(Press-News.org) Researchers have taken a key step towards recovering specific brain functions in sufferers of brain disease and injuries by successfully restoring the decision-making processes in monkeys.
By placing a neural device onto the front part of the monkeys' brains, the researchers, from Wake Forest Baptist Medical Centre, University of Kentucky and University of Southern California, were able to recover, and even improve, the monkeys' ability to make decisions when their normal cognitive functioning was disrupted.
The study, which has been published today, 14 September, in IOP Publishing's Journal of Neural Engineering, involved the use of a neural prosthesis, which consisted of an array of electrodes measuring the signals from neurons in the brain to calculate how the monkeys' ability to perform a memory task could be restored.
In the delayed match-to-sample task an image was flashed onto a screen and, after a delay, the monkeys were prompted to select the same image on the screen from a sampling which included 1-7 other images. Five monkeys (all rhesus, Macaca mulatta) were involved in the experiment and were trained for two years to perform to a 70-75 per cent proficiency in the task.
The movement of the monkeys' arms were tracked with a camera and translated to movements of the cursor on the screen; they were awarded with a drop of juice when they correctly matched an image.
The prosthesis was placed into two cortical layers – L2/3 and L5 – of the brain and recorded brain activity within structures known as minicolumns in the prefrontal cortex area.
Once it was confirmed that minicolumn communication between layers L2/3 and L5 was involved in decision making, it was supressed by administering the dopamine-modifying drug, cocaine, to the monkeys. The task was performed again but this time the researchers deployed a 'multi-input multi-output nonlinear' (MIMO) model to stimulate the neurons that were used in the task.
"The MIMO model is a specific type of calculation which looks for the complex mathematical relationship between an input (L2/3) and an output (L5). In the case of neural activity, the output is typically the pattern of firing of individual neurons during the task.
"Inputs to that pattern may be blood flow, temperature, the electrical activity of other neurons, and even the prior electrical activity of the same cell," said lead author of the study Professor Robert Hampson.
By recording the inputs from layer L2/3 neurons, the MIMO model could predict the output of layer L5 neurons and thus, through the electrodes, electrically stimulate the same necessary L5 neurons. The results showed that the MIMO model was exceedingly effective in recovering performance of the task and was even able to improve performance under normal conditions.
"The reason the MIMO model was effective in improving performance in the task was because we specifically 'tuned' the model to analyze the firing of neurons that occurred when the animals correctly performed the behavioral task; the brain doesn't always produce the full 'correct' pattern on every trial," said senior author Professor Sam Deadwyler
On the utilization of this method in the treatment of human brain conditions, Professor Deadwyler continued: "In the case of brain injury or disease where larger areas are affected, the system would record the inputs to that area from other areas and, when they occur, program the delivery of the appropriate output patterns to brain regions that normally receive signals from the injured area, thereby restoring lost brain function."
All animal procedures were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Wake Forest University, in accordance with U.S. Department of Agriculture, International Association for the Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care, and National Institutes of Health guidelines.
###
Notes to Editors
Contact
1. For further information, a full draft of the journal paper or contact with one of the researchers, contact IOP Press Officer, Michael Bishop: Tel: 0117 930 1032
E-mail: Michael.bishop@iop.org
Facilitation and restoration of cognitive function in primate prefrontal cortex by a neuroprosthesis that utilizes minicolumn-specific neural firing
2. The published version of the paper "Facilitation and restoration of cognitive function in primate prefrontal cortex by a neuroprosthesis that utilizes minicolumn-specific neural firing" Robert E Hampson et al 2012 J. Neural Eng. 9 056012 will be freely available online from 14 September.
Journal of Neural Engineering
3. Journal of Neural Engineering was created to help scientists, clinicians and engineers to understand, replace, repair and enhance the nervous system.
IOP Publishing
4. IOP Publishing provides publications through which leading-edge scientific research is distributed worldwide. IOP Publishing is central to the Institute of Physics (IOP), a not-for-profit society. Any financial surplus earned by IOP Publishing goes to support science through the activities of IOP. Beyond our traditional journals programme, we make high-value scientific information easily accessible through an ever-evolving portfolio of community websites, magazines, conference proceedings and a multitude of electronic services. Focused on making the most of new technologies, we're continually improving our electronic interfaces to make it easier for researchers to find exactly what they need, when they need it, in the format that suits them best. Go to http://ioppublishing.org/.
The Institute of Physics
5. The Institute of Physics is a leading scientific society promoting physics and bringing physicists together for the benefit of all.
It has a worldwide membership of around 40 000 comprising physicists from all sectors, as well as those with an interest in physics. It works to advance physics research, application and education; and engages with policymakers and the public to develop awareness and understanding of physics. Its publishing company, IOP Publishing, is a world leader in professional scientific Go to www.iop.org
Neural implant recovers ability to make decisions
2012-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Charting the SH2 pool
2012-09-14
New research published in BioMed Central's open access journal Cell Communication and Signaling describes a large set of interactions (interactome) which maps the range of phosphotyrosine (pTyr)-dependent interactions with SH2 domains underlying insulin (Ins), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling pathways.
