(Press-News.org) (Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Sunscreens, lotions, and cosmetics contain tiny metal nanoparticles that wash down the drain at the end of the day, or are discharged after manufacturing. Those nanoparticles eventually end up in agricultural soil, which is a cause for concern, according to a group of environmental scientists that recently carried out the first major study of soybeans grown in soil contaminated by two manufactured nanomaterials (MNMs).
The team was led by scientists at UC Santa Barbara's Bren School of Environmental Science & Management. The team is also affiliated with the UC Center for Environmental Implications of Nanotechnology (CEIN), a $24 million collaboration based at UCLA, with researchers from UCSB, UC Davis, UC Riverside, University of Texas at El Paso, Columbia University, and other national and international partners. The results of the study are published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Our society has become more environmentally aware in the last few decades, and that results in our government and scientists asking questions about the safety of new types of chemical ingredients," said senior author Patricia Holden, a professor with the Bren School. "That's reflected by this type of research."
She explained that the research, which is funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), is helping to discover potential environmental implications of a new industry that includes nanomaterials. The ultimate goal is to help find more environmentally compatible substitutes, Holden said.
Soybean was chosen for the study due to its importance as a food crop –– it is the fifth largest crop in global agricultural production and second in the U.S. –– and because it is vulnerable to MNMs. The findings showed that crop yield and quality are affected by the addition of MNMs to the soil.
The scientists studied the effects of two common nanoparticles, zinc oxide and cerium oxide, on soybeans grown in soil in greenhouses. Zinc oxide is used in cosmetics, lotions, and sunscreens. Cerium oxide is used as an ingredient in catalytic converters to minimize carbon monoxide production, and in fuel to increase fuel combustion. Cerium can enter soil through the atmosphere when fuel additives are released with diesel fuel combustion.
The zinc oxide nanoparticles may dissolve, or they may remain as a particle, or re-form as a particle, as they are processed through wastewater treatment. At the final stage of wastewater treatment there is a solid material, called biosolids, which is applied to soils in many parts of the U.S. This solid material fertilizes the soil, returning nitrogen and phosphorus that are captured during wastewater treatment. This is also a point at which zinc oxide and cerium oxide can enter the soil.
The scientists noted that the EPA requires pretreatment programs to limit direct industrial metal discharge into publicly owned wastewater treatment plants. However, the research team conveyed that "MNMs –– while measurable in the wastewater treatment plant systems –– are neither monitored nor regulated, have a high affinity for activated sludge bacteria, and thus concentrate in biosolids."
The authors pointed out that soybean crops are farmed with equipment powered by fossil fuels, and thus MNMs can also be deposited into the soil through exhaust.
The study showed that soybean plants grown in soil that contained zinc oxide bioaccumulated zinc; they absorbed it into the stems, leaves, and beans. Food quality was affected, although it may not be harmful to humans to eat the soybeans if the zinc is in the form of ions or salts, in the plants, according to Holden.
In the case of cerium oxide, the nanoparticles did not bioaccumulate, but plant growth was stunted. Changes occurred in the root nodules, where symbiotic bacteria normally accumulate and convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, which fertilizes the plant. The changes in the root nodules indicate that greater use of synthetic fertilizers might be necessary with the buildup of MNMs in the soil.
Holden commented on the likelihood of high concentrations of these nanoparticles in agriculture: "There could be hotspots, places where you have accumulation, including near manufacturing sites where the materials are being made, or if there are spills. We have very limited information about the quantity or state of these synthetic nanomaterials in the environment right now. We know they're being used in consumer goods, and we know they're going down the drain."
First author John H. Priester is a staff scientist in the Holden lab at UCSB. Other co-authors from UC CEIN are Yuan Ge, Randall E. Mielke, Allison M. Horst, Shelly Cole Moritz, Roger M. Nisbet, Joshua P. Schimel, Jose A. Hernandez-Viezcas, Lijuan Zhao, and Jorge L. Gardea-Torresdey. Co-authors Katherine Espinosa and Reid G. Palmer are affiliated with Iowa State University; Jeff Gelb is affiliated with Xradia Corporation; and Sharon L. Walker is with UC Riverside. NASA/JPL-Caltech, the USDA, and The University of Texas at El Paso were substantially involved in the research.
INFORMATION:
UCSB scientists examine effects of manufactured nanoparticles on soybean crops
2012-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Information overload in the era of 'big data'
2012-08-21
Botany is plagued by the same problem as the rest of science and society: our ability to generate data quickly and cheaply is surpassing our ability to access and analyze it. In this age of big data, scientists facing too much information rely on computers to search large data sets for patterns that are beyond the capability of humans to recognize—but computers can only interpret data based on the strict set of rules in their programming.
