(Press-News.org) A global assessment of the oesophageal adenocarcinoma epidemic Online First doi 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302412
The global "epidemic" of one type of gullet cancer (adenocarcinoma) seems to have started in the UK during the 1950s, sparked by some as yet unknown, but common, factor, suggests research published online in Gut.
There are two distinct types of gullet (oesophageal) cancer—squamous and adenocarcinoma, the latter typically affecting the lower third of the oesophagus.
It was first realised that diagnoses of adenocarcinoma were increasing rapidly in several regions of the world in the mid-1980s. But the reasons behind this dramatic increase still remain something of an enigma.
In a bid to identify any discernible patterns, the authors looked at data from 16 population based cancer registries in eight countries, going back between 29 and 54 years.
The eight countries comprised Australia, Denmark, England, Finland, Norway, Scotland, Sweden and the US.
They calculated the rates of the disease that would be expected to be diagnosed, according to the age of the population and looked at the timelines to see if there were particular flash points at which diagnoses suddenly increased.
They found that the incidence of oesophageal adenocarcinoma continued to increase rapidly in all 16 registries, and there is little evidence that this trend is beginning to plateau.
Men continue to be between three and nine times as likely to develop the disease as women—a pattern that has remained consistent over time.
Although experienced at different periods, with a gap of around 30 years, in around half the registers, a low and seemingly stable rate of new diagnoses shifted abruptly to a rapidly and consistently linear increase.
In the remainder of the registries, the rate had gone beyond a low and stable phase, and was already rising when registration started.
The timeline analysis indicated that the first discernible surge probably occurred around 1960 in Scotland and England, with a similar surge in the US starting in the mid-1970s, and another beginning in 1991 in Sweden, the last country among those studied, to experience this.
The authors suggest that as the analysis was restricted to countries and regions with reliable and longstanding data, it seems unlikely that more than a fraction of these patterns could be attributable to mistakes in correctly identifying the cases.
And as there has been little change in the proportion of patients with localised disease or death rates, changes in diagnostic accuracy are unlikely to explain the trends either.
Obesity, which is linked to acid reflux—a well known cause of the disease—has been rising rapidly too, but the pattern does not fully match that of oesophageal adenocarcinoma, say the authors, nor does it explain the gender difference seen in this type of cancer.
Smoking, an increase in acid reflux, and a fall in Helicobacter pylori infections have all probably played a part in rising incidence, say the authors. But they add: "They are unlikely to explain either the abrupt change or the astounding rate of increase."
And they conclude: "Therefore, it seems reasonable to hypothesise that the effects of a strong, highly prevalent and yet unidentified causal factor—first introduced in the UK in the middle of the 20th century—have been superimposed on the effects of known risk factors."
### END
Global 'epidemic' of gullet cancer seems to have started in UK in 1950s
Common, but as yet unidentified factor, behind sudden surge in cases around the world
2012-08-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Large health gaps found among black, Latino, and white fifth-graders
2012-08-23
Boston, Mass., August 23, 2012 – Substantial racial and ethnic disparities were found for a broad set of harmful health-related issues in a new study of 5th graders from various regions of the U.S. conducted by Boston Children's Hospital and a consortium of research institutions. Black and Latino children were more likely than white children to report everything from witnessing violence to engaging in less exercise to riding in cars without wearing seatbelts. At the same time, the study found that children of all races and ethnicities did better on these health indicators ...
Children's body fatness linked to decisions made in the womb
2012-08-23
New born human infants have the largest brains among primates, but also the highest proportion of body fat. Before birth, if the supply of nutrients from the mother through the placenta is limited or unbalanced, the developing baby faces a dilemma: should resources be allocated to brain growth, or to fat deposition for use as an energy reserve during the early months after birth?
Scientists at the University of Southampton have shown that this decision could have an effect on how fat we are as children.
In new research, published in the journal PLoS ONE today (22 August ...
Imaging study sheds new light on alcohol-related birth defects
2012-08-23
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – A collaborative research effort by scientists at the University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Duke University, and University College of London in the UK, sheds new light on alcohol-related birth defects.
