(Press-News.org) Health coverage for the poorest Americans could be in jeopardy in many states as a result of the U.S. Supreme Court's ruling last month on the Affordable Care Act, according to a new legal analysis. The report examines federal and state Medicaid options following the United States Supreme Court's ruling in NFIB v Sebelius and appears in the August issue of the journal Health Affairs.
"Some states will use the court's decision as an excuse to delay or refuse to participate in the expansion of Medicaid as outlined in the Affordable Care Act," says lead author of the report, Sara Rosenbaum, Harold and Jane Hirsh Professor of Health Law and Policy, George Washington University School of Public Health and Health Services in Washington, D.C. "The ruling allows states to decline the expansion yet still continue to collect federal funding to operate a status quo Medicaid program, leaving millions of impoverished children and adults at risk for lack of coverage."
At the same time, the expansion would create new jobs as federal funding to pay for health care begins to flow into poor communities. Between 2014 and 2016 the federal government will pay for 100 percent of the cost of the Medicaid expansion and 90 percent of the costs by 2020 and thereafter. That influx of federal funds would represent a much-needed boost to thousands of communities affected by poverty, elevated unemployment and other signs of economic distress, according to the analysis.
In the end, the economic benefits of going forward might sway states that have been opposed to the expansion in the past. And the analysis notes that states that still balk may face considerable political opposition and an outpouring of concern from consumers, insurers, local governments, and health care providers. States that still refuse to set up the expansion will have to explain why they are turning away a "boatload of federal funds designed to cure Medicaid's greatest flaw," Rosenbaum said.
Since 1965 Medicaid has provided coverage for poor children and pregnant women, as well as low income people who are elderly or disabled. At the same time, the program has excluded millions of adults who are deeply impoverished. The Affordable Care Act, signed into law by President Obama in 2010, addressed this historic coverage gap by extending Medicaid to all nonelderly Americans whose incomes are below 133 percent of poverty.
But states immediately objected to the Medicaid requirement, and ultimately 26 sued, claiming that the expansion was unconstitutional. The Supreme Court upheld the Medicaid expansion in its June ruling but at the same time sharply limited the federal government's ability to enforce that provision. The Court's ruling means that states can opt out of the Medicaid expansion without running the risk that they will lose all Medicaid funding.
At the same time, the Supreme Court decision does not give the federal government complete power to allow states to set up a partial expansion of Medicaid. Some states have already indicated they favor a modified expansion of Medicaid but it is not clear that the court ruling will allow such flexibility on the part of the federal government.
Still, many states appear ready to take advantage of the economic benefits associated with a full-scale Medicaid expansion, Rosenbaum noted. Particularly important, she stated, is the fact that the Supreme Court decision preserved the expansion itself for states that decide to move ahead quickly. Had the Court not preserved that aspect of the law, the largest single expansion of Medicaid would have been lost.
"The potential financial value of the Medicaid expansion to states is enormous," Rosenbaum said. The enhanced federal funding that comes along with implementation is crucial to the survival of public hospitals, community health centers, and other safety net providers that often represent the provider of last resort for millions of uninsured Americans. The expansion in Medicaid, if fully implemented, would significantly reduce the burden of uncompensated care, said the analysis.
INFORMATION:
To view this report: http://content.healthaffairs.org/content/31/8/1663.abstract
About the George Washington University School of Public Health and Health Services:
Established in July 1997, the School of Public Health and Health Services brought together three longstanding university programs in the schools of medicine, business, and education that we have since expanded substantially. Today, more than 1,100 students from nearly every U.S. state and more than 40 nations pursue undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral-level degrees in public health. Our student body is one of the most ethnically diverse among the nation's private schools of public health. http://sphhs.gwumc.edu/
END
URBANA – The trade in ivory was largely outlawed in 1989, but poaching continues and remains a serious threat to the African elephant. Seizures of large amounts of ivory, sometimes over a ton, continue to occur. Research by Alfred Roca, an assistant professor at the university, could be the basis for the development of new law enforcement tools.
Roca has found a way to determine where the ivory comes from. With funding from the Division of International Conservation of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, he and his collaborators have sampled elephants at 22 locations ...
