(Press-News.org) Researchers from the Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research analysed data on the diet, exercise and personality type of more than 7000 people.
The study found those who believe their life can be changed by their own actions ate healthier food, exercised more, smoked less and avoided binge drinking.
Professor Deborah Cobb-Clark, Director of the Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, said those who have a greater faith in 'luck' or 'fate' are more likely to live an unhealthy life.
"Our research shows a direct link between the type of personality a person has and a healthy lifestyle," she said.
Professor Cobb-Clark hoped the study would help inform public health policies on conditions such as obesity.
"The main policy response to the obesity epidemic has been the provision of better information, but information alone is insufficient to change people's eating habits," she said.
"Understanding the psychological underpinning of a person's eating patterns and exercise habits is central to understanding obesity."
The study also found men and women hold different views on the benefits of a healthy lifestyle.
Men wanted physical results from their healthy choices, while women were more receptive to the everyday enjoyment of leading a healthy lifestyle.
Professor Cobb-Clarke said the research demonstrated the need for more targeted policy responses.
"What works well for women may not work well for men," she said.
"Gender specific policy initiatives which respond to these objectives may be particularly helpful in promoting healthy lifestyles."
###The study used data from the Household, Income and Labour Dynamics in Australia (HILDA) Survey.
Healthy outlook leads to a healthy lifestyle: study
2012-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
X-rays unravel mysterious degradation of a Van Gogh painting
2012-09-14
Hamburg / Grenoble 14 September 2012 (jointly released by the ESRF and DESY): With a sophisticated X-ray analysis scientists have identified why parts of the Van Gogh painting "Flowers in a blue vase" have changed colour over time: a supposedly protective varnish applied after the master's death has made some bright yellow flowers turn to an orange-grey colour. The origin of this alteration is a hitherto unknown degradation process at the interface between paint and varnish, which studies at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility ESRF in Grenoble (France) and at Deutsches ...
Scripps Research Institute scientists show protein linked to hunger also implicated in alcoholism
2012-09-14
LA JOLLA, CA – Researchers at The Scripps Research Institute have found new links between a protein that controls our urge to eat and brain cells involved in the development of alcoholism. The discovery points to new possibilities for designing drugs to treat alcoholism and other addictions.
The new study, published online ahead of print by the journal Neuropsychopharmacology, focuses on the peptide ghrelin, which is known to stimulate eating.
"This is the first study to characterize the effects of ghrelin on neurons in a brain region called the central nucleus of the ...
Roman military camp dating back to conquest of Gaul throws light on part of world history
2012-09-14
In the vicinity of Hermeskeil, a small town some 30 kilometers southeast of the city of Trier in the Hunsrueck region in the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate, archaeologists from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have confirmed the location of the oldest Roman military fortification known in Germany to date. These findings shed new light on the Roman conquest of Gaul. The camp was presumably built during Julius Caesars' Gallic War in the late 50s B.C. Nearby lies a late Celtic settlement with monumental fortifications known as the "Hunnenring" or "Circle ...
Learning faster with neurodegenerative disease
2012-09-14
People who bear the genetic mutation for Huntington's disease learn faster than healthy people. The more pronounced the mutation was, the more quickly they learned. This is reported by researchers from the Ruhr-Universität Bochum and from Dortmund in the journal Current Biology. The team has thus demonstrated for the first time that neurodegenerative diseases can go hand in hand with increased learning efficiency. "It is possible that the same mechanisms that lead to the degenerative changes in the central nervous system also cause the considerably better learning efficiency" ...
Whole-genome scan helps select best treatment for childhood cancer
2012-09-14
A whole-genome scan to identify large-scale chromosomal damage can help doctors choose the best treatment option for children with neuroblastoma, one of the most common types of childhood cancer, finds an international collaboration jointly led by The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
The researchers called for all children diagnosed with neuroblastoma worldwide to have a whole-genome scan as a standard part of their treatment.
Neuroblastoma, a cancer of the developing nervous system, is sometimes very treatable but other forms are highly aggressive, making the ...
New test to crack down on sporting drugs-cheat test
2012-09-14
Scientists from three UK universities have developed a new test to catch drugs-cheats in sport.
Over the last 10 years, the GH-2004 team, which is based the University of Southampton, has been developing a test for Growth Hormone misuse in sport with funding from the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) and US Anti-Doping Agency and with support from UK Anti-Doping.
The test, developed by scientists at the University of Southampton, King's College London and University of Kent at Canterbury, is based on the measurement of two proteins in the blood, insulin-like growth factor-I ...
Researchers find our inner reptile hearts
2012-09-14
Since the early 1900s, scientists have been wondering how birds and mammals could have developed almost identical conduction systems independently of each other when their common ancestor was a cold-blooded reptile with a sponge-like inner heart that has virtually no conduction bundles.
The studies show that it is simply the spongy inner tissue in the foetal heart that gets stretched out to become a fine network of conductive tissue in adult birds and mammals. And this knowledge can be put to use in the future.
### END ...
Environment: Speaking the same language on noise exposure
2012-09-14
Quantifying noise exposure will be significantly easier thanks to a new set of common noise assessment methods published today. Comparable data on noise exposure in Europe is a prerequisite to set up EU policies to reduce noise pollution, a growing health and economic concern all over Europe. The new methods – known as Common Noise Assessment Methods in Europe (CNOSSOS-EU) – were drawn up by the European Commission's in-house science service, the Joint Research Centre. They assess noise from road, rail and air traffic and from industry, and will provide consistent and comparable ...
X-rays reveal the self-defence mechanisms of bacteria
2012-09-14
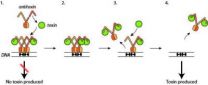
Many pathogenic bacteria are able to go into a dormant state by producing persister cells that are not susceptible to conventional antibiotics. This causes serious problems in the treatment of life-threatening diseases such as tuberculosis, where the presence of persister cells often leads to a resurgence of infection following medical treatment.
At the molecular level, the formation of persister cells is due to the presence of toxins that are produced by the bacteria themselves, and which enable them to enter the dormant state. During this hibernation period, the bacteria ...
Radar measurements of highest precision
2012-09-14
This press release is available in German.
Precise determination of distances is of increasing importance in fabrication technology, for instance, when actuating robots, producing micromechanical components, or controlling machine tools. Frequently, glass scales, inductive sensors, or laser measurement systems are used for distance measurements. Glass scales are very precise and reach micrometer precision. However, they are too inflexible and expensive for daily use. Inductive sensors measuring distances with a coil, magnetic field, and movement work in a contact-free ...