(Press-News.org) According to a NOAA-led paper published today in the journal Conservation Biology, high levels of background noise, mainly due to ships, have reduced the ability of critically endangered North Atlantic right whales to communicate with each other by about two-thirds.
From 2007 until 2010, scientists from Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary, Cornell Lab of Ornithology, NOAA Fisheries Northeast Fisheries Science Center, and Marine Acoustics Inc. used an array of acoustic recorders to monitor noise levels, measure levels of sound associated with vessels, and to record distinctive sounds made by multiple species of endangered baleen whales, including "up-calls" made by right whales to maintain contact with each other.
NOAA Fisheries Northeast Fisheries Science Center documented more than 22,000 right whale contact calls as part of the study during April 2008, and software developed by Cornell and Marine Acoustics Inc. of Arlington, Va., aided in modeling ship noise propagation throughout the study area.
Vessel-tracking data from the U.S. Coast Guard's Automatic Identification System was used to calculate noise from vessels inside and outside the sanctuary. By further comparing noise levels from commercial ships today with historically lower noise conditions nearly a half-century ago, the authors estimate that right whales have lost, on average, 63 to 67 percent of their communication space in the sanctuary and surrounding waters.
"A good analogy would be a visually impaired person, who relies on hearing to move safely within their community, which is located near a noisy airport," said Leila Hatch, Ph.D., NOAA's Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary marine ecologist and lead author of the paper. "Large whales, such as right whales, rely on their ability to hear far more than their ability to see. Chronic noise is likely reducing their opportunities to gather and share vital information that helps them find food and mates, navigate, avoid predators and take care of their young."
North Atlantic right whales, which live along North America's east coast from Nova Scotia to Florida, are one of the world's rarest large animals and are on the brink of extinction. Recent estimates put the population of North Atlantic right whales at approximately 350 to 550 animals.
"We had already shown that the noise from an individual ship could make it nearly impossible for a right whale to be heard by other whales," said Christopher Clark, Ph.D., director of Cornell's bioacoustics research program and a co-author of the work. "What we've shown here is that in today's ocean off Boston, compared to 40 or 50 years ago, the cumulative noise from all the shipping traffic is making it difficult for all the right whales in the area to hear each other most of the time, not just once in a while. Basically, the whales off Boston now find themselves living in a world full of our acoustic smog."
The authors suggest that the impacts of chronic and wide-ranging noise should be incorporated into comprehensive plans that seek to manage the cumulative effects of offshore human activities on marine species and their habitats.
"We are starting to quantify the implication of chronic, human-created ocean noise for marine animals," said Holly Bamford, deputy assistant administrator of the National Ocean Service. "Now, we need to ask how we can adapt our management tools to better address these problems."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded under the National Oceanographic Partnership Program. The paper published in Conservation Biology can be found online at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2012.01908.x/abstract.
More information on the study is available online at http://stellwagen.noaa.gov/science/passive_acoustics_current.html.
NOAA's mission is to understand and predict changes in the Earth's environment, from the depths of the ocean to the surface of the sun, and to conserve and manage our coastal and marine resources. Join us on Facebook, Twitter and our other social media channels at http://www.noaa.gov/socialmedia/.
END
VIDEO:
This video shows the annual cycle of global and Asian fatal landslides (for the full dataset described in the research paper).
They have been divided into the 52 weeks...
Click here for more information.
Landslides kill ten times more people across the world than was previously thought, according to research by Durham University, UK.
A new database of hazards shows that 32,300 people died in landslides between 2004 and 2010. Previous estimates ranged from 3,000 ...
WASHINGTON — A new report from the National Research Council presents a prioritized program of basic and applied research for 2013-2022 that will advance scientific understanding of the sun, sun-Earth connections and the origins of "space weather," and the sun's interactions with other bodies in the solar system. This second decadal survey in solar and space physics -- the product of a 18-month effort by more than 85 solar and space physicists and space system engineers -- lays out four scientific goals for the next 10 years along with guiding principles and recommended ...
VIDEO:
This animation shows how large numbers of stars form in the Phoenix Cluster. It begins by showing several galaxies in the cluster and hot gas (in red). This hot gas...
Click here for more information.
Astronomers have found an extraordinary galaxy cluster, one of the largest objects in the universe, that is breaking several important cosmic records. Observations of the Phoenix cluster with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, the National Science Foundation's South ...
A new study by researchers at the University of California, San Diego, and Emory University has uncovered fundamental details about the hexamer structures that make up the tiniest droplets of water, the key component of life – and one that scientists still don't fully understand.
The research, recently published in The Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), provides a new interpretation for experimental measurements as well as a vital test for future studies of our most precious resource. Moreover, understanding the properties of water at the molecular level ...
A massive galaxy cluster nearly six billion light years from Earth has been discovered with an astounding and unexpected burst of star formation – more prodigious than any galaxy cluster yet observed, an international team of astronomers and NASA announced today.
In a wide-ranging discussion on the eve of the announcement, two of the leading astronomers on the project talked about the record-breaking galaxy cluster, called Phoenix, and how its surprising properties are prompting astronomers to re-think how galaxy clusters – among the largest structures in the universe ...
A long-time staple of science fiction is the tractor beam, a technology in which light is used to move massive objects – recall the tractor beam in the movie Star Wars that captured the Millennium Falcon and pulled it into the Death Star. While tractor beams of this sort remain science fiction, beams of light today are being used to mechanically manipulate atoms or tiny glass beads, with rapid progress being made to control increasingly larger objects. Those who see major roles for optomechanical systems in a host of future technologies will take heart in the latest results ...
JUPITER, FL, August 15, 2012 – Working with a national team of researchers, a scientist from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute has shown for the first time a link between low levels of a specific hormone and increased risk of metabolic disease in humans.
The study, published online ahead of print in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, focuses on the hormone adropin, which was previously identified by Scripps Research Associate Professor Andrew Butler's laboratory during an investigation of obese and insulin-resistant mice. Adropin is ...
Astronomers have found an extraordinary galaxy cluster — one of the largest objects in the universe — that is breaking several important cosmic records. The discovery of this cluster, known as the Phoenix Cluster, made with the National Science Foundation's South Pole Telescope, may force astronomers to rethink how these colossal structures, and the galaxies that inhabit them, evolve.
Follow-up observations made in ultraviolet, optical and infrared wavelengths show that stars are forming in this object at the highest rate ever seen in the middle of a galaxy cluster. The ...
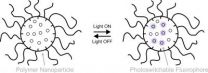
CORAL GABLES, FL (August, 15, 2012)--University of Miami scientists have developed a way to switch fluorescent molecules on and off within aqueous environments, by strategically trapping the molecules inside water-soluble particles and controlling them with ultraviolet light. The new system can be used to develop better fluorescent probes for biomedical research.
Previous studies have used water-soluble particles to bring organic molecules into water. What is novel about this system is the use of a photoswitching mechanism in combination with these particles.
The findings ...
A National Science Foundation-funded radio telescope in Antarctica has found an extraordinary galaxy cluster that may force astronomers to rethink how galaxy clusters and the galaxies that inhabit them evolve.
The galaxy cluster was discovered some 5.7 billion light years from Earth by the 10-meter wide South Pole Telescope (SPT) located at NSF's Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica, which is funded by NSF's Office of Polar Programs.
NSF manages the U.S. Antarctic Program, through which it coordinates all U.S research and required logistical support on the ...