. NASA infrared data revealed strong thunderstorms on August 5 that ...
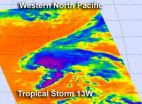
When NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared view of the northwestern Pacific's latest tropical storm, Tropical Storm 13W, the data revealed the bulk of the heavy rainfall on the northern side of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 13W on August 6 at 0205 UTC (Aug. 5 10:05 a.m. EDT). The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms (purple) and heaviest rainfall north and east of the center of circulation.
Infrared imagery shows temperature and the higher ...
Microbes, sponges, and worms—the side effects of pollution and heavy fishing—are adding insult to injury in Kenya's imperiled reef systems, according to a recent study by the Wildlife Conservation Society and the University of Azores.
The authors of the study have found that pollution and overfishing on reef systems have an ecological cascading effect—the proliferation of microbes, sponges, and worms—that further degrade corals, a discovery that underlines the complexity of reefs and possible solutions.
The study appears in the online edition of Marine Ecology Progress ...
The sixth tropical storm of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season formed over the past weekend, and NASA kept an on its progression. Tropical Storm Florence was born in the eastern Atlantic and weakened when it interacted with dry air.
On Friday, August 3, the low pressure area known as "System 90L" was being watched for development. It was located south of the Cape Verde Islands off the African coast. By the early evening (Eastern Daylight Time) it quickly organized. System 90L strengthened and became Tropical Storm Florence in the eastern Atlantic. Over August 4 and 5 ...
ZURICH — Scientists have yet to fully unravel the mysteries of rainbows, but a group of researchers from Disney Research, Zürich, UC San Diego, Universidad de Zaragoza, and Horley, UK, have used simulations of these natural wonders to unlock the secret to a rare optical phenomenon known as the twinned rainbow.
Unlike the more common double-rainbow, which consists of two separate and concentric rainbow arcs, the elusive twinned rainbow appears as two rainbows arcs that split from a single base rainbow. Sometimes it is even observed in combination with a double rainbow. ...
"Pants on fire" isn't the only problem liars face. New research from the University of Notre Dame shows that when people managed to reduce their lies in given weeks across a 10-week study, they reported significantly improved physical and mental health in those same weeks.
Funded by a grant from the John Templeton Foundation, the "Science of Honesty" study was presented recently at the American Psychological Association's 120th annual convention.
"We found that the participants could purposefully and dramatically reduce their everyday lies, and that in turn was associated ...
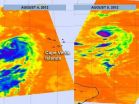
Two NASA satellites have captured data on the activity of Typhoon Haikui as it nears the China coast. NASA's Terra satellite provided a visible look at the storm, while NASA's Aqua satellite investigated it in infrared light. Both showed some strong thunderstorms within that were likely packing heavy rainfall.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Haikui on August 5. The AIRS instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms and heaviest rainfall in all quadrants of the storm except the northern area. The strongest storms ...
ZURICH – Computer graphic artists often struggle to render smoke and dust in a way that makes a scene look realistic, but researchers at Disney Research, Zürich, Karlsruhe Technical Institute in Germany, and the University of Montreal in Canada have developed a new and efficient way to simulate how light is absorbed and scattered in such scenes.
"Our technique could be used to simulate anything from vast cloudscapes, to everyday 'solid' objects such as a glass of orange juice, a piece of fruit or virtually any organic substance," said Dr. Wojciech Jarosz of Disney Research ...
Leslie Henderson is concerned about steroid abuse, not necessarily by sports luminaries like Barry Bonds and Mark McGwire, but rather by adolescents.
"There is this disconnect among young people that somehow your emotions, your thought processes—things that have to do with your brain—are separate and different from what steroids may be doing to your body—your muscles, your heart, or your liver, or anything like that," says Henderson, a professor of physiology and neurobiology, and of biochemistry at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth. She is also the senior associate ...
MAYWOOD, Il. -- When a patient undergoes a cardiac catheterization procedure such as a balloon angioplasty, there's a slight risk of a stroke or other neurological complication.
While the risk is extremely small, neurologists nevertheless may expect to see catheterization-induced complications because so many procedures are performed, Loyola neurologists write in the journal MedLink Neurology.
Cardiac catheterizations include diagnostic angiograms, balloon angioplasties and stent placements. More than 1.4 million procedures are successfully performed each year. Cardiac ...