Investing in quality of care for diabetic patients reduces costs
2012-08-07
(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS (August 6, 2012) – University of Minnesota School of Public Health researchers have found that medical group practices can reduce costs for patients with diabetes by investing in improved quality of care.
In the study, which appears in the August issue of Health Affairs, University of Minnesota researchers analyzed 234 medical group practices providing care for more than 133,000 diabetic patients. After developing a "quality of care" score based on select patient care initiatives, researchers found that medical providers saved an average of $51 in health care costs per diabetic patient for every one-percentage-point increase in their quality of care score.
"Our research should be reassuring for physicians who are joining (or forming) value-based Accountable Care Organizations," said the study's lead author John E. Kralewski, senior research fellow at the Medica Research Institute and professor emeritus at the University of Minnesota School of Public Health. "Our data show that they can provide high quality care while meeting the cost savings expectations of ACOs. Moreover, our study supports the contention that health care reform initiatives can reduce costs without eroding quality of care. Our data indicate that higher quality is one way to reduce costs."
According to researchers, near-term cost savings resulted, in part, from decreased inappropriate emergency department use and decreased avoidable hospital admissions, such as cholesterol screenings.
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Health Care Financing and Organization Program.
About the School of Public Health
For more than 60 years, the University of Minnesota School of Public Health has been among the top accredited schools of public health in the nation. With a mission focused on research, teaching, and service, the school attracts nearly $100 million in sponsored research each year, has more than 100 faculty members and more than 1,300 students, and is engaged in community outreach activities locally, nationally and in dozens of countries worldwide. For more information, visit www.sph.umn.edu. The School's Centers for Public Health Education and Outreach promotes lifelong learning to bridge academic and public health practice communities.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-08-07
In a large epidemiologic study, researchers at UCLA's Jonsson Cancer Center found that the children of U.S.-born Latina women are at higher risk of having retinoblastoma, a malignant tumor of the retina which typically occurs in children under six.
The study, which focused on babies born in California, also found that offspring of older fathers were at greater risk for retinoblastoma, as were children born to women with sexually transmitted diseases and those born in multiple births, which may indicate an increased risk from in vitro fertilization. Those findings confirmed ...
2012-08-07
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Most people think of seafood as either wild or farmed, but in fact both categories may apply to the fish you pick up from your grocery store. In recent years, for example, as much as 40 percent of the Alaskan salmon catch originated in fish hatcheries, although it may be labeled "all wild, never farmed."
An article produced by a working group of UC Santa Barbara's National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis (NCEAS) recommends that when a combination of seafood production techniques are used, this be acknowledged in the marketplace. ...
2012-08-07
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Young children who are able to pay attention and persist on a task have a 50 percent greater chance of completing college, according to a new study at Oregon State University.
Tracking a group of 430 preschool-age children, the study gives compelling evidence that social and behavioral skills, such as paying attention, following directions and completing a task may be even more crucial than academic abilities.
And the good news for parents and educators, the researchers said, is that attention and persistence skills are malleable and can be taught.
The ...
2012-08-07
Despite a twenty-five year old law that bans "patient dumping" the practice continues to put uninsured Americans at risk, according to a national team of researchers led by a professor at the George Washington School of Public Health and Health Services. Patient dumping is the practice of turning away or transferring uninsured patients with emergency medical conditions.
The study, which appears in the August issue of Health Affairs, suggests that hospitals still practice "patient dumping" which is in violation of the law. The researchers investigate and present five ...
2012-08-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A study from University of Illinois economics professors demonstrates a new method to analyze the relationships among voters' issue preferences, the candidates' policy positions and voter behavior.
Estimating the distribution of voter preferences and the extent of policy divergence between the candidates' platforms, economics professors Stefan Krasa and Mattias Polborn are able to separate observed changes in voter behavior into those driven by voter radicalization versus those caused by increased policy differences between the two parties.
"We have ...
2012-08-07
Health coverage for the poorest Americans could be in jeopardy in many states as a result of the U.S. Supreme Court's ruling last month on the Affordable Care Act, according to a new legal analysis. The report examines federal and state Medicaid options following the United States Supreme Court's ruling in NFIB v Sebelius and appears in the August issue of the journal Health Affairs.
"Some states will use the court's decision as an excuse to delay or refuse to participate in the expansion of Medicaid as outlined in the Affordable Care Act," says lead author of the report, ...
2012-08-07
URBANA – The trade in ivory was largely outlawed in 1989, but poaching continues and remains a serious threat to the African elephant. Seizures of large amounts of ivory, sometimes over a ton, continue to occur. Research by Alfred Roca, an assistant professor at the university, could be the basis for the development of new law enforcement tools.
Roca has found a way to determine where the ivory comes from. With funding from the Division of International Conservation of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, he and his collaborators have sampled elephants at 22 locations ...
2012-08-07
ZURICH — Though sophisticated three-dimensional imagery is abundant in computer-generated games and movies, a group of researchers from Disney Research, Zürich, University of California, San Diego, Limbic Software, and RWTH Aachen University say they have gained insights to improve the rendering of those images by envisioning a flat, two-dimensional world.
The fundamental physics of light is easier to understand in that 2D world than in a 3D environment, they said, and enabled them to develop simplified equations for governing the behavior of light. This in turn allowed ...
2012-08-07
VIDEO:
An animation of satellite observations shows the progression of Tropical Storm Ernesto from Aug. 4-6, 2012. The animation begins when Ernesto was south of Jamaica and ends when the storm...
Click here for more information.
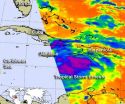
Tropical Storm Ernesto continues to track through the Caribbean and satellite data and NOAA hurricane hunter aircraft revealed a strengthening storm mid-day on Monday, August 6. NASA infrared data revealed strong thunderstorms on August 5 that ...
2012-08-07
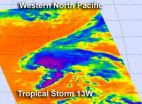
When NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared view of the northwestern Pacific's latest tropical storm, Tropical Storm 13W, the data revealed the bulk of the heavy rainfall on the northern side of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 13W on August 6 at 0205 UTC (Aug. 5 10:05 a.m. EDT). The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms (purple) and heaviest rainfall north and east of the center of circulation.
Infrared imagery shows temperature and the higher ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Investing in quality of care for diabetic patients reduces costs