(Press-News.org) Alexandria, Va., USA – In a study titled "Prevalence of Periodontis in Adults in the United States: 2009 and 2010," lead author Paul Eke, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, estimates the prevalence, severity and extent of periodontitis in the adult U.S population using data from the 2009 and 2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) cycle. The study is published in the Journal of Dental Research, the official publication of the International and American Associations for Dental Research (IADR/AADR).
Estimates were derived from a sample of 3,742 adults 30 years and older with one or more natural teeth of the civilian non-institutionalized population. Attachment loss and probing depth were measured at six sites per tooth on all teeth (except the third molars). The study is important because it is the first national probability sample that has employed a full-mouth periodontal examination protocol versus previous partial mouth examinations.
Of the sample presented, 47.2 percent, representing 64.7 million adults, had periodontitis distributed as 8.7 percent, 30.0 percent and 8.5 percent with mild, moderate and severe periodontitis respectively. For adults 65 years and older, 64 percent had either moderate or severe periodontitis. These estimates are far higher than previous national estimates.
Periodontitis was highest in males, Mexican Americans, adults with less than high school education, adults below 100% Federal Poverty Levels, and current smokers. This survey has provided direct evidence for a high burden of periodontitis in the adult U.S. population, especially among adults 65 and older.
"The IADR/AADR Journal of Dental Research is pleased to publish this study about the prevalence of periodontis in adult Americans," said JDR Editor-in-Chief William Giannobile. "This study provides an in-depth look at the socio-demographic breakdown of periodontal disease in U.S. adults."
A perspective article titled "The prevalence of periodontics in the US: Forget what you were told" was written by Panos Papapanou, Columbia University. In it, Papapanou writes that the data presented by Eke et al. challenge us to rethink certain issues and to conduct the appropriate research that will produce evidence-based answers.
###
Visit http://jdr.sagepub.com/content/early/recent for links to the complete articles or contact Ingrid L. Thomas at ithomas@iadr.org to request the PDFs.
About the Journal of Dental Research
The IADR/AADR Journal of Dental Research is a multidisciplinary journal dedicated to the dissemination of new knowledge in all sciences relevant to dentistry and the oral cavity and associated structures in health and disease.
About the International Association for Dental Research
The International Association for Dental Research (IADR) is a nonprofit organization with more than 12,000 individual members worldwide, dedicated to: (1) advancing research and increasing knowledge to improve oral health, (2) supporting the oral health research community, and (3) facilitating the communication and application of research findings for the improvement of oral health worldwide. To learn more, visit www.iadr.org. The American Association for Dental Research (AADR) is the largest Division of IADR, with nearly 4,000 members in the United States. To learn more, visit www.aadronline.com.
END
VIDEO:
An animation of NOAA's GOES-13 satellite observations from Aug. 28-30, 2012, shows Hurricane Isaac make two landfalls in southeastern Louisiana on Aug. 28 at 7:45 p.m. EDT (1145 UTC) and...
Click here for more information.
NASA satellites are providing forecasters with data on rainfall rates within Tropical Storm Isaac as it continues to track over Louisiana, Mississippi and spread northward into the lower Mississippi Valley. Isaac has a large supply of rain, drawing ...
Pregnant women who are highly exposed to common environmental chemicals - polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFCs) - have babies that are smaller at birth and larger at 20 months of age, according to a study from Emory University's Rollins School of Public Health published online in the August 30 edition of Environmental Health Perspectives.
PFCs are used in the production of fluoropolymers and are found widely in protective coatings of packaging products, clothes, furniture and non-stick cookware. They are persistent compounds found abundantly in the environment and human exposure ...
Leaders often use rousing speeches to evoke powerful emotions, and those emotions may predict when a group will commit an act of violence or terrorism, according to new research published in the journal Behavioral Sciences of Terrorism and Political Aggression. Analysis of speeches delivered by government, activist and terrorist leaders found that leaders' expressions of anger, contempt and disgust spiked immediately before their group committed an act of violence.
"When leaders express a combination of anger, contempt and disgust in their speeches, it seems to be instrumental ...
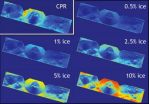
Small patches of ice could make up at most five to ten percent of material in walls of Shackleton crater.
Scientists using the Mini-RF radar on NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) have estimated the maximum amount of ice likely to be found inside a permanently shadowed lunar crater located near the moon's South Pole. As much as five to ten percent of material, by weight, could be patchy ice, according to the team of researchers led by Bradley Thomson at Boston University's Center for Remote Sensing, in Mass.
"These terrific results from the Mini-RF team contribute ...
Leipzig. More than 250 international scientists will be meeting in the first week of September in Leipzig to share their experiences on the latest methods and applications using stable isotopes. Stable isotopes are a tool that can be used in a wide range of areas in natural sciences and medicine as, with their help, it is possible to establish the origin of substances, and dynamic processes can be made visible. For example, it is possible to establish where a red wine really comes from, the cause of water damage, how the concentration of carbon dioxide at the South Pole ...
As the nation's fastest-growing immigrant group, Asian Americans are likely to be a key constituency in the 2012 presidential election, but this community is far from a monolithic voting bloc, says Russell Jeung, associate professor of Asian American studies at San Francisco State University.
Jeung has published an analysis of Asian American voting patterns in the 2008 presidential election, including a breakdown of nine ethnic groups and 11 religious affiliations that make up the Asian American vote.
"Usually people act in a racial bloc or a religious bloc," Jeung ...
In the foothills of the Santa Cruz Mountains two closely related species of mice share a habitat and a genetic lineage, but have very different social lives. The California mouse (Peromyscus californicus) is characterized by a lifetime of monogamy; the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) is sexually promiscuous.
Researchers at the University of California Berkeley recently showed how these differences in sexual behavior impact the bacteria hosted by each species as well as the diversity of the genes that control immunity. The results were published in the May 2012 edition ...
(CHICAGO)-- Assessment of sexual function should be incorporated into cardiovascular risk evaluation for all men, regardless of the presence or absence of known cardiovascular disease, according to Dr. Ajay Nehra, lead author of a report by the Princeton Consensus (Expert Panel) Conference, a collaboration of 22 international, multispecialty researchers. Nehra is vice chairperson, professor and director of Men's Health in the Department of Urology at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a red flag in younger men, less than 55 years of ...
This release is available in German.
The analyses of an international team of researchers led by Svante Pääbo of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, show that the genetic variation of Denisovans was extremely low, suggesting that although they were present in large parts of Asia, their population was never large for long periods of time. In addition, a comprehensive list documents the genetic changes that set apart modern humans from their archaic relatives. Some of these changes concern genes that are associated with brain function ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. — Bacteria in hyenas' scent glands may be the key controllers of communication.
The results, featured in the current issue of Scientific Reports, show a clear relationship between the diversity of hyena clans and the distinct microbial communities that reside in their scent glands, said Kevin Theis, the paper's lead author and Michigan State University postdoctoral researcher.
"A critical component of every animal's behavioral repertoire is an effective communication system," said Theis, who co-authored the study with Kay Holekamp, MSU zoologist. ...