(Press-News.org) Researchers, doctors and patients tend to agree that during the high-risk period after an attempted suicide, the treatment of choice is close contact, follow-up and personal interaction in order to prevent a tragic repeat. Now, however, new research shows that this strategy does not work. These surprising results from Mental Health Services in the Capital Region of Denmark and the University of Copenhagen have just been published in the British Medical Journal.
Researchers from Mental Health Services in the Capital Region of Denmark and the University of Copenhagen have just concluded a large study on the effect of an assertive outreach and intervention programme for young people after an attempted suicide. The surprising conclusion is that increased attention and support for the patient do not have a significant effect.
– Our results show that there is no difference between receiving standard treatment after an attempted suicide, or receiving assertive outreach intervention in addition, explains Britt Morthorst, research assistant, Psychiatric Centre Copenhagen and the Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, who led the study.
The study was conducted at the Research Unit of Psychiatric Centre Copenhagen from 2007 to 2010. A total of 243 patients who had recently attempted suicide participated in the study; 123 in the additional intervention group and 120 in the control group. In the study, the frequency of repeated attempt was 17% for both groups. This figure can also be found in the international literature on this topic, and describes the risk factor entailed by a prior suicide attempt.
Standard treatment just as good
Standard treatment after an attempted suicide is usually provided by the patient's own general practitioner or a psychologist, and is adapted to the patient's physical and mental health. Generally it is up to the patient to seek help and initiate a course of treatment. In the study reported here, standard treatment was supplemented by treatment at the Competence Centre for Suicide Prevention under the auspices of Mental Health Services in the Capital Region of Denmark.
Under the additional intervention programme, specially-trained nurses visited patients a few days after their discharge from hospital and maintained especially close contact with them for up to six months, with between eight and 20 out-reach consultations in addition to standard treatment. Contact covered meetings with patients in the patient's home, and also included accompanying patients to doctors' appointments and meetings with social services. The option of telephone and texting contact was also part of the package.
Greater focus on danger signals prior to first suicide attempt
However, close contact is not what it takes to stop the negative spiral involved in repeated suicide attempts. At the end of the study, researchers were forced to conclude that in the year after treatment, there were as many attempted suicides in the group that had received additional intervention as in the control group that received standard treatment.
Thus there is no difference to be found in either hospital registers or in the data gathered from self-reporting by participants in the study:
Unfortunately, the conclusion must be that neither standard treatment nor additional assertive outreach is good enough. My suggestion is that we try to get hold of young people at risk before they attempt suicide the first time. We are looking with interest at some American Teen-Screen programmes, which look at young people's mental health generally, to see if we can identify any danger signals to which we could respond earlier, explains Britt Morthorst.
###Read the article in British Medical Journal: http://www.bmj.com/highwire/filestream/599203/field_highwire_article_pdf/0.pdf?bcsi_scan_454e4c1bfe3a6284=eKxTMzigoVP1xe1s09tM71xjozcNAAAA35GHDA==&bcsi_scan_filename=0.pdf
Close contact with young people at risk of suicide has no effect
2012-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rewired visual input to sound-processing part of the brain leads to compromised hearing
2012-08-22
ATLANTA – Scientists at Georgia State University have found that the ability to hear is lessened when, as a result of injury, a region of the brain responsible for processing sounds receives both visual and auditory inputs.
Yu-Ting Mao, a former graduate student under Sarah L. Pallas, professor of neuroscience, explored how the brain's ability to change, or neuroplasticity, affected the brain's ability to process sounds when both visual and auditory information is sent to the auditory thalamus.
The study was published in the Journal of Neuroscience.
The auditory thalamus ...
Intense prep for law school admission test alters brain structure
2012-08-22
Intensive preparation for the Law School Admission Test (LSAT) actually changes the microscopic structure of the brain, physically bolstering the connections between areas of the brain important for reasoning, according to neuroscientists at the University of California, Berkeley.
The results suggest that training people in reasoning skills – the main focus of LSAT prep courses – can reinforce the brain's circuits involved in thinking and reasoning and could even up people's IQ scores.
"The fact that performance on the LSAT can be improved with practice is not new. ...
Study shows long-term effects of radiation in pediatric cancer patients
2012-08-22
For many pediatric cancer patients, total body irradiation (TBI) is a necessary part of treatment during bone marrow transplant– it's a key component of long term survival. But lengthened survival creates the ability to notice long term effects of radiation as these youngest cancer patients age. A University of Colorado Cancer Center study recently published in the journal Pediatric Blood & Cancer details these late effects of radiation.
"These kids basically lie on a table and truly do get radiation from head to toe. There is a little blocking of the lungs, but nothing ...
New laboratory test assesses how DNA damage affects protein synthesis
2012-08-22
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — Transcription is a cellular process by which genetic information from DNA is copied to messenger RNA for protein production. But anticancer drugs and environmental chemicals can sometimes interrupt this flow of genetic information by causing modifications in DNA.
Chemists at the University of California, Riverside have now developed a test in the lab to examine how such DNA modifications lead to aberrant transcription and ultimately a disruption in protein synthesis.
The chemists report that the method, called "competitive transcription and adduct ...
NASA sees an active tropical Atlantic again
2012-08-22
The Atlantic Ocean is kicking into high gear with low pressure areas that have a chance at becoming tropical depressions, storms and hurricanes. Satellite imagery from NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites have provided visible, infrared and microwave data on four low pressure areas. In addition, NASA's GOES Project has been producing imagery of all systems using NOAA's GOES-13 satellite to see post-Tropical Storm Gordon, Tropical Depression 9, and Systems 95L and 96L.
Tropical Storm Gordon is no longer a tropical storm and is fizzling out east of the Azores. Tropical Depression ...
Thinking and choosing in the brain
2012-08-22
PASADENA, Calif.—The frontal lobes are the largest part of the human brain, and thought to be the part that expanded most during human evolution. Damage to the frontal lobes—which are located just behind and above the eyes—can result in profound impairments in higher-level reasoning and decision making. To find out more about what different parts of the frontal lobes do, neuroscientists at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) recently teamed up with researchers at the world's largest registry of brain-lesion patients. By mapping the brain lesions of these patients, ...
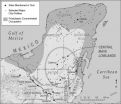
Multiple factors, including climate change, led to collapse and depopulation of ancient Maya
2012-08-22
TEMPE, Ariz. — A new analysis of complex interactions between humans and the environment preceding the 9th century collapse and abandonment of the Central Maya Lowlands in the Yucatán Peninsula points to a series of events — some natural, like climate change; some human-made, including large-scale landscape alterations and shifts in trade routes — that have lessons for contemporary decision-makers and sustainability scientists.
In their revised model of the collapse of the ancient Maya, social scientists B.L. "Billie" Turner and Jeremy "Jerry" A. Sabloff provide an up-to-date, ...
Time flies when you're having goal-motivated fun
2012-08-22
Though the seconds may tick by on the clock at a regular pace, our experience of the 'fourth dimension' is anything but uniform. When we're waiting in line or sitting in a boring meeting, time seems to slow down to a trickle. And when we get caught up in something completely engrossing – a gripping thriller, for example – we may lose sense of time altogether.
But what about the idea that time flies when we're having fun? New research from psychological science suggests that the familiar adage may really be true, with a caveat: time flies when we're have goal-motivated ...
Self-charging power cell converts and stores energy in a single unit
2012-08-22
Researchers have developed a self-charging power cell that directly converts mechanical energy to chemical energy, storing the power until it is released as electrical current. By eliminating the need to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy for charging a battery, the new hybrid generator-storage cell utilizes mechanical energy more efficiently than systems using separate generators and batteries.
At the heart of the self-charging power cell is a piezoelectric membrane that drives lithium ions from one side of the cell to the other when the membrane is deformed ...
NASA satellites see 2 intensifying northwestern Pacific tropical cyclones
2012-08-22
There's double trouble in the northwestern Pacific Ocean in the form of Typhoon Tembin and Tropical Storm Bolaven. NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites teamed up to provide a look at both storms in one view.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument flies onboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites and the MODIS instrument on each captured a storm when both satellites flew over them on August 21 after midnight (Eastern Daylight Time). The two MODIS images which featured Bolaven and Tembin over the Philippine Sea were combined by NASA's MODIS Rapid ...