(Press-News.org) In the United States, clinicians are struggling to provide better and more affordable health care to more people—while keeping up with new scientific developments. The idea of a "learning health system" is one proposed solution for rapidly applying the best available scientific evidence in real-time clinical practice. In the August 7 Annals of Internal Medicine, a Group Health Cooperative team describes the experience of turning this intriguing concept into action.
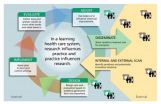
"In a learning health system, evidence and practice come together in a virtuous cycle, influencing each other," first author Sarah M. Greene, MPH, said. "At Group Health, we strive to translate evidence into practice and policy quickly. At the same time, we try to align our research with the questions that clinicians and administrators need to answer ASAP."
Ms. Greene is a director of strategy and business development at Group Health, a nonprofit health system that provides care and coverage in Washington state. She is also an affiliate investigator at Group Health's research arm, Group Health Research Institute. Her coauthors were Robert J. Reid, MD, PhD; Group Health's associate medical director for research translation and an associate investigator at Group Health Research Institute; and Eric B. Larson, MD, MPH, Group Health's vice president for research and Group Health Research Institute's executive director.
"Researchers and clinicians are realizing that innovation is not enough to fix the nation's health care system," Dr. Larson said. "We need to move innovations immediately into real-world health care settings, and learning health systems are a way to do this."
Strong leadership support and a growing partnership between research and clinical operations have made it possible for Group Health to evolve as a learning health system, Ms. Greene explained. This partnership has fostered a culture and an infrastructure to facilitate rapid learning.
"Ongoing communication, engagement, and flexibility are essential," Dr. Reid said. "The learning system always asks, 'how can we keep improving?'"
This shared ongoing commitment to leverage scientific knowledge and evaluate changes in real time for rapid, point-of-care improvements has enabled Group Health to move various innovations forward in recent years:
Patient-centered "medical home" primary care teams at each of its 25 medical centers
More judicious prescribing of long-term opioids for chronic noncancer pain
Shared decision making to ensure that treatments are more consistent with patients' values and preferences
Studying high-end imaging (e.g., CT scans) throughout the organization, with the ultimate goal of performing these tests when really needed
Value-based benefit design, using incentives and disincentives to steer patients toward the most effective, evidence-based services—and away from unproven ones
"Too often, researchers and clinicians operate in separate worlds, with different time horizons," Ms. Greene said. Although the pace of research is accelerating, she added, it is still far slower than the urgent time frame inherent in clinical care.
"Researchers who seek to improve care should reconsider spreading our findings only through journal articles and conference presentations," she said. "We need to think carefully about dissemination tools that really work well for reaching clinical leaders." Broader internal and external dissemination includes newsletters, trade publications, websites, reports in the media, and meetings with stakeholders including patients, clinicians, and administrators.
Like the other 18 members of the HMO Research Network, Group Health is a care-delivery system that has its own research arm (Group Health Research Institute). Operating both clinical and research functions makes it easier for a health organization to become a learning health system, Ms. Greene said. So do recent developments in health information technology and a growing health data infrastructure to access and apply evidence in real time.
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) defines a learning health system as "one in which progress in science, informatics, and care culture align to generate new knowledge as an ongoing, natural byproduct of the care experience, and seamlessly refine and deliver best practices for continuous improvement in health and health care." Ms Greene and Dr Larson participated in proceedings at the IOM that ultimately developed these ideas.
"The nation's investment in medical research demands that we do more with the knowledge we generate," the authors conclude in their Annals article. "Rapid-learning health systems can ensure return on that investment."
INFORMATION:
Group Health Research Institute
Group Health Research Institute is the research arm of Seattle-based Group Health Cooperative, a consumer-governed, nonprofit health care system. Founded in 1947, Group Health Cooperative coordinates health care and coverage. Group Health Research Institute changed its name from Group Health Center for Health Studies in 2009. Since 1983, the Institute has conducted nonproprietary public-interest research on preventing, diagnosing, and treating major health problems. Government and private research grants provide its main funding.
HMO Research Network
The HMO Research Network includes 19 research centers, each associated with a health care delivery system. Researchers at the centers collaborate on multi-site studies in real-world health care settings across the United States and in Israel. With access to information on more than 16 million ethnically and geographically diverse patients, these researchers are finding solutions for common and rare health problems. Since 1994, the Network has been answering pressing questions about keeping people healthy and delivering effective care.
