(Press-News.org)
Western scrub jays summon others to screech over the body of a dead jay, according to new research from the University of California, Davis. The birds' cacophonous "funerals" can last for up to half an hour.
Anecdotal reports have suggested that other animals, including elephants, chimpanzees and birds in the crow family, react to dead of their species, said Teresa Iglesias, the UC Davis graduate student who carried out the work. But few experimental studies have explored this behavior.
The new research by Iglesias and her colleagues appears in the Aug. 27 issue of the journal Animal Behaviour.
Western scrub jays live in breeding pairs and are not particularly social birds.
"They're really territorial and not at all friendly with other scrub-jays," Iglesias said.
Working in the backyards of homes in Davis, Calif., Iglesias set up feeding tables to encourage visits from the jays. Then she videotaped their behavior when she placed a dead jay on the ground. She compared these reactions with the birds' behavior when confronted with a dead jay that had been stuffed and mounted on a perch, a stuffed horned owl, and wood painted to represent jay feathers.
On encountering a dead jay, prostrate on the ground, jays flew into a tree and began a series of loud, screeching calls that attracted other jays. The summoned birds perched on trees and fences around the body and joined in the calling. These cacophonous gatherings could last from a few seconds to as long as 30 minutes.
Jays formed similar cacophonous gatherings in response to a mounted owl, but ignored painted wood. When confronted with a mounted jay, the birds swooped in on it as if it were an intruder.
Jays typically gathered within seconds of the first bird calling, Iglesias said. If they did not, the first jay would often fly higher into a tree, apparently to call more widely.
"It looked like they were actively trying to attract attention," she said.
The purpose of the calls seems to be to alert other birds of danger, Iglesias said. But why the calls summon others, rather than warning them off, is unclear. Having more jays present might mean more eyes to locate a predator, or more numbers to drive it away, she speculates.
There might also be a learning component to the gatherings, if they help teach young jays about dangers in the environment, Iglesias said.
While reactions of animals to their dead are sometimes called "funerals," that does not imply that there is an emotional or ritual element to the behavior, Iglesias said. We simply don't know enough about the emotional life of animals to understand that.
But Iglesias isn't ruling it out. "I think there's a huge possibility that there is much more to learn about the social and emotional lives of birds," she said.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the paper are UC Davis scientists Gail Patricelli, a professor of evolution and ecology, and Richard McElreath, an associate professor of anthropology.
Their work was supported by a Gates Millennium Graduate Scholarship from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and UC Davis funds to support graduate students.
Scrub jays react to their dead
2012-09-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Protein linked to therapy resistance in breast cancer
2012-09-12
A gene that may possibly belong to an entire new family of oncogenes has been linked by researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) to the resistance of breast cancer to a well-regarded and widely used cancer therapy.
One of the world's leading breast cancer researchers, Mina Bissell, Distinguished Scientist with Berkeley Lab's Life Sciences Division, led a study in which a protein known as FAM83A was linked to resistance to the cancer drugs known as EGFR-TKIs (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase ...
What are the effects of the Great Recession on local governments?
2012-09-12
Freezing positions and cutting workforces
Trimming pension and health care costs and passing them to employees
Lowering service delivery levels, but not imposing many new fees
Using technology to reduce costs where possible
Receiving added pressure but little help from States and the Federal Government
This important new research sheds light on the challenges faced by city and county governments that must provide most basic services. Unlike federal or state governments, these local governments have limited ability to generate revenue and are often mandated to pay for ...
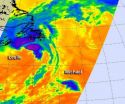
NASA infrared data reveals fading Tropical Storm Leslie and peanut-shaped Michael
2012-09-12
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over the Atlantic on Sept. 11 it caught Tropical Storm Leslie's clouds over Newfoundland and peanut-shaped Tropical Storm Michael to its southwest. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured infrared data on Tropical Storms Leslie and Michael when it passed overhead on Sept. 11.
Michael Appears Peanut-Shaped on Satellite Imagery
Tropical Storm Michael forecast to become a remnant low later today, Sept. 11, but as of 11 a.m. EDT Michael still had maximum sustained winds near 45 mph (75 kmh). It was located about 1,090 ...
Yellow lights mean drivers have to make right choice -- if they have time
2012-09-12
A couple of years ago, Hesham Rakha misjudged a yellow traffic light and entered an intersection just as the light turned red. A police officer handed him a ticket.
"There are circumstances, as you approach a yellow light, where the decision is easy. If you are close to the intersection, you keep going. If you are far away, you stop. If you are almost at the intersection, you have to keep going because if you try to stop, you could cause a rear-end crash with the vehicle behind you and would be in the middle of the intersection anyway," said Rakha, professor of civil ...
Genetic make-up of children explains how they fight malaria infection
2012-09-12
Researchers from Sainte-Justine University Hospital Center and University of Montreal have identified several novel genes that make some children more efficient than others in the way their immune system responds to malaria infection. This world-first in integrative efforts to track down genes predisposing to specific immune responses to malaria and ultimately to identify the most suitable targets for vaccines or treatments was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences by lead author Dr. Youssef Idaghdour and senior author Pr. Philip Awadalla, whose ...
Scientists discover how the brain ages
2012-09-12
The ageing process has its roots deep within the cells and molecules that make up our bodies. Experts have previously identified the molecular pathway that react to cell damage and stems the cell's ability to divide, known as cell senescence.
However, in cells that do not have this ability to divide, such as neurons in the brain and elsewhere, little was understood of the ageing process. Now a team of scientists at Newcastle University, led by Professor Thomas von Zglinicki have shown that these cells follow the same pathway.
This challenges previous assumptions ...
Uncertain about health outcomes, male stroke survivors more likely to suffer depression than females
2012-09-12
Philadelphia, PA, September 12, 2012 – Post-stroke depression is a major issue affecting approximately 33% of stroke survivors. A new study published in the current issue of Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation reports that the level to which survivors are uncertain about the outcome of their illness is strongly linked to depression. The relationship is more pronounced for men than for women.
"Male stroke survivors in the US who subscribe to traditional health-related beliefs may be accustomed to, and value highly, being in control of their health," says ...
Information theory helps unravel DNA's genetic code
2012-09-12
DNA consists of regions called exons, which code for the synthesis of proteins, interspersed with noncoding regions called introns. Being able to predict the different regions in a new and unannotated genome is one of the biggest challenges facing biologists today. Now researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology in Delhi have used techniques from information theory to identify DNA introns and exons an order of magnitude faster than previously developed methods. The researchers were able to achieve this breakthrough in speed by looking at how electrical charges are ...
Going with the flow
2012-09-12
Scientists who study tissue engineering and test new drugs often need to sort, rotate, move, and otherwise manipulate individual cells. They can do this by prodding the cells into place with a mechanical probe or coaxing them in the desired direction with acoustic waves, electric fields, or flowing fluids. Techniques that rely on direct physical contact can position individual cells with a high level of precision while non-contact techniques are often faster for sorting large numbers of cells. An international team of researchers has now developed a way to manipulate cells ...
Less wear, longer life for memory storage device
2012-09-12
Probe storage devices read and write data by making nanoscale marks on a surface through physical contact. The technology may one day extend the data density limits of conventional magnetic and optical storage, but current probes have limited lifespans due to mechanical wear. A research team, led by Intel Corp., has now developed a long-lasting ultrahigh-density probe storage device by coating the tips of the probes with a thin metal film. The team's device features an array of 5,000 ultrasharp probes that is integrated with on-chip electronic circuits. The probes write ...