(Press-News.org) Eighty-nine million Americans were without health insurance for at least one month during the period from 2004 to 2007, and 23 million lost coverage more than once during that time, according to researchers at Penn State and Harvard University.
"These findings call attention to the continuing instability and insecurity of health insurance in our country," said Pamela Farley Short, professor of health policy and administration, Penn State. "With more than a third of all Americans under age 65 being uninsured at some point in a four-year period, it's easy to see that the problem of being uninsured is a big one that affects lots of people."
To do their analysis, the researchers used data from the U.S. Census Bureau's Survey of Income and Program Participation, which collects information from the same individuals every four months over a four-year period. The team examined changes in insurance coverage among people ages 4 to 64 from 2004 to 2007, which is the most recent period for which four-year data are available.
The researchers found that, of the 89 million people who were uninsured during the period from 2004 to 2007, 12 million were continually uninsured; 11 million gained coverage at some point; 11.5 lost coverage; 14 million experienced a single gap in coverage; and 6 million had a temporary spell of coverage, but were otherwise uninsured. In addition, 23 million people lost health insurance more than once during the four-year period.
The results of the analysis appeared online in a recent issue of Medical Care Research and Review.
"There is clear evidence that people who are uninsured use fewer services than people who have insurance; they postpone prevention and ignore serious problems because they don't feel they can afford the care," Short said. "As a result, some even die for lack of insurance."
But not only do people with gaps in their coverage suffer; those who remain insured and pay premiums suffer as well.
"When people get caught without health insurance, hospitals and emergency rooms are still required to care for them," Short said. "Someone has to pay for those services."
According to the survey, low-income people are particularly susceptible to periodic losses of health insurance coverage. The survey revealed that a little over 64 percent of adults and nearly 60 percent of children who are below 200 percent of the federal poverty level -- equivalent to $46,100/year for a family of four -- were uninsured for at least one month during the four-year period.
"Even though low-income people are disproportionately affected by gaps in health insurance, none of us is really safe," Short said. "Any one of us could be afflicted with a serious health problem that could cause us to lose our jobs and our access to employment-based insurance, which is how most of us get insurance."
In addition to losing or changing jobs, gaps in insurance coverage can occur when people divorce and when children age out of their parents' plans or public insurance programs.
"We all have a stake in this problem of providing everyone with continuing access to affordable insurance," Short said. "Promoting stability and minimizing uninsured gaps should be high priorities as federal and state officials proceed with the implementation of national health care reforms."
###
The Commonwealth Fund supported this work.
Deborah Graefe, research associate at Penn State; Katherine Swartz, professor of health policy and economics at Harvard University; and Namrata Uberoi, graduate student in health policy and administration at Penn State, also were involved with the research.
Language use in books mirrors trends in gender equality over the generations in the US, according to a new study by Jean Twenge, from San Diego State University, and colleagues. Their work explores how the language in the full text of more than one million books reflects cultural change in U.S. women's status. The study is published online in Springer's journal Sex Roles.
Twenge and colleagues, W. Keith Campbell and Brittany Gentile of the University of Georgia, examined whether the use of gendered pronouns such as 'he' and 'she' mirrored women's status between 1900-2008, ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Various misconceptions surrounding the continued viability of Medicare can be debunked or discredited, making it more important than ever for voters and policymakers to fully understand the program's existing contours and limitations, according to a paper published by a University of Illinois expert on retirement benefits.
Law professor Richard L. Kaplan says Medicare has become one of the most controversial federal programs for numerous reasons, but misinformation has played a key role in fostering criticism of it.
"Medicare is an important and complicated ...
According to theoretical physicists João da Cruz and Pedro Lind from Lisbon University, Portugal, imposing minimum capital levels for banks may not prevent the insolvency of a minority of banks from triggering a widespread banking system collapse. In a study recently published in EPJ B1, the researchers explain why this measure could instead lead to larger crises.
The authors created a model of banks' behaviour to assess the conditions needed to avoid "avalanches" of insolvent banks. Their model is based on a physical system of particles representing how banks are attracted ...
Los Angeles, CA (August 09, 2012) Poorly-performing medical implants have hit the headlines recently, and the trend looks set to continue: the September issue of the Journal of Hand Surgery (JHS) homes in on the unacceptable performance of hand implants for osteoarthritis patients. Citing several recent studies, the editorial asks why these implants – which perform worse that certain hip replacement implants now deemed unacceptable – are still widely used. JHS is an online and print, orthopedic surgery journal published by SAGE.
The issue reports on a number of thumb ...
Fresno, Calif. – Consuming grapes may help protect heart health in people with metabolic syndrome, according to new research published in the Journal of Nutrition. Researchers observed a reduction in key risk factors for heart disease in men with metabolic syndrome: reduced blood pressure, improved blood flow and reduced inflammation. Natural components found in grapes, known as polyphenols, are thought to be responsible for these beneficial effects.
The randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study, led by principal investigator Dr. Maria Luz Fernandez and Jacqueline ...
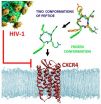
Researchers from Munich and Naples have shown that minimal modification of a synthetic peptide with anti-HIV activity results in a new compound with more than two orders of magnitude higher binding affinity to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and greatly improved anti-HIV activity. This could be a step toward the design of new, more effective drugs against AIDS, inflammatory diseases, and some forms of cancer.
Different strains of HIV-1 use either the chemokine receptor CCR5 or CXCR4 for entry into immune cells. While drugs that block usage of CCR5 by the virus are already ...
PITTSBURGH—Pine trees are one of the biggest contributors to air pollution. They give off gases that react with airborne chemicals – many of which are produced by human activity – creating tiny, invisible particles that muddy the air. New research from a team led by Carnegie Mellon University's Neil Donahue shows that the biogenic particles formed from pine tree emissions are much more chemically interesting and dynamic than previously thought. The study provides the first experimental evidence that such compounds are chemically transformed by free radicals, the same compounds ...
During the Neolithic Age (approximately 10000 BCE), early man evolved from hunter-gatherer to farmer and agriculturalist, living in larger, permanent settlements with a variety of domesticated animals and plant life. This transition brought about significant changes in terms of the economy, architecture, man's relationship to the environment, and more.
Now Dr. Ran Barkai of Tel Aviv University's Department of Archaeology and Ancient Near Eastern Civilizations has shed new light on this milestone in human evolution, demonstrating a direct connection between the development ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. – A Rhode Island Hospital researcher has found that the majority of bariatric surgery patients being treated for obesity have clinically significant obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), but report fewer symptoms than other sleep disorders patients. The study by Katherine M. Sharkey, M.D., Ph.D., of the department of medicine, division of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine at Rhode Island Hospital, and University Medicine, is published online in advance of print in the journal Sleep and Breathing.
"Patients with obstructive sleep apnea frequently complain ...
ARLINGTON, VA, August 9, 2012—The Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society (JPIDS) today released the largest and most rigorous evaluation to date of the impact on reducing the days of antibiotic therapy in a children's hospital using a prospective-audit-with-feedback antibiotic stewardship program (ASP). The study utilized a control group of the 25-member children's hospitals of the Child Health Corporation of America. A companion article describes how the ASP was created within this 317-bed tertiary care children's hospital and clinicians' attitudes toward ...