(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.H. -- Looking at a hagfish – an eyeless, snot-covered, worm-like scavenger of the deep –the last thing that comes to mind is sex. Yet the reproductive functioning of these ancient vertebrates is such an enduring enigma that a gold medal was once offered to anyone who could elucidate it.
Although the prize expired, unclaimed, long ago, University of New Hampshire professor of biochemistry Stacia Sower and colleagues at two Japanese universities have identified the first reproductive hormone of the hagfish – a gonadatropin -- representing a significant step toward unraveling the mystery of hagfish reproduction. Their findings, "Evolutionary origin of a functional gonadotropin in the pituitary of the most primitive vertebrate, hagfish," were published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academies of Science (PNAS) in September.
"This is a significant breakthrough with hagfish," says Sower, who was second senior author on this paper, co-authored by principal investigator Katsuhisa Uchida and Sower's long-time collaborator Masumi Nozaki, both of Niigata University in Japan. Gonadatropins (GTHs) are a protein secreted from the pituitary, stimulating the gonads (ovaries and testes) to produce and release the sex steroid hormones which prompt their growth and maturation. GTHs are produced in response to hypothalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), what Sower calls the "master molecule" for reproduction in vertebrates; its discovery remains the holy grail of understanding hagfish reproduction.
At 500 million years old, hagfish are the oldest living vertebrate, predating the dinosaurs. "They're one of evolution's great success stories," says Sower, who has devoted the majority of her 30-year career researching hagfish and the similarly un-charismatic lamprey eels. "Here's this animal with a backbone that we don't know anything about." They're notoriously difficult to study, in part because their habitat is the ocean floor at 100 meters or more.
Yet their important evolutionary position makes hagfish worthy of scientific inquiry. "We look at the evolution of the hormones and receptors and say, 'have they retrained characteristics of their ancestral forms, or are they more similar to higher vertebrates?'" says Sower. "They're a key to understanding the evolution of later evolved vertebrates."
Compounding the urgency of better understanding hagfish reproduction is their growing importance as a fishery in the Gulf of Maine. Despite their vicious nature and least appealing characteristic – the stress-induced secretion of mucous from up to 200 slime glands along their bodies – hagfish are prized, particularly in Asian markets. Their tough, soft skin is marketed as "eel" skin for wallets, belts and other items ("Because they're not going to sell something that says 'hagfish,'" says Sower, pulling out her own flawless 20-year-old eel skin wallet).
Fished in the Gulf of Maine since 1992, hagfish have been fished out of the waters off Korea and Japan and overfished on the U.S. West coast. They also play a significant role in nutrient cycling and ocean-floor clean-up, feeding primarily on dead and dying fish. Lacking knowledge on their reproductive functions – how, when and where they spawn – the hagfish could be fished to extinction, says Sower.
Sower, who directs the Center for Molecular and Comparative Endocrinology at UNH, has worked with Nozaki on hagfish reproduction since both scientists were postdoctoral researchers at the University of Washington in 1980. The two, along with Hiroshi Kawauchi of Kitasato University in Japan, have shared students and researchers through a formal collaboration that's produced more than 30 papers. It's also, notes Sower, produced many failures as they've labored to identify the hagfish GTH.
"Now we're filling in the gaps of what we know," she says.
###
To download a copy of the paper, go to http://www.pnas.org/content/107/36/15832.long.
This work was supported in part by a grant from the National Science Foundation.
The University of New Hampshire, founded in 1866, is a world-class public research university with the feel of a New England liberal arts college. A land, sea, and space-grant university, UNH is the state's flagship public institution, enrolling 12,200 undergraduate and 2,200 graduate students.
Photographs available to download:
http://www.unh.edu/news/cj_nr/2010/oct/bp04hagfish_02.jpg
Caption: University of New Hampshire professor of biochemistry Stacia Sower and colleagues have identified the first reproductive hormone of the hagfish, the world's oldest living vertebrate. Credit: Courtesy of Stacia Sower.
http://www.unh.edu/news/cj_nr/2010/oct/bp04hagfish_01.jpg
Caption: UNH professor Stacia Sower and researchers in her lab collect hagfish from the Gulf of Maine for study. Credit: Courtesy of Stacia Sower.
http://www.unh.edu/news/cj_nr/2010/oct/bp04hagfish_03.jpg
Caption: UNH professor Stacia Sower (in orange) and researchers in her lab collect hagfish from the Gulf of Maine for study. Credit: Courtesy of Stacia Sower.
END
Researchers from Northwestern University and NorthShore University HealthSystem (NorthShore) have developed a method to detect early signs of lung cancer by examining cheek cells in humans using pioneering biophotonics technology.