A 'learning health system' moves from idea to action
Group Health experience shows how practice and research can inform each other
2012-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers peek at the early evolution of sex chromosomes
2012-08-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Two new studies offer insight into sex chromosome evolution by focusing on papaya, a multimillion dollar crop plant with a sexual problem (as far as growers are concerned) and a complicated past. The findings are described in two papers in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research reveals that the papaya sex chromosomes have undergone dramatic changes in their short evolutionary histories (they are about 7 million years old; by comparison, human sex chromosomes began their evolution more than 167 million years ago). One of the ...
Researchers find evidence of ritual use of 'black drink' at Cahokia
2012-08-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — People living 700 to 900 years ago in Cahokia, a massive settlement near the confluence of the Missouri and Mississippi Rivers, ritually used a caffeinated brew made from the leaves of a holly tree that grew hundreds of miles away, researchers report.
The discovery – made by analyzing plant residues in pottery beakers from Cahokia and its surroundings – is the earliest known use of this "black drink" in North America. It pushes back the date by at least 500 years, and adds to the evidence that a broad cultural and trade network thrived in the Midwest ...
Generic language helps fuel stereotypes, NYU, Princeton researchers find
2012-08-07
Hearing generic language to describe a category of people, such as "boys have short hair," can lead children to endorse a range of other stereotypes about the category, a study by researchers at New York University and Princeton University has found. Their research, which appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), also points to more effective methods to reduce stereotyping and prejudice.
The study focused on "social essentialism," or the belief that certain social categories, such as race or gender, mark fundamentally distinct kinds of people. ...
Gladstone scientists discover that epilepsy drug reverses memory loss in animal model of AD
2012-08-07
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—August 6, 2012— Scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have discovered that an FDA-approved anti-epileptic drug reverses memory loss and alleviates other Alzheimer's-related impairments in an animal model of the disease.
Scientists in the laboratory of Lennart Mucke, MD, who directs neurological research at Gladstone, conducted the research on mice genetically modified to simulate key aspects of Alzheimer's disease. In the study, they show how levetiracetam—a drug commonly prescribed for patients who suffer from epilepsy—suppresses abnormal brain activity ...
New genetic study defines the genetic map of the Jewish Diasporas
2012-08-07
VIDEO:
Harry Ostrer, M.D., discusses how his research into a new genetic analysis focusing on Jews from North Africa has provided an overall genetic map of the Jewish Diasporas. Dr....
Click here for more information.
August 6, 2012 — (Bronx, NY) — A new genetic analysis focusing on Jews from North Africa has provided an overall genetic map of the Jewish Diasporas. The findings support the historical record of Middle Eastern Jews settling in North Africa during Classical Antiquity, ...
Behavioral intervention can reduce tics in adults with Tourette syndrome
2012-08-07
Specially designed comprehensive behavioral therapy is more effective than sessions offering patient support and education in helping adults with Tourette syndrome manage their tics – sudden, repetitive motions or vocalizations – according to a study in the August issue of Archives of General Psychiatry. The findings come from a team of investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH)/Harvard Medical School, Yale University, the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, and other institutions.
"The program we tested, which teaches patients new ways ...
Weight training associated with lower risk of type 2 diabetes in study of men
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – Weight training was linked with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes in a study of male health professionals, and those men who engaged in weight training and aerobic exercise for at least 150 minutes a week had the greatest reduction in risk, according to a report published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), but the role of weight training in the primary prevention of the disease is largely unknown, according to ...
Physical activity associated with lower risk of death in patients with diabetes
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – Higher levels of physical activity were related to lower risk of death in patients with diabetes, according to a report published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Increased physical activity (PA) has long been considered a key element in diabetes management. Patients with diabetes are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and premature death, so researchers note it is important to determine whether PA can produce similar beneficial effects in this high-risk population. While other studies have suggested that ...
Weight training associated with reduced risk of type 2 diabetes
2012-08-07
Boston, MA – Men who do weight training regularly—for example, for 30 minutes per day, five days per week—may be able to reduce their risk of type 2 diabetes by up to 34%, according to a new study by Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) and University of Southern Denmark researchers. And if they combine weight training and aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking or running, they may be able to reduce their risk even further—up to 59%.
This is the first study to examine the role of weight training in the prevention of type 2 diabetes. The results suggest that, because ...
Study examines racial/ethnic disparities in cranial CT among children
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – The odds of undergoing cranial computed tomography (CT) among children with minor blunt head trauma who were at higher risk for clinically important traumatic brain injury did not appear to differ by race/ethnicity in a secondary analysis of a study of injured children, according to a report in the August issue of Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, a JAMA Network publication. However, there may have been differences for children at intermediate or lowest risk.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of pediatric illness and death in the U.S., ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
[Press-News.org] A 'learning health system' moves from idea to actionGroup Health experience shows how practice and research can inform each other