In the control of cell signaling pathways SH2 domains can be thought of as a master connector and tyrosine kinases the switch. SH2 domains interact with phosphorylated tyrosine containing peptides on receptors and other ...
Met Office model to better predict extreme winters
2012-09-14
Severe UK winters, like the 'big freeze' of 2009/10, can now be better forecast months in advance using the Met Office's latest model, new research suggests.
A new study, published today, Friday 14 September, in IOP Publishing's journal Environmental Research Letters, compares the latest seasonal forecast system to the one previously used and shows that it can better warn the UK of extreme winter weather conditions.
Dubbed the 'high-top' system, it is different from the previous system as it takes into account phenomenon known as sudden stratospheric warmings (SSWs), ...
Foraging baboons are picky punters
2012-09-14
In a study published today in The American Naturalist, a group of scientists led by the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) have used a technique developed to study human consumer choices to investigate what influences a baboon's foraging decisions. The technique, known as discrete choice modelling, has rarely been used before in animal behaviour research. It showed how baboons not only consider many social and non-social factors when making foraging decisions, but also how they change these factors depending on their habitat and their own social traits.
Over a six month ...
Children's intensive care units performing well despite low staffing levels
2012-09-14
Standards of care in children's intensive care units come under scrutiny in a new audit report published today by the University of Leeds and the University of Leicester.
The report, commissioned by the Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership and carried out by the Paediatric Intensive Care Audit Network (PICANet) showed that death rates in children's intensive care units are low and continue to fall. However, there continues to be a higher risk of mortality for children of south Asian origin observed in earlier years.
This national audit also found that only 5 children's ...
Sharing the research on car-sharing
2012-09-14
Montreal, September 13, 2012 – Share and share alike is a concept we all learn as youngsters. Of course, when it comes to something as personal – and expensive – as a car, sharing's not so easy. Due to rising fuel costs hitting hard, increased concerns about the environment and overcrowded cities, car-sharing services like Communauto are becoming a popular way to get around. Can they be more popular still?
Researchers from the Concordia Institute of Information Systems Engineering can answer this question with a resounding "yes." They have piloted a computer model that ...
Do SAT scores help or hurt in decisions about who will do well in college?
2012-09-14
Every year, nervous high school juniors and seniors, clutching #2 pencils and armed with hours of test preparation, sit down and take the SAT. At their most basic, these tests focus on verbal, math, and writing ability, and performance on these tests has been linked to subsequent academic performance. As a result, college admissions teams use SAT scores along with other information, such as high school grades, in choosing their incoming freshman classes.
It is perhaps no surprise, then, that the SAT has been the subject of much scrutiny. Some researchers have asserted ...
Kids with food allergies can fall through the cracks
2012-09-14
CHICAGO --- More can be done to properly manage the care of American children with food allergies, especially when it comes to diagnostic testing and recognizing non-visual symptoms of severe allergic reactions, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study.
"Every child with a food allergy should be diagnosed by a physician, have access to life-saving medication such as an epinephrine autoinjector and receive confirmation of the disease through diagnostic testing," said lead author Ruchi Gupta, M.D., an associate professor of pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg ...
Honestly? Just sign here -- first
2012-09-14
Toronto – Tax collectors and insurance agencies trying to boost honest reporting could improve compliance simply by asking people to sign their forms at the beginning instead of at the end.
That's because attesting to the truthfulness of the information before a form is filled out tends to activate people's moral sense, making it harder for them to fudge their numbers after, says a new paper.
"Based on our previous research we knew that an honour code is useful, but we were wondering how much the location mattered," says Nina Mazar, an assistant professor of marketing ...
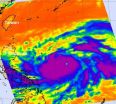
NASA sees Sanba become a super typhoon
2012-09-14
Tropical Storm Sanba exploded in intensity between Sept. 12 and 13, becoming a major Category 4 Typhoon on the Saffir-Simpson Scale. NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data that showed a large area of powerful thunderstorms around the center of circulation, dropping heavy rain over the western North Pacific Ocean.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Super Typhoon Sanba on Sept. 13 at 0447 UTC (12:47 a.m. EDT). The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument captured an infrared image of Sanba and found an eye about 20 nautical miles (23 miles/37 km) wide, surrounded ...
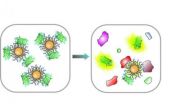
UMass Amherst chemists develop nose-like sensor array to 'smell' cancer diagnoses
2012-09-14
AMHERST, Mass. – In the fight against cancer, knowing the enemy's exact identity is crucial for diagnosis and treatment, especially in metastatic cancers, those that spread between organs and tissues. Now chemists led by Vincent Rotello at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have developed a rapid, sensitive way to detect microscopic levels of many different metastatic cell types in living tissue. Findings appear in the current issue of the journal ACS Nano.
In a pre-clinical non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis model in mice developed by Frank Jirik and colleagues ...