New tools called ontologies provide the rules computers need to transform information into knowledge, by attaching meaning to data, ...
Stroke disrupts how brain controls muscle synergies
2012-08-21
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- The simple act of picking up a pencil requires the coordination of dozens of muscles: The eyes and head must turn toward the object as the hand reaches forward and the fingers grasp it. To make this job more manageable, the brain's motor cortex has implemented a system of shortcuts. Instead of controlling each muscle independently, the cortex is believed to activate muscles in groups, known as "muscle synergies." These synergies can be combined in different ways to achieve a wide range of movements.
A new study from MIT, Harvard Medical School and the ...
Nanoparticles added to platelets double internal injury survival rate
2012-08-21
Nanoparticles tailored to latch onto blood platelets rapidly create healthy clots and nearly double the survival rate in the vital first hour after injury, new research shows.
"We knew an injection of these nanoparticles stopped bleeding faster, but now we know the bleeding is stopped in time to increase survival following trauma," said Erin Lavik, a professor of biomedical engineering at Case Western Reserve University and leader of the effort.
The researchers are developing synthetic platelets that first responders and battlefield medics could carry with them to stabilize ...
Breast density does not influence breast cancer death among breast cancer patients
2012-08-21
The risk of dying from breast cancer was not related to high mammographic breast density in breast cancer patients, according to a study published August 20 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
One of the strongest risk factors for non-familial breast cancer is elevated mammographic breast density. While women with elevated mammographic breast density have a higher risk of developing breast cancer, it is not established whether a higher density indicates a lower chance of survival in breast cancer patients.
In order to determine if higher mammographic breast ...
NASA satellites capture 3 days of Hurricane Gordon's Atlantic track
2012-08-21
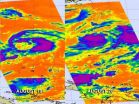
NASA's Terra and Aqua satellite have captured Hurricane Gordon over three days as it neared the Azores Islands in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. Gordon weakened to a tropical storm on August 20.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, is an instrument that flies onboard NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites and provides high-resolution imagery to users. When NASA's Terra satellite flew over Gordon on August 17 at 9:30 a.m. EDT it was a tropical storm and did not have a visible eye. It was followed up by a fly over of NASA's Aqua satellite on August 18 at ...
First evidence discovered of planet's destruction by its star
2012-08-21
The first evidence of a planet's destruction by its aging star has been discovered by an international team of astronomers. The evidence indicates that the missing planet was devoured as the star began expanding into a "red giant" -- the stellar equivalent of advanced age. "A similar fate may await the inner planets in our solar system, when the Sun becomes a red giant and expands all the way out to Earth's orbit some five-billion years from now," said Alexander Wolszczan, Evan Pugh Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics at Penn State University, who is one of the members ...
NASA watches as Tropical Storm Bolaven develops
2012-08-21
Tropical Storm Bolaven was born over the weekend of August 18-19 in the western North Pacific, and NASA captured infrared satellite imagery of its birth and growth.
NASA's Aqua satellite has been monitoring the birth and progress of Tropical Storm Bolaven in the western North Pacific from Aug 19-20, 2012. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument has provided infrared satellite imagery that shows the development of colder thunderstorm cloud-top temperatures, that were indicative of strengthening storms. Tropical Storm Bolaven also took more of a rounded shape ...
Infants' avoidance of drop-off reflects specific motor ability, not fear
2012-08-21
Researchers have long studied infants' perceptions of safe and risky ground by observing their willingness to cross a visual cliff, a large drop-off covered with a solid glass surface. In crawling, infants grow more likely to avoid the apparent drop-off, leading researchers to conclude that they have a fear of heights. Now a new study has found that although infants learn to avoid the drop-off while crawling, this knowledge doesn't transfer to walking. This suggests that what infants learn is to perceive the limits of their ability to crawl or walk, not a generalized fear ...
Ethnic and political violence increases children's aggressive behavior
2012-08-21
Ethnic and political violence in the Middle East can increase violence in families, schools, and communities, which can in turn boost children's aggressiveness, especially among 8-year-olds. Those are the findings of a new study that examined children and their parents in the Middle East.
"The study has important implications for understanding how political struggles can spill over into the everyday lives of families and children, and suggests that intervention might be necessary in a number of different social areas to protect children from the adverse impacts of exposure ...
For poorer children, living in a high-cost area hurts development
2012-08-21
Young children in lower-income families who live in high-cost areas don't do as well academically as their counterparts in low-cost areas, according to a new study.
The study, by researchers at Child Trends and the University of California (UCLA), appears in the journal Child Development.
"Among families with incomes below 300 percent of the federal poverty threshold—that's below $66,339 for a family of four—living in a region with a higher cost of living was related to lower academic achievement in first grade," according to Nina Chien, a research scientist with Child ...