ZURICH — Though sophisticated three-dimensional imagery is abundant in computer-generated games and movies, a group of researchers from Disney Research, Zürich, University of California, San Diego, Limbic Software, and RWTH Aachen University say they have gained insights to improve the rendering of those images by envisioning a flat, two-dimensional world.
The fundamental physics of light is easier to understand in that 2D world than in a 3D environment, they said, and enabled them to develop simplified equations for governing the behavior of light. This in turn allowed ...
VIDEO:
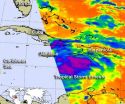
An animation of satellite observations shows the progression of Tropical Storm Ernesto from Aug. 4-6, 2012. The animation begins when Ernesto was south of Jamaica and ends when the storm...
Click here for more information.
Tropical Storm Ernesto continues to track through the Caribbean and satellite data and NOAA hurricane hunter aircraft revealed a strengthening storm mid-day on Monday, August 6. NASA infrared data revealed strong thunderstorms on August 5 that ...
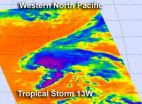
When NASA's Aqua satellite captured an infrared view of the northwestern Pacific's latest tropical storm, Tropical Storm 13W, the data revealed the bulk of the heavy rainfall on the northern side of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm 13W on August 6 at 0205 UTC (Aug. 5 10:05 a.m. EDT). The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms (purple) and heaviest rainfall north and east of the center of circulation.
Infrared imagery shows temperature and the higher ...
Microbes, sponges, and worms—the side effects of pollution and heavy fishing—are adding insult to injury in Kenya's imperiled reef systems, according to a recent study by the Wildlife Conservation Society and the University of Azores.
The authors of the study have found that pollution and overfishing on reef systems have an ecological cascading effect—the proliferation of microbes, sponges, and worms—that further degrade corals, a discovery that underlines the complexity of reefs and possible solutions.
The study appears in the online edition of Marine Ecology Progress ...
The sixth tropical storm of the Atlantic Ocean hurricane season formed over the past weekend, and NASA kept an on its progression. Tropical Storm Florence was born in the eastern Atlantic and weakened when it interacted with dry air.
On Friday, August 3, the low pressure area known as "System 90L" was being watched for development. It was located south of the Cape Verde Islands off the African coast. By the early evening (Eastern Daylight Time) it quickly organized. System 90L strengthened and became Tropical Storm Florence in the eastern Atlantic. Over August 4 and 5 ...
ZURICH — Scientists have yet to fully unravel the mysteries of rainbows, but a group of researchers from Disney Research, Zürich, UC San Diego, Universidad de Zaragoza, and Horley, UK, have used simulations of these natural wonders to unlock the secret to a rare optical phenomenon known as the twinned rainbow.
Unlike the more common double-rainbow, which consists of two separate and concentric rainbow arcs, the elusive twinned rainbow appears as two rainbows arcs that split from a single base rainbow. Sometimes it is even observed in combination with a double rainbow. ...
"Pants on fire" isn't the only problem liars face. New research from the University of Notre Dame shows that when people managed to reduce their lies in given weeks across a 10-week study, they reported significantly improved physical and mental health in those same weeks.
Funded by a grant from the John Templeton Foundation, the "Science of Honesty" study was presented recently at the American Psychological Association's 120th annual convention.
"We found that the participants could purposefully and dramatically reduce their everyday lies, and that in turn was associated ...
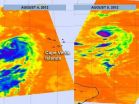
Two NASA satellites have captured data on the activity of Typhoon Haikui as it nears the China coast. NASA's Terra satellite provided a visible look at the storm, while NASA's Aqua satellite investigated it in infrared light. Both showed some strong thunderstorms within that were likely packing heavy rainfall.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Typhoon Haikui on August 5. The AIRS instrument captured an infrared image of the cloud temperatures that showed the strongest storms and heaviest rainfall in all quadrants of the storm except the northern area. The strongest storms ...
ZURICH – Computer graphic artists often struggle to render smoke and dust in a way that makes a scene look realistic, but researchers at Disney Research, Zürich, Karlsruhe Technical Institute in Germany, and the University of Montreal in Canada have developed a new and efficient way to simulate how light is absorbed and scattered in such scenes.
"Our technique could be used to simulate anything from vast cloudscapes, to everyday 'solid' objects such as a glass of orange juice, a piece of fruit or virtually any organic substance," said Dr. Wojciech Jarosz of Disney Research ...