(Press-News.org) Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: A non-invasive imaging strategy which integrates non-invasive CT angiography (CTA) and CT myocardial perfusion imaging (CTP) has robust diagnostic accuracy for identifying patients with flow-limiting coronary artery disease in need of myocardial revascularisation, according to results of the CORE320 study presented here today by Dr Joao AC Lima from Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, USA.
The CORE320 study is a prospective multicentre international trial which evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of combined non-invasive CTA and CTP as compared with invasive angiography (ICA) and single photon computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging (SPECT-MPI). The primary objective was to determine whether combined noninvasive CTA and CTP could reliably determine the presence or absence of flow limiting coronary stenoses as defined by the combination of ICA and SPECT-MPI.
Patients between 45 and 85 years of age with suspected or known coronary artery disease and clinically referred for ICA were eligible for participation. The study enrolled 436 patients, of whom 381 successfully completed all imaging at 16 centers in eight countries (Canada, USA, Brazil, the Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, Japan, and Singapore).
The study design included four imaging components: CTA, stress CTP, ICA, and SPECT-MPI, as displayed in the Figure below. Images were evaluated in double blinded core laboratories. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used as the primary diagnostic parameter. The study was sponsored by Toshiba Medical Systems.
Sixty-six percent of the study participants were male, the median (interquartile range [IQR]) age was 62 [56,68], body mass index 27 [24,30], and Agatston calcium score 162 [9, 530]. Participants had a history of traditional risk factors for coronary artery disease - 34% were diabetic, 26% had a history of previous myocardial infarction, 29% had prior percutaneous coronary intervention, 78% were positive for hypertension, 68% were positive for dislipidemia, and 45% had a family history of coronary artery disease.
The prevalence of obstructive coronary artery disease defined by combined ICA and SPECT/MPI was 38% and for ICA alone 59%. The patient-based diagnostic accuracy (AUC) of combined CTA and CTP for detecting or excluding flow-limiting CAD was 0.87 (95% CI 0.83-0.91), and 0.89 (95% CI 0.86-0.93) when the ICA stenosis reference standards were ≥50% and ≥70% respectively. CTP increased the diagnostic accuracy of CTA alone to delineate flow-limiting disease (AUC 0.87 [95%CI 0.83-0.91] vs. 0.81 [95%CI 0.77-0.86], respectively, p END
CT angiography and perfusion to assess coronary artery disease: The CORE320 study
2012-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chinese scientists successfully crack the genome of diploid cotton
2012-08-28
August 28, 2012, Shenzhen, China – The international research team led by Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and BGI have completed the genome sequence and analysis of a diploid cotton-- Gossypium raimondii. The cotton genome provides an invaluable resource for the study and genetic improvement of cotton quality and output, and sheds new lights on understanding the genetic characteristics and evolutionary mechanism underlying cotton and its close relatives. The study was published online in Nature Genetics. (http://www.nature.com/ng/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/ng.2371.html).
Cotton, ...
The FAME 2 trial
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) had a lower need for urgent revascularisation when receiving fractional flow reserve (FFR)-guided PCI plus the best available medical therapy (MT) than when receiving MT alone. The results, from a final analysis of the FAME 2 trial, were presented today during a Hot Line session of ESC Congress 2012 in Munich. Treatment guided by fractional flow reserve assessment helped reduce the risk of urgent revascularisation by a factor of eight.
The FAME 2 (FFR-Guided Percutaneous Coronary Intervention ...
Zebrafish study explains why the circadian rhythm affects your health
2012-08-28
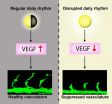
Disruptions to the circadian rhythm can affect the growth of blood vessels in the body, thus causing illnesses such as diabetes, obesity, and cancer, according to a new study from Linköping University and Karolinska Institutet in Sweden.
The circadian rhythm is regulated by a "clock" that reacts to both incoming light and genetic factors.
In an article now being published in the scientific journal Cell Reports, it is demonstrated for the first time that disruption of the circadian rhythm immediately inhibit blood vessel growth in zebra fish embryos.
Professor Yihai Cao ...
Global platelet reactivity and high risk ACS patients
2012-08-28
Global platelet reactivity is more effective than responsiveness to clopidogrel in identifying acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients at high risk of ischemic events, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2012.
The results from the RECLOSE 2-ACS study were presented by Dr Rossella Marcucci from the University of Florence.
The Responsiveness to Clopidogrel and Stent thrombosis 2 – ACS (RECLOSE 2-ACS) study is a prospective, observational, referral centre cohort study of 1,789 patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention ...
Botany student proves 'New England Banksia' a distinct species
2012-08-28
The New England Banksia is largely restricted to the eastern edge of the New England Tableland, and is common in places along Waterfall Way. Ms Stimpson's research has raised this flowering plant, until now classified as a variety of the Hairpin Banksia (B. spinulosa), to the taxonomic level of a distinct species. The study was published in the open access journal PhytoKeys.
"I love the Proteaceae – the family of flowering plants that includes the Banksia and Grevillea genera in Australia and Protea in South Africa," Ms Stimpson said. "Surprisingly, molecular evidence ...
Women 40% less likely to die after TAVI than men
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 27 2012: Women with severe aortic stenosis are 40% less likely to die after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) than men, reveals the latest data from the largest study to date of gender differences in outcomes after TAVI. The findings were presented at ESC Congress 2012 by Professor Karin Humphries from St. Paul's Hospital.
More than 1.5 million people in the US suffer from aortic stenosis, a progressive disease where the aortic valve becomes obstructed, leading to life-threatening heart problems. If left untreated, half of all patients ...
TAVI improves quality of life in patients with severe aortic stenosis for at least 1 year
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) leads to meaningful improvements in health-related quality of life in patients with severe aortic stenosis that are maintained for at least 1 year, according to a study presented at ESC Congress 2012. The results from the German transcatheter aortic valve interventions registry were presented by Professor Till Neumann, MD, from Essen, Germany.
Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease with increasing incidence especially with regard to the ageing of the population. Today, ...
Lifestyle changes could prevent 400 cardiac events and 200 deaths in Swedish PCI patients
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 27 2012: Up to 400 cardiac events and 200 deaths in Swedish PCI patients could be avoided by following a heart healthy lifestyle, according to research from the SPICI study presented at ESC Congress 2012. The results were presented at ESC press conference by Professor Joep Perk from Linnaeus University and at the scientific session by Dr Roland CARLSSON.
The benefits of adherence to a heart healthy lifestyle in combination with drug treatment after an acute myocardial infarction treated with coronary artery balloon intervention (PCI) have recently ...
Smoking after stroke increases death risk by 3-fold
2012-08-28
Munich, Germany – August 28 2012: Patients who resume smoking after a stroke increase their risk of death by three-fold, according to research presented at ESC Congress 2012 by Professor Furio Colivicchi from San Filippo Neri Hospital. The researchers also found that the earlier patients resume smoking, the greater their risk of death with one year.
"It is well established that smoking increases the risk of having a stroke," said Professor Colivicchi. "Quitting smoking after an acute ischemic stroke may be more effective than any medication in reducing the risk of further ...
African research identifies strong candidate for possible single-dose malaria cure
2012-08-28
A recently discovered compound from the aminopyridine class not only has the potential to become part of a single-dose cure for all strains of malaria, but might also be able to block transmission of the parasite from person to person, according to a research collaboration involving the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV), based in Switzerland, and the Drug Discovery and Development Centre (H3-D) at the University of Cape Town, South Africa. On the basis of initial results it was selected by MMV for further development – making it the first compound researched on African ...