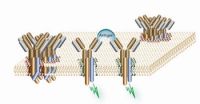
VTT printed hemoglobin test on paper
Bioactivity presents new opportunities for paper
2010-10-07
(Press-News.org) VTT printed the paper with antibodies that react to the sample. The test result can be read in the form of a line, for example, which either does or does not appear depending on the sample – just like in the pregnancy tests already familiar to consumers. It is also possible to print instructional images or text, for example, either on or alongside the test.
Printed paper test can be used to test quickly and easily for the presence of a given substance. The test can be adapted to different purposes by exchanging the identifying antibody printed on the paper for another, for example. The test's subject may be many different types of liquid or substances soluble in water.
The paper can be manufactured using normal printing equipment. However, the delicate biomolecules require different handling and storage procedures to those followed with normal printing colours.
"The ongoing aims of the study are to apply new technology to different samples, and to identify new areas of application. The technology also presents new opportunities in terms of product design in comparison with the traditional diagnostic tests," comments Tomi Erho, who is in charge of the Bioactive Paper project. He also reminds that paper as a biodegradable natural material is a splendid substrate for multiple applications.
Novel products well-suited for mass production can be created by combining bio, paper and print technology. The technology can be applied in rapid diagnostics in the areas of health, wellbeing and the environment, or to bring additional features to packaging or labelling. The technology also presents new possibilities for ensuring product authenticity and impeding falsification.
The result is part of a series of projects over the period 2007� aimed at developing bioactive paper. The projects are funded primarily by Tekes, the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation. VTT's partners in R&D work have been the Aalto University, Åbo Akademi University and the University of Lapland. The commercial partners in funding and in the management team have been UPM-Kymmene Corporation, Tervakoski Oy, BASF, Orion Diagnostica Oy, Hansaprint Ltd, Oy Medix Biochemica Ab, Starcke Securities and Eagle Filter Ltd.
INFORMATION:
PHOTO of a bioactive paper:
http://www.vtt.fi/img/news/2010/bioaktiivinenpaperi0-100_MUSTA.jpg
CAPTION: The picture shows haemoglobin tests printed on paper, the left half of which indicates that the sample does not contain detectable amounts of haemoglobin. Two bars running across the right side of the test means the sample does contain a detectable amount of haemoglobin.
For more information, please contact:
VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland
Tomi Erho, Senior Research Scientist
tel. +358 20 722 5671
tomi.erho@vtt.fi
Further information on VTT:
Olli Ernvall, Senior Vice President, Communications
Tel. +358 20 722 6747
olli.ernvall@vtt.fi
www.vtt.fi
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-10-07
CHAPEL HILL – A clinical trial designed to replace the genetic defect causing the most common form of muscular dystrophy has uncovered an unexpected aspect of the disease. The trial, based on therapy designed by scientists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine, showed that some patients mount an immune response to the dystrophin protein even before they have received the gene therapy.
The puzzling results, which came from trials at Columbus Children's Hospital in Ohio, suggest that the immune systems of a number of patients -- once thought ...
2010-10-07
Insecure Web browsers and the growing number of complex applets and browser plug-in applications are allowing malicious software to spread faster than ever on the Internet. Some websites are installing malicious code, such as spyware, on computers without the user's knowledge or consent.
These so-called "drive-by downloads" signal a shift away from using spam and malicious e-mail attachments to infect computers. Approximately 560,000 websites -- and 5.5 million Web pages on those sites -- were infected with malware during the fourth quarter of 2009.
A new tool that ...
2010-10-07
It's an experience shared by everyone: You run into someone you know, but his or her name escapes you.
Now, Temple psychologist Ingrid Olson has found a way to improve the recall of proper names.
Olson dedicates her research to understanding human memory. In a recent study, she found that electric stimulation of the right anterior temporal lobe of the brain improved the recall of proper names in young adults by 11 percent. Her study appears this month in the journal Neuropsychologia.
"We know a lot about how to make people's memory worse, but we don't know very ...
2010-10-07
Fish byproducts may be a new source of fish feed, thanks to research by U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)-funded scientists in Hawaii.
Research scientist Dong-Fang Deng and her colleagues with the Oceanic Institute in Waimanalo, Hawaii, are collaborating with USDA food technologist Peter Bechtel to develop the new fish feeds. Bechtel is with the USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) Subarctic Agricultural Research Unit in Kodiak, Alaska. ARS is the USDA's principal intramural scientific research agency.
The scientists are taking fish parts that would normally ...
2010-10-07
In order to track down pathogens and render them harmless, the immune system must be able to recognize myriad different foreign substances and react to them. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and the Centre for Biological Signalling Studies BIOSS at the University of Freiburg have discovered how the immune system's B-cells can be activated by numerous substances from our environment. The receptor molecules on the surface of the B-cells are only activated when the receptor subunits separate following the binding of foreign substances. These findings ...
2010-10-07
A $5 million National Science Foundation (NSF) grant to upgrade and expand a set of radio frequency antennas at Owens Valley Solar Array (OVSA) http://www.ovsa.njit.edu/ has been awarded to NJIT. The new facility is expected to help scientists better understand the nature of solar flares which greatly interest government, industry and the military.
"Space weather incidents such as coronal mass ejections and solar flares can cause problems with cell phone reception, GPS systems, power grids and other technologies," said NJIT Distinguished Professor Dale Gary, a world-renowned ...
2010-10-07
Chevy Chase, MD— A new consensus statement published in the September, 2010, issue of The Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (JCEM) finds that the increasing recognition that beta-cell failure occurs much earlier and severely than commonly believed suggests that regular glycemia screening, early identification of patients at metabolic risk and prompt and aggressive intervention deserves greater emphasis.
The consensus statement is based on the findings of a working group of basic researchers, clinical endocrinologists and primary care ...
2010-10-07
BETHESDA, Md., Oct. 6, 2010 – Massachusetts General Hospital researchers say they have determined how iron contributes to the production of brain-destroying plaques found in Alzheimer's patients.
The team, whose study results appear in this week's Journal of Biological Chemistry, report that there is a very close link between elevated levels of iron in the brain and the enhanced production of the amyloid precursor protein, which in Alzheimer's disease breaks down into a peptide that makes up the destructive plaques.
Dr. Jack T. Rogers, the head of the hospital's neurochemistry ...
2010-10-07
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — With bits of DNA extracted from century-old museum specimens, researchers have found a place for the extinct passenger pigeon in the family tree of pigeons and doves, identifying for the first time this unique bird's closest living avian relatives.
The new analysis, which appears this month in Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, reveals that the passenger pigeon was most closely related to other North and South American pigeons, and not to the mourning dove, as was once suspected.
Naturalists have long lamented that one of North America's most ...
2010-10-07
Despite progress in decoding the genome, scientists estimate that fully 95 percent of our DNA represents dark, unknown territory. In the October 1 issue of the journal Cell researchers at The Wistar Institute shed new light on the genetic unknown with the discovery of the ability of long non-coding RNA (ncRNA) to promote gene expression. The researchers believe these long ncRNA molecules may represent so-called gene enhancer elements—short regions of DNA that can increase gene transcription. While scientists have known about gene enhancers for decades, there has been no ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] VTT printed hemoglobin test on paper
Bioactivity presents new opportunities for paper