The project, led by Kathleen K. Sulik, PhD, a professor in the Department of Cell and Developmental Biology and the Bowles Center for Alcohol Studies at UNC, could help enhance how doctors diagnose birth defects caused by alcohol exposure in the womb. The findings also illustrate how the precise timing of that exposure could determine the ...
Moms linked to teen oral health, says CWRU dental study
2012-08-23
A mother's emotional health and education level during her child's earliest years influence oral health at age 14, according to a new study from Case Western Reserve University's School of Dental Medicine.
Researchers started with the oral health of the teens and worked backwards to age 3 to find out what factors in their past influenced their oral health outcomes.
While mothers were interviewed, lead investigator Suchitra Nelson, professor in the dental school, believes it can apply to whoever is the child's primary caregiver.
Nelson's team examined the teeth of 224 ...
Super-strong, high-tech material found to be toxic to aquatic animals
2012-08-23
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are some of the strongest materials on Earth and are used to strengthen composite materials, such as those used in high-performance tennis rackets. CNTs have potential uses in everything from medicine to electronics to construction. However, CNTs are not without risks. A joint study by the University of Missouri and United States Geological Survey found that they can be toxic to aquatic animals. The researchers urge that care be taken to prevent the release of CNTs into the environment as the materials enter mass production.
"The great promise ...
Nematodes with pest-fighting potential identified
2012-08-23
This press release is available in Spanish.
Formosan subterranean termites could be in for a real headache. U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) scientists have identified species of roundworms, or "nematodes," that invade the termite brains and offer a potential bio-based approach to controlling them. Other nematodes that were identified invaded tarantula brains.
The Formosan termite, a nonnative species from Asia, feeds on cellulose from the heartwood of trees, the wood support beams of buildings, and other sources. It causes an estimated $1 billion annually in ...
Cramming for a test? Don't do it, say UCLA researchers
2012-08-23
Every high school kid has done it: putting off studying for that exam until the last minute, then pulling a caffeine-fueled all-nighter in an attempt to cram as much information into their heads as they can.
Now, new research at UCLA says don't bother.
The problem is the trade-off between study and sleep. Studying, of course, is a key contributor to academic achievement, but what students may fail to appreciate is that adequate sleep is also important for academics, researchers say.
In the study, UCLA professor of psychiatry Andrew J. Fuligni, UCLA graduate ...
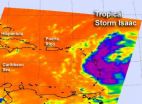
NASA sees Tropical Storm Isaac and Tropical Depression 10 racing in Atlantic
2012-08-23
VIDEO:
This animation of satellite observations from August 19-22, 2012, shows the development and movement of Tropical Storm Isaac toward the Lesser Antilles. This visualization was created by the NASA GOES...
Click here for more information.
There are now two active tropical cyclones in the Atlantic and NASA is generating satellite imagery to monitor their march westward. Tropical Storm Issac is already bringing rainfall to the Lesser Antilles today, Aug. 22, Tropical ...
University of Colorado analysis of election factors points to Romney win
2012-08-23
A University of Colorado analysis of state-by-state factors leading to the Electoral College selection of every U.S. president since 1980 forecasts that the 2012 winner will be Mitt Romney.
The key is the economy, say political science professors Kenneth Bickers of CU-Boulder and Michael Berry of CU Denver. Their prediction model stresses economic data from the 50 states and the District of Columbia, including both state and national unemployment figures as well as changes in real per capita income, among other factors.
"Based on our forecasting model, it becomes clear ...
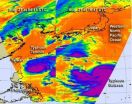
Double trouble continues in the Philippine Sea: Tembin and Bolaven
2012-08-23
Typhoon Tembin and Typhoon Bolaven continue to churn in the Philippine Sea, and infrared satellite data from NASA showed the power within both storms.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies onboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured imagery of both storms on Aug. 21 in two different overpasses. Aqua flies over the same locations during early morning and early afternoon (local time) as it orbits the Earth. Aqua passed over the Philippine Sea on Aug. 21 at 04:41 UTC (12:41 a.m. EDT) and 16:47 UTC (12:47 p.m. EDT). The two satellite passes were combined ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
[Press-News.org] Global 'epidemic' of gullet cancer seems to have started in UK in 1950sCommon, but as yet unidentified factor, behind sudden surge in cases around the world