"By examining the lining of the cheek with this optical technology, we have the potential to prescreen patients at high risk for lung cancer, such as those who smoke, and identify the individuals who would likely benefit from more invasive and expensive tests versus those who don't need additional tests," said Hemant K. Roy, M.D., director ...
Berkeley – Exposure to dirty air is linked to decreased function of a gene that appears to increase the severity of asthma in children, according to a joint study by researchers at Stanford University and the University of California, Berkeley.
While air pollution is known to be a source of immediate inflammation, this new study provides one of the first pieces of direct evidence that explains how some ambient air pollutants could have long-term effects.
The findings, published in the October 2010 issue of the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, come from ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Doppler weather radar will significantly improve forecasting models used to track monsoon systems influencing the monsoon in and around India, according to a research collaboration including Purdue University, the National Center for Atmospheric Research and the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi.
Dev Niyogi, a Purdue associate professor of agronomy and earth and atmospheric sciences, said modeling of a monsoon depression track can have a margin of error of about 200 kilometers for landfall, which can be significant for storms that produce as ...
The GOES-13 satellite passed over a low pressure area designated as "System 97L" earlier today and captured a visible image of the low in the eastern Caribbean Sea. System 97L appears in a good place for development into a tropical depression in the next day or two.
The National Hurricane Center currently gives the low pressure area known as System 97L an "80 percent chance of developing into a tropical depression in the next 48 hours." The low pressure area is located just north of the Virgin Islands near 19.0 North latitude and 65.3 West longitude. The visible image ...
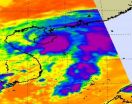
The northwestern Pacific Ocean is just as active as the Atlantic Ocean this hurricane season. The fourteenth tropical depression formed near Hainan Island, China this morning and its birth was captured by a NASA infrared satellite instrument. The NASA image showed the depression's strong thunderstorms near its center and east of its center.
NASA's Aqua satellite flew over Tropical Depression 14W (TD14W) today, October 5 at 06:05 UTC (2:05 a.m. EDT). Infrared imagery from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument onboard the Aqua satellite revealed a concentrated ...
A new species of dinosaur discovered in Arizona suggests dinosaurs did not spread throughout the world by overpowering other species, but by taking advantage of a natural catastrophe that wiped out their competitors.
The new dinosaur, named Sarahsaurus, was studied by an international team of scientists, including Robert R. Reisz, professor and chair of biology at the University of Toronto Mississauga, Tim Rowe, professor of paleontology at the University of Texas at Austin's Jackson School of Geosciences and Hans-Dieter Sues, curator of vertebrate paleontology at the ...
The Red Planet bleeds. Not blood, but its atmosphere, slowly trickling away to space. The culprit is our sun, which is using its own breath, the solar wind, and its radiation to rob Mars of its air. The crime may have condemned the planet's surface, once apparently promising for life, to a cold and sterile existence.
Features on Mars resembling dry riverbeds, and the discovery of minerals that form in the presence of water, indicate that Mars once had a thicker atmosphere and was warm enough for liquid water to flow on the surface. However, somehow that thick atmosphere ...
GREENBELT, Md. – NASA's mission to investigate the mystery of how Mars lost much of its atmosphere passed a critical milestone on October 4, 2010. NASA has given approval for the development and 2013 launch of the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission.
Clues on the Martian surface, such as features resembling dry riverbeds and minerals that only form in the presence of liquid water, suggest that Mars once had a denser atmosphere, which supported the presence of liquid water on the surface. As part of a dramatic climate change, most of the Martian atmosphere ...
With the Major League Baseball Division Series set to begin, associate math professor Bruce Bukiet at NJIT is performing his analysis of the probability of each team advancing to the League Championship Series. "Going into these series, the Philadelphia Phillies have a 64 percent chance of defeating the Cincinnati Reds in their best of five game series," he said.
"The Texas Rangers, New York Yankees and San Francisco Giants have slight advantages to win series over their opponents, the Tampa Bay Rays, Minnesota Twins and Atlanta Braves respectively in the first round ...
DALLAS – Oct. 6, 2010 – A set of proteins found in blood serum shows promise as a sensitive and accurate way to diagnose Alzheimer's disease, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have found as part of a statewide study.
An analysis of the proteins, plus a clinical exam, proved 94 percent accurate in detecting suspected Alzheimer's and 84 percent accurate in ruling it out in people without the disease, the researchers said.
"This research uses a novel technology that makes it possible to analyze several biomarkers in a single blood sample in a cost-effective ...