Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for Aug. 7, 2012 issue
2012-08-07
(Press-News.org) 1. Tuning into Contextual Clues May Help Doctors Improve Antibiotic Prescribing Habits
Appropriate use of antibiotics can improve patient outcomes and reduce risk for antibiotic resistance. Febrile respiratory illnesses, or FRI, often present with vague, cold-like symptoms, making it difficult to discern whether the illness is viral or bacterial. Since there are few bedside clues that reliably distinguish viral from bacterial, physicians rely on contextual factors to aid treatment decisions. Contextual factors include epidemiology (for example, flu pandemic period) and recent clinical experience (for example, the number of patients seen in the past week with similar symptoms). Researchers studied electronic health records for 28,301 patients presenting with FRI during flu seasons between 2006 and 2011 to examine how context influences physicians' antibiotic prescribing habits. They found that physicians were more likely to prescribe antibiotics during flu season, but significantly less likely to do so during a pandemic period. Prescriptions for antivirals increased from 5.5 percent of all FRI encounters during flu season to 12.6 percent during pandemic. Physicians who saw 12 or more patients with FRI in the previous week were less likely to prescribe antibiotics and more likely to prescribe antivirals. According to the researchers, teaching physicians to pay attention to contextual clues may improve appropriate prescribing of antibiotics. Informatics tools could provide clinicians with locally relevant, up-to-date data on epidemiological factors. This could be another "meaningful use" for electronic health records.
2. Consider Blacks and Whites the Same When Evaluating HbA1C Levels for Diabetes Diagnosis
Recent studies have highlighted racial differences in hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) levels. At the same blood glucose levels, black patients have higher HbA1C levels than white patients. This distinction has led some experts to propose setting a higher HbA1C threshold for diagnosing diabetes in black patients. Retinopathy (damage to the retina that can lead to blindness) is a common complication of diabetes. Retinopathy can be prevented if diabetic patients are diagnosed and treated early. Researchers studied 2,408 white patients and 1,008 black patients aged 40 or older to compare the relationships between HbA1C level and the prevalence of retinopathy. The researchers found that the prevalence of retinopathy begins to increase at a lower HbA1C level in black patients than in white patients. For this reason, the authors recommend against setting a higher diagnostic threshold of HbA1C in black patients.
### END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-08-07
MINNEAPOLIS – Fainting has a strong genetic predisposition, according to new research published in the August 7, 2012, print issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Fainting, also called vasovagal syncope, is a brief loss of consciousness when your body reacts to certain triggers, such as emotional distress or the sight of blood.
"The question of whether fainting is caused by genetic factors, environmental factors or a mixture of both has been the subject of debate," said study author Samuel F. Berkovic, MD, FRS, with the University ...
2012-08-07
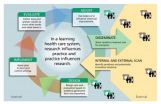
In the United States, clinicians are struggling to provide better and more affordable health care to more people—while keeping up with new scientific developments. The idea of a "learning health system" is one proposed solution for rapidly applying the best available scientific evidence in real-time clinical practice. In the August 7 Annals of Internal Medicine, a Group Health Cooperative team describes the experience of turning this intriguing concept into action.
"In a learning health system, evidence and practice come together in a virtuous cycle, influencing each ...
2012-08-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Two new studies offer insight into sex chromosome evolution by focusing on papaya, a multimillion dollar crop plant with a sexual problem (as far as growers are concerned) and a complicated past. The findings are described in two papers in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research reveals that the papaya sex chromosomes have undergone dramatic changes in their short evolutionary histories (they are about 7 million years old; by comparison, human sex chromosomes began their evolution more than 167 million years ago). One of the ...
2012-08-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — People living 700 to 900 years ago in Cahokia, a massive settlement near the confluence of the Missouri and Mississippi Rivers, ritually used a caffeinated brew made from the leaves of a holly tree that grew hundreds of miles away, researchers report.
The discovery – made by analyzing plant residues in pottery beakers from Cahokia and its surroundings – is the earliest known use of this "black drink" in North America. It pushes back the date by at least 500 years, and adds to the evidence that a broad cultural and trade network thrived in the Midwest ...
2012-08-07
Hearing generic language to describe a category of people, such as "boys have short hair," can lead children to endorse a range of other stereotypes about the category, a study by researchers at New York University and Princeton University has found. Their research, which appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), also points to more effective methods to reduce stereotyping and prejudice.
The study focused on "social essentialism," or the belief that certain social categories, such as race or gender, mark fundamentally distinct kinds of people. ...
2012-08-07
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—August 6, 2012— Scientists at the Gladstone Institutes have discovered that an FDA-approved anti-epileptic drug reverses memory loss and alleviates other Alzheimer's-related impairments in an animal model of the disease.
Scientists in the laboratory of Lennart Mucke, MD, who directs neurological research at Gladstone, conducted the research on mice genetically modified to simulate key aspects of Alzheimer's disease. In the study, they show how levetiracetam—a drug commonly prescribed for patients who suffer from epilepsy—suppresses abnormal brain activity ...
2012-08-07
VIDEO:
Harry Ostrer, M.D., discusses how his research into a new genetic analysis focusing on Jews from North Africa has provided an overall genetic map of the Jewish Diasporas. Dr....
Click here for more information.
August 6, 2012 — (Bronx, NY) — A new genetic analysis focusing on Jews from North Africa has provided an overall genetic map of the Jewish Diasporas. The findings support the historical record of Middle Eastern Jews settling in North Africa during Classical Antiquity, ...
2012-08-07
Specially designed comprehensive behavioral therapy is more effective than sessions offering patient support and education in helping adults with Tourette syndrome manage their tics – sudden, repetitive motions or vocalizations – according to a study in the August issue of Archives of General Psychiatry. The findings come from a team of investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH)/Harvard Medical School, Yale University, the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, and other institutions.
"The program we tested, which teaches patients new ways ...
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – Weight training was linked with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes in a study of male health professionals, and those men who engaged in weight training and aerobic exercise for at least 150 minutes a week had the greatest reduction in risk, according to a report published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), but the role of weight training in the primary prevention of the disease is largely unknown, according to ...
2012-08-07
CHICAGO – Higher levels of physical activity were related to lower risk of death in patients with diabetes, according to a report published Online First by Archives of Internal Medicine, a JAMA Network publication.
Increased physical activity (PA) has long been considered a key element in diabetes management. Patients with diabetes are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) and premature death, so researchers note it is important to determine whether PA can produce similar beneficial effects in this high-risk population. While other studies have suggested that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Annals of Internal Medicine tip sheet for Aug. 7, 